When it comes to the uniqueness of each individual person, we mean not only the details of appearance, the originality of the pattern of lines on the palms, but also the characteristics of the skin. Did you know that the structure, color shade and phototype of the skin is unique? It depends on the combination of genes from both parents, as well as non-standard combinations formed when germ cells join. Human skin is determined by genetics, and will have its qualities throughout life, regardless of what external influence is exerted on the integument.
Causes of skin cancer
Currently, there is no clear answer to the question of what causes skin cancer. Like many other oncological diseases, skin tumors are considered a multi-etiological pathology. There are several predisposing factors, the presence of which increases the risk of developing a tumor focus. These include:
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays on the skin. A similar situation occurs with prolonged and frequent exposure to sunlight, visiting a solarium, or working outside. Residents of the southern regions are at risk of developing skin cancer.
- Having light skin. Lack of melanin production increases the likelihood of skin tumors.
- Skin burn. A high degree of burn is accompanied by scarring of the skin. This process contributes to the emergence of latent carcinogenesis.
- Irradiation. Exposure to radioactive, ionizing rays has a detrimental effect on the skin. The risk of radiation dermatitis increases.
- Presence of skin contact with toxic substances. This group of carcinogens includes arsenic, aluminum, titanium, nickel and other heavy metals.
- Immunodeficiency. Conditions in which the body's protective functions decrease predispose to the formation of a tumor focus.
- Age. Most often, skin tumors affect people over 50 years of age.
- Concomitant systemic diseases. Doctors identify a group of pathologies in which the risk of developing skin cancer increases significantly. These include systemic lupus erythematosus, leukemia, and chronic skin diseases.
- Heredity. The presence of a skin tumor in previous generations of relatives is not a major risk factor. However, family history in combination with other predisposing conditions increases the possibility of developing skin cancer.
- Tattooing. In this case, there are two risk factors. This is a violation of the integrity of the skin and the introduction of paint with carcinogenic substances. Cheap tattoo ink may contain impurities of aluminum, titanium, and arsenic.
- A large number of nevi. Doctors urge you to monitor the condition of moles and contact a specialist if there is the slightest change. Traumatization of nevi increases the possibility of developing skin cancer.
- Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking. Chronic intoxication has a detrimental effect on the body as a whole. Against this background, the risk of tumor formation increases several times.
- Eating foods high in nitrates.
Oncologists identify several precancerous conditions, the presence of which significantly increases the risk of developing skin cancer. These include:
- Xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Bowen's disease.
- Paget's disease.
- Hyperkeratosis.
- Cutaneous horn.
- Late stage radiation sickness.
- Dermatitis and dermatoses.
Causes and risk factors
The following people are at particular risk of developing skin tumors:
- With Bowen's disease;
- Those who are elderly;
- Light-skinned, with a genetically reduced melanin content;
- With senile keratoma;
- With melanoma-dangerous pigment spots;
- Having Queyra's erythroplasia;
- Suffering from cutaneous horn;
- With xeroderma pigmentosum;
- Having inflammatory skin pathologies;
- Suffering from nicotine addiction;
- Staying in the open sun for a long time;
- Abuse of visiting the solarium.
In addition to the risk group, doctors identify some other factors that contribute to the development of skin malignancy:
- Complication due to dermatitis of radiation origin;
- Chemical exposure to carcinogens, such as arsenic compounds, tar found in cigarettes, or lubricants;
- Damage at the site of an old scar;
- Radiation exposure;
- Consumption of products containing carcinogenic substances such as nitrites, nitrates, marinades, smoked foods, preservatives and excessively fatty foods;
- Exposure to various types of thermal factors or thermal radiation;
- Violation of the integrity of the mole;
- Oncology at the site where there was previously a deep burn;
- Abuse of tattooing;
- Presence of hepatitis or HIV infection;
- Living in southern countries.
Symptoms and signs of skin cancer
The clinical picture of skin cancer development depends on its type. Often the first signs of a tumor are mistaken for other skin diseases. This results in untimely consultation with a doctor and the spread of the malignant process. Common signs for all types of skin cancer are:
- The appearance of a small spot or lump on the skin. The color of the formation can be pinkish, gray-yellow. It is noteworthy that the color of the neoplasm differs from moles and freckles.
- Uneven shape and asymmetric contours of the pathological focus.
- The appearance of itching and slight discomfort in the area of the tumor process. This symptom appears some time after the formation of cancer.
- Progressive growth of the tumor.
- Fatigue, weakness, sudden loss of strength.
- Decreased appetite, resulting in sudden weight loss.
- As cancer develops, regional lymph nodes are affected.
If any of the above symptoms appear, it is recommended to seek medical help. Depending on the type of skin cancer, the following symptoms are distinguished:
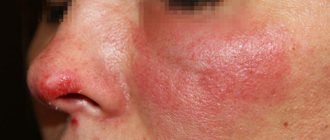
1. Basalioma. It is the most common form of skin tumor. It is characterized by a favorable prognosis when detected at the initial stage. Appears in the form of a nodule, painless on palpation. It has a grayish-pink color. The surface of the nodule is usually smooth. Scale formation is possible. As the tumor process spreads, the affected area increases. The neoplasm is covered with a bloody film. The predominant localization of basal cell carcinoma is the face, neck, and arm area. Basalioma does not cause a significant change in condition. This is the reason for late seeking medical help.
2. Squamous cell carcinoma. At an early stage, it looks like a dense red or brown nodule. A tumor of this type is prone to rapid decay, and therefore, as the process progresses, an ulcer forms. Its edges are heterogeneous, the ulcer often bleeds. Squamous cell carcinoma quickly grows into nearby tissues. If detected at a late stage, metastasis to regional lymph nodes or organs is possible.
3. Melanoma. Refers to an aggressive type of tumor. Most often, melanoma occurs at the site of an injured nevus, which increases in size, changes color and acquires uneven contours. A characteristic feature of this type of cancer is the asymmetric form of formation, as well as a tendency to bleed. The malignant neoplasm itches and increases in size. As the process progresses, the tumor turns into an ulcer. Melanoma progresses rapidly and often metastasizes.
4. Adenocarcinoma. At the initial stage of development, it looks like a dense nodule. It is most often localized in the armpit area, under the breast. With the development of the tumor process, adenocarcinoma grows into nearby tissues. This type of tumor is detected extremely rarely and is characterized by slow growth.
What formations on the skin should raise suspicion?
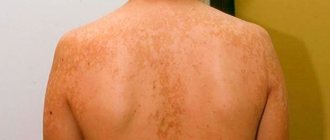
Most moles, brown spots and growths on the skin are harmless - but not always. If you have a lot of moles and freckles, you need to be very careful about any changes in pigmentation. When a mole begins to bleed or ooze fluid , you need to go to a dermatologist.
It is also necessary to monitor new formations on the skin. Many skin cancers are essentially colorless. They often appear as pink or pearly papules or scaly patches. These are signs of a primary neoplasm, and it is advisable to show them to the doctor. Bleeding and weeping skin lesions are of particular concern.
Types of skin cancer
Depending on the type of cells from which the tumor is formed, there are several main types of skin cancer. Determining the structure of the tumor is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and carry out appropriate treatment. In addition, the speed of its spread and further prognosis depend on the type of cancer. Oncologists distinguish the following types of skin cancer:
1. Basal cell (basalioma). Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer. It originates from the basal cells of the epithelium. Basalioma is characterized by slow, sudden development and a relatively favorable course. Unlike other types of skin cancer, it rarely metastasizes. Basal cell carcinoma is usually localized in the area of the nose, bridge of the nose, eyebrow, upper lip and nasolabial fold. A rare location for this type of cancer is the neck and ears. There are several forms of basal cell carcinoma:
- Nodal. The most common location of nodular basal cell carcinoma is the head and neck area. At an early stage it looks like nodules up to 5 mm in size. As the tumor process develops, the nodules merge with each other. At a late stage, nodular basalioma is a deep ulcer with necrotic areas.
- Superficial. This type of basal cell carcinoma is located on the trunk and limbs. The tumor looks like a round pink spot with ulcerations. Superficial basal cell carcinoma is considered the most favorable and non-aggressive form of skin cancer.
- Scleroderma-like. Refers to an aggressive type of cancer. Located in the deep layers of the skin. The most common location for this type of tumor is the head and neck. Basalioma has the appearance of a plaque, which in the later stages of the process has the appearance of a depressed scar.
- Cystic. A rarely detected form of basal cell carcinoma, externally similar to a cyst.
- Fibroepithelial. Located in the lumbar region. Basal cell carcinoma has the appearance of a pedunculated polyp. The fibroepithelial form is extremely rare and has a favorable course and prognosis.
2. Melanoma. Refers to an aggressive type of skin cancer that originates from melanocytes. Melanoma is characterized by rapid growth and invasion into neighboring tissues. This type of skin cancer metastasizes not only to regional lymph nodes, but also to organs. A favorable prognosis for melanoma is only possible if the tumor is diagnosed at an early stage. Women with fair skin are at risk for developing skin cancer.
3. Squamous. Squamous cell carcinoma is the 3rd most common type of skin cancer. It develops from the outer layers of the skin. It is characterized by slow development, which increases the possibility of detecting a tumor at an early stage. At the initial stage, squamous cell skin cancer looks like a red lump up to 2 cm in diameter.
The above forms of skin cancer are diagnosed most often. They account for about 90% of all detected oncological processes of the skin. In addition, there is skin appendage cancer, which is extremely rare. This type of tumor includes:
- Adenocarcinoma. Comes from the sweat and sebaceous glands. Characterized by slow growth. Outwardly it looks like a dark blue node, localized in the groin and chest area. Adenocarcinoma does not tend to grow into adjacent tissues, and metastasis rarely occurs. The tumor is removed surgically.
- Verrucous carcinoma. Refers to a very rare form of squamous cell carcinoma. Outwardly it resembles a wart, so detection at an early stage is difficult. A distinctive feature of verrucous carcinoma is its bleeding.
Consequences
Each type of skin cancer has its own set of cells with varying aggressiveness, which is why such neoplasms behave differently.
Why are skin cancers dangerous?
- Basalioma
is not prone to metastasis, is characterized by slow growth, and is often found in the nose. - Squamous cell skin cancer
, on the contrary, grows rapidly and metastasizes throughout the body. - The most dangerous form is considered melanoma
, which is difficult to treat and often causes a lot of complications.
What does the initial stage look like?
Symptoms of a skin tumor depend on its type. Growth rate, color, and tendency to metastasize are characteristic of each form of cancer. However, at the initial stage, several symptoms are common to all types of tumor. These include:
- The presence of a formation on the surface of the skin with unclear shapes and asymmetrical contours.
- The appearance of itching and changes in the color of the lesion as the process progresses.
- A sharp loss of strength, increased fatigue.
- Loss of appetite, sudden weight loss.
- The presence of pain in the area of the tumor.
Skin cancer develops through 4 stages. Each reflects the size of the lesion, its spread to surrounding tissues, and the presence or absence of metastases. Depending on this, the following symptoms of skin tumors are distinguished:
- First stage. At this stage of skin cancer formation, there are no specific signs. The size of the tumor focus is up to 2 mm. In this case, the general condition does not change. Detecting cancer at the first stage is possible only with a thorough self-examination of the skin.
- Second stage. The growth of the tumor leads to the appearance of the first subjective signs. These include itching and pain in the area of the pathological focus. The cancer increases in size up to 4 mm.
- Third stage. The tumor focus has a diameter of more than 4 mm. At this stage of skin cancer, the process spreads to regional lymph nodes.
- Fourth stage. Late stage skin cancer is characterized by the appearance of metastases. The tumor grows into nearby tissues. The clinical picture is accompanied by the appearance of symptoms of tumor intoxication (cachexia, weakness, lack of appetite, headache).
Lack of medical care in the early stages of skin cancer leads to rapid progression of the process. As the tumor develops, nearby organs and lymph nodes are affected. The appearance of the lesion in the form of an ulcer contributes to the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. There are often deaths due to the development of sepsis.
Sources
- Kapickis M., Beinarovica I. Fascial Epicondylar Augmentation in Cases of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome With Ulnar Nerve Instability. // Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33900059
- Leow JM., Clement ND., McQueen MM., Duckworth AD. The rate and associated risk factors for acute carpal tunnel syndrome complicating a fracture of the distal radius. // Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33891155
- Levina Y., Dantuluri PK. Radial Tunnel Syndrome. // Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33890229
- Billig JI., Lu YT., Hayward RA., Sears ED. Surgical Timing for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Comparison of Health Care Delivery in the Veterans Administration and Private Sector. // J Hand Surg Am - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33867201
- Low J., Kong A., Castro G., Rodriguez de la Vega P., Lozano J., Varella M. Association Between Diabetes Mellitus and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Results From the United States National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. // Cureus - 2022 - Vol13 - N3 - p.e13844; PMID:33859898
- Abdolrazaghi HA., Khansari M., Mirshahi M., Ahmadi Pishkuhi M. Effectiveness of Tendon and Nerve Gliding Exercises in the Treatment of Patients With Mild Idiopathic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. // Hand (NY) - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.15589447211006857; PMID:33855879
- Ho TY., Chen SR., Li TY., Li CY., Lam KHS., Chen LC., Md YW. Prognostic factors in carpal tunnel syndrome treated with 5% dextrose perineural injection: A retrospective study. // Int J Med Sci - 2022 - Vol18 - N9 - p.1960-1965; PMID:33850465
- Goyal R., Mercado A.E., Ring D., Crijns TJ. Most YouTube Videos About Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Have the Potential to Reinforce Misconceptions. // Clin Orthop Relat Res - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33847604
- Wee TC., Simon NG. Asymptomatic common extensor tendon pathology in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. // Muscle Nerve - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33847378
- Lallukka T., Shiri R., Alexanderson K., Ervasti J., Mittendorfer-Rutz E., Virtanen M. Sickness absence and disability pension after carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis: A register-based study of patients and matched references in Sweden. // Scand J Public Health - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.14034948211002729; PMID:33845698
Etiological factors of scalp cancer
The etiology of cancer is still not fully understood, but the following etiofactors are reliably known:
- Male gender. Skin cancer affects both men and women, but according to statistics, men are more likely to get it.
- Complicated family history. The risk of developing skin cancer increases when close relatives are diagnosed with this disease.
- Elderly age. Skin cancer is most often diagnosed in people after fifty years of age.
- Life history of exposure to UV rays and sunburn.
- Light skin and hair, blue eyes.
- Freckles and/or multiple nevi, etc.
Any neoplasm on the skin of the face can be dangerous, but it is necessary to undergo examination in case of asymmetry, unevenness of its edges, if its color is not uniform or it changes, and if there is a change in size.
Expert opinion
Author:
Alexey Andreevich Moiseev
Oncologist, chemotherapist, Ph.D.
Every year, 9,000 cases of newly diagnosed melanoma are registered in Russia. This aggressive malignant tumor is responsible for the death of 40% of patients. Such statistics indicate that the country's population is not sufficiently aware of the symptoms of melanoma. As a result, a visit to a doctor occurs in the later stages, when treatment is considered ineffective.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital determine the location of melanoma and prescribe treatment appropriate to the stage of tumor development. An individual approach to the problem of each patient allows us to reduce the number of deaths. A tumor detected in time is characterized by a favorable prognosis for recovery. The later melanoma is detected, the longer the treatment process will be. Its success depends on many factors. The main treatments for melanoma are surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Depending on the condition, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
You can diagnose the presence of skin cancer yourself at home. Doctors recommend regularly examining the skin, especially nevi, for the appearance of pathological formations.
How to determine your phototype
It is quite easy to determine the phototype of your skin, using the generally accepted classification, which is a synthesis of the scales of two authors: one proposed by Fitzpatrick, and the second by Harold F. Lancer. There are six phototypes in total, the first four of which are characteristic of the population of Europe, as well as of Russia.
So, to determine which phototype your skin belongs to, we suggest answering a few questions:
- What color are your eyes?
- Light
- Blue, gray, green
- Dark
- Brown
- Black
- What is your skin color?
- Pink
- Pale
- Beige
- Brown
- Dark brown
- What kind of hair do you have?
- Ginger
- Blonde or light brown
- Chestnut or light brown
- Dark blond or brown
- Black
- Do you have freckles on your face and body?
- Quite a lot all over the body
- Small amount on face and body
- Very little on the face
- Virtually none
- Not at all
- What happens to your skin after prolonged exposure to the sun?
- Painful blisters and peeling skin
- Painless blisters and peeling skin
- Mild peeling, burning
- Unpleasant sensations are rare
- No burns and/or peeling
- How does your skin tan?
- Never tans
- In rare cases
- Sometimes
- Often
- Always
- How tan does your skin get?
- Doesn't become
- Slightly tanned
- Well tanned
- Very tanned
- Very dark
Diagnosis of skin cancer
An integrated approach to diagnosing skin cancer is the key to timely detection of the tumor process. In order to determine the presence of skin cancer, it is necessary to conduct an examination. The first signs of skin cancer can be detected on your own. For this purpose, the ACORD principle is used.
- A – asymmetry. A lesion that has an uneven and asymmetrical shape requires close attention from a doctor.
- K – edge. A malignant neoplasm of the skin is characterized by jagged edges. The appearance of such a sign requires immediate contact with a dermatologist.
- O – coloring. Skin cancer is characterized by the appearance of a red, dark blue, or black lesion.
- R – size. The tumor process often has a diameter greater than 6 mm.
- D – dynamics. The growth of education in size requires a visit to a doctor.
The appearance of any of the above symptoms requires immediate medical attention. At the appointment, the specialist examines the formation using an epiluminescent microscope, which allows him to differentiate various skin diseases.
- Collecting anamnesis of illness and life. At the doctor's appointment, complaints are collected, the time of occurrence of the pathological formation, and the presence of predisposing factors. Precancerous diseases are determined, and the rate of development of the lesion is determined.
- General analysis of urine and blood. Laboratory diagnostics allows us to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Blood test for tumor markers. Specific markers for the presence of skin cancer are TA 90 and SU 100. Their determination is diagnosed already in the early stages of the tumor process.
- Tissue biopsy of pathological formation. It is one of the most important methods for diagnosing skin cancer. Histological examination makes it possible to differentiate the neoplasm, determine its stage and type. In cases where there is a metastatic lesion, a biopsy of the affected areas is performed.
- MRI and CT diagnostics. Instrumental research methods are carried out to identify metastases.
- PET-CT. This diagnostic method allows you to determine the localization of metastases. The study is carried out using a contrast agent injected into the body before tomography.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics helps to identify damage to the lymph nodes, as well as changes in other organs if metastases are suspected.
Detection of skin cancer at the initial stage of development allows for timely treatment and provides a favorable prognosis. Therefore, if you have the first signs of the disease, you should seek medical help.
ABCDE technique for cancer detection
The first five letters of the English alphabet are a guide to help you recognize the signs of cancer.
- A is asymmetry. Most skin cancer lesions are asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of the hearth, the two halves won't line up, so it looks different from round to oval.
- B is the border. The borders of cancers tend to be jagged and may have jagged edges, while regular moles tend to have smoother, more even borders.
- C is color. Multiple colors are a warning sign. While benign moles are usually one shade of brown, cancerous moles can be various shades of tan, brown, or black. Red, white, or blue colors may also appear as they grow.
- D is the diameter. It is already worth paying attention to the spring if its size is more than 6 mm. Some experts say it's also important to look for any damage, regardless of size, that is darker than others. Sometimes, amelanotic melanomas are colorless.
- E is for evolution. Any change in the size, shape, color or height of a spot on your skin, or any new symptom in your skin, such as bleeding, itching or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma.
If you notice these warning signs or anything new, changing, or unusual on your skin, contact your dermatologist immediately.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the tumor is the most affordable method of treating skin cancer. Surgery is most effective in the early stages of cancer development due to the lack of tumor growth into nearby tissues. The surgeon removes the tumor and all affected areas. In the presence of metastatic lesions of the lymph nodes, their removal is indicated. If an aggressive form of the tumor develops, surgical intervention alone is not enough to completely get rid of the pathological focus.
A modern method of surgery to remove skin cancer is micrographic surgery using the MONS method. In this case, tumor cells are removed layer by layer under microscopic control. Each removed layer is sent for histological examination.
How to cure pathology
The therapeutic process is complex. After identifying the specific type and stage of cancer, the doctor selects an adequate treatment plan. The main methods used in the treatment of skin cancer:
- Surgical treatment consists of open removal of the tumor. It is used for oncology of the limbs, body or to get rid of metastases.
- Radiotherapy involves irradiation when surgical treatment is not feasible or when oncology re-develops;
- The chemotherapy approach is traditionally used to treat recurrent forms of cancer, as well as for large tumor sizes. The technique is based on the use of drugs that have a destructive effect on cancer cells. Often, with such treatment, a special anti-cancer ointment is used, which is indicated to be applied to the tumor daily for several weeks;
- The photodynamic method has been successfully used in the treatment of cancer localized in the upper layers of the skin. The technique is based on the use of a specialized drug applied to the area where the oncology is located, after which this area is subjected to light treatment, under the influence of which the applied drug is activated and destroys cancer cells;
- Laser treatment successfully eliminates cancer cells using a highly active beam of rays;
- The fulguration method involves removing cancer cells using special instruments, after which the operation area is treated with current, which kills the remaining cancer cells;
- Cryotherapy is justified only in the case of a shallow tumor location. The technique involves freezing the malignant material with liquid nitrogen.
Along with the above procedures, immunostimulating therapy is prescribed, which increases the body’s resistance to cancer cells. For this purpose, Interferon, 5-fluorouracil, Imiquimod, Aldesleukin, Dacarbazine and other drugs are prescribed.
Nutrition
Skin cancer requires a radical revision of the diet.
It is necessary to provide the body with a high content of retinol and carotene, found mainly in dairy products, fish oil, eggs, carrots, green tea, corn, tomatoes, soy, etc.
There are many products that can suppress the growth of malignant cells:
- Greenery;
- Garlic;
- Carrot;
- Citrus;
- Cabbage;
- Hot red pepper;
- Beet;
- Whole grain.
Chemotherapy
It is carried out both as an independent method of treatment and in combination with surgical intervention. Prescribing chemotherapy before surgery is intended to reduce the pathological focus. The purpose of this method of treating skin cancer after surgery is designed to completely destroy cancer cells.
The disadvantage of this method is the inability to exclude the effects of drugs on healthy cells. The question of the need for chemotherapy is decided by the attending physician based on the individual characteristics of the development of the tumor process.
Drug treatment
As the tumor process progresses, corresponding clinical symptoms appear. The main ones include pain and itching. To symptomatically combat these symptoms, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve pain due to skin cancer.
| Stage | TNM | Treatment method |
| 1 | T1-4N0M0 | At the initial stage of the tumor process, treatment consists of surgery with excision of the pathological focus. |
| 2 | T1-4N0M0 | At this stage, the tumor does not metastasize or grow into nearby tissues. Therefore, surgical intervention is considered sufficient treatment. |
| 3 | рTN1-3M0 | The stage is characterized by growth into nearby tissues and damage to regional lymph nodes. Therefore, the scope of treatment is:
|
| 4 | pTрNM1 | The spread of the tumor process affects the lymph nodes and organs. The fourth stage is characterized by multiple metastases. The volume of therapy depends on the general condition and is selected strictly individually. Treatment is as follows:
|
Prevention
The main cause of most types of skin cancer is ultraviolet radiation. Accordingly, to prevent the disease it is necessary:
- go to the beach less often;
- use sunscreen;
- avoid visiting the beach during hours of maximum sun activity - from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m.;
- do not visit the solarium;
- wear clothing that protects most of the body from the sun's rays.
People with fair skin should especially follow these recommendations, as they are more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation.
In mobile applications or the Internet, you can look at the UV index (provided by weather forecast services) and use it to determine how intense sun protection should be at the moment. Recommendations, depending on the UV index value:
- 0-2 – no protection needed.
- 3-7 – it is advisable to stay in the shade, wear long sleeves and a hat, and use sunscreen.
- 8 – it is advisable to stay indoors.
For people with fair skin, sunscreens with SPF 30-50 or more are suitable. They are applied to the skin half an hour before leaving the house. On the beach, the cream is applied every 2 hours, as well as every time after swimming or intense sweating. The amount of cream should be sufficient:
- on hand – 0.5 teaspoon;
- on the head and neck – 0.5 teaspoon;
- leg, back or chest - 1 teaspoon.
To protect the head and neck, the best option is a hat with a wide brim (at least 10 cm).
Risk factors for melanoma are considered to be the presence of at least 10 dysplastic nevi, 100 any nevi on the skin, or one giant nevus - occupying 5% or more of the body area. To reduce the risk of tumors, it is advisable to remove all moles larger than 6 mm in diameter.
Actinic keratosis is considered the main precancerous disease for non-melanoma malignant tumors. Under the influence of sunlight, dense plaques appear on exposed parts of the body. They can be removed to avoid malignant transformation.
Forecast
The average life expectancy of patients diagnosed with skin cancer depends on several factors. These include the type of cancer, its stage, and the presence or absence of metastases. Detection of a tumor focus at the initial stage contributes to timely treatment and minimal risk of complications. In addition, each type of cancer has its own prognosis. Squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas are characterized by a favorable course and prognosis. Melanoma is an aggressive type of tumor that tends to grow rapidly and metastasize. The average five-year survival rate after skin cancer is diagnosed is:
- 80-100% when skin surface cancer is detected in the first stages.
- Up to 50% when skin cancer is detected at a late stage.
- Up to 25% in the presence of metastases in regional lymph nodes and other organs.
In order to minimize the risk of developing a tumor, it is necessary to prevent skin cancer. It is recommended to limit the time spent under ultraviolet rays and avoid excessive consumption of alcohol and nicotine. If there is an occupational hazard, it is required to undergo an annual medical examination to detect pathology at an early stage. In addition, it is necessary to wear protective suits that limit skin contact with carcinogenic substances. One of the cancer prevention measures is self-examination of the skin. Any changes require immediate medical attention to diagnose the disease.
Metastasis and life expectancy
Most often, melanoma metastasizes with skin cancer, spreading throughout the body through the blood and lymphatic pathways. After surgical excision of melanoma, 9 out of a dozen patients develop metastases over a 5-year period, which are usually localized in the subcutaneous tissue and on the surface of the skin.
With such metastasis, the patient’s life expectancy ranges from six months to one and a half years. If metastasis occurs in internal organs or the brain, then the life expectancy of patients with skin cancer is reduced to 3-6 months.
How is skin cancer treated?
The Moscow Yusupov Hospital has been diagnosing and treating skin tumors for many years. Thanks to modern equipment, skin cancer can be detected in the shortest possible time, and its type and stage can be accurately determined. This is necessary to determine further treatment tactics.
Highly qualified doctors of the medical institution select individual therapy, taking into account the obtained diagnostic data. In their work, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use current recommendations for the treatment of skin cancer. You can make an appointment with an oncodermatologist and learn more about prices by phone.
Phototypes: cheat sheet
| Skin type | Phototype | Ethnic scale |
| I | Prone to burns when tanning, does not acquire a bronze tint, and does not tan at all | Irish, Scots |
| II | Characterized by the occurrence of sunburn and the difficulty of obtaining a tan. Owners of this type of skin | central Europeans |
| III | It may succumb to the negative effects of the sun and become covered in blisters, but it is extremely rare. As a rule, the skin easily gets a golden tan, and after a while it becomes dark. | Italians, Portuguese |
| IV | Virtually no burns, quickly acquires an even, attractive tan | Natural olive or yellow skin tone (Hispanics, fair Hispanics) |
| V | It is distinguished by its natural dark complexion. Has a brown tint. Suitable for quick and easy tanning | Natural dark, brown skin (East Indian) |
| VI | Natural black leather | Naturally black leather |
Having correctly determined your phototype, you can more intelligently approach the choice of decorative cosmetics, as well as care products and protective products that protect the skin from burns. Also, having information about your phototype, you can avoid mistakes that arise when carrying out a number of procedures (laser rejuvenation, cosmetic procedures, etc.).
A professional cosmetologist at the Abrielle Aesthetic Surgery Clinic can choose the right skin care for your phototype. To schedule a consultation, call the clinic and 8(921)99-22-335.