About the disease
Atopic dermatitis
is a chronic, genetically determined skin lesion of an allergic nature. It can be caused by many completely different factors - allergens entering the child’s body through food (from products), contact (when skin comes into contact with clothing) or respiratory route (by inhaling pollen, dust).
At the first appearance of any rash in the baby
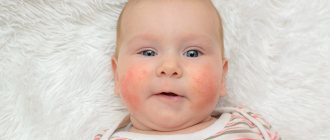
Parents should be aware that in young children, signs of atopic dermatitis usually appear on the face, elbows or knees, and possibly other areas of the body.
In older children and adults
The rash most often appears in the popliteal areas, on the inner surfaces of the elbows, on the side of the neck, on the wrists, ankles, hands and face.
Parents and even doctors can often confuse atopic dermatitis with prickly heat, which is why it is important not to miss every suspicious rash and carry out a timely diagnosis.
Diagnostics
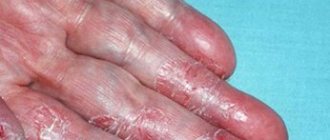
A dermatologist diagnoses contact dermatitis. To clarify the diagnosis and in more severe cases, consultations or constant observations of a dermatologist and allergist may be required. First of all, diagnosis is based on clinical manifestations and anamnesis. The nature of the rash, its location and the shape of the rash are assessed. When collecting anamnesis, it is important to pay attention to the work of the patient and his spouse, hobbies, cosmetics used, pets and much more. If there is no effect of treatment, a severe clinical form, or if allergic contact dermatitis is suspected, skin patch tests are performed. They help identify possible allergens that caused a pathological reaction.
Symptoms
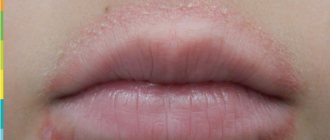
- Regular appearance of an itchy red rash.
- The appearance of thickening, spots, scales, and dry skin in certain areas of the skin.
- Presence of allergic rhinitis, asthma and/or atopic dermatitis in the child’s relatives.
- Remember that only a doctor can diagnose atopic dermatitis and choose the right course of treatment.
Atopic dermatitis, sadly, cannot be cured, but there are many medications that can reduce redness and itching and help control atopic dermatitis, reducing the impact of the disease on a person's life.
In 90% of people, atopic dermatitis is diagnosed within the first five years of life.
During exacerbations of atopic dermatitis, there is a tendency to re-affect the same areas of the body.
Based on information from an article by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia, as well as on the basis of text from the Medical Encyclopedia
Treatment and prognosis
First of all, it is necessary to find out the cause and get rid of its effects. During the treatment period, it is necessary to avoid water procedures at the affected area. Treatment is divided into external and internal. Cold compresses and bandages are applied externally.
The affected area can be treated with antiseptics and bandages with regenerating ointments and creams used. Glucocorticosteroids are used both internally and externally. Antihistamines will reduce further development of the allergic reaction and itching.
Treatment of contact dermatitis occurs on an outpatient basis, but in severe cases it can also be transferred to a hospital.
Interesting Facts
- Atopic dermatitis in children usually develops in early childhood (most often at 2-3 months) and goes away by 3-4 years, but can remain for life.
- Atopic dermatitis in newborns appears no earlier than two months after birth.
- It has been established that atopic dermatitis develops in 81% of children if both parents are sick, in 59% if only one of the parents is sick and the other has an allergic pathology of the respiratory tract, and in 56% if only one of the parents is sick.
- Atopic dermatitis is not contagious—it cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Source: Article of the Union of Pediatricians + Baranov A. A. (ed.). Pediatrics. Clinical recommendations.
What other specialized care?
– Emollients are fats and fat-like substances included in cosmetic products created specifically for the care of dry, damaged skin. On the skin, emollient creates a thin film similar in structure to the natural lipid layer, which prevents moisture loss and protects the skin from the effects of traumatic factors (friction by clothing, sweat, tap water, soap, washing powder, low temperature).
Emollients should be applied generously in a thick layer to the entire skin, even to those areas that have no visible damage. But if the product contains urea or a person has violations of the integrity of the skin, then this should not be done.
You need to apply emollient after each wash; during periods of exacerbation, the frequency can reach 5-6 times a day. Emollients do not need to be rubbed into the skin - we apply them gently. The goal is to create a protective film on the surface. There are no contraindications or addiction to long-term use of such drugs.
Prevention
As for preventive measures, unfortunately, they do not exist as such.
According to the Union of Pediatricians of Russia, “there is no reliable evidence that exclusive breastfeeding, limiting exposure to aeroallergens and/or early introduction of complementary foods influence the risk of developing atopic dermatitis, however, exclusive breastfeeding during the first 3 months of life may delay the development of atopic dermatitis in predisposed children by an average of 4.5 years.”
It is noted that the hypoallergenic diet of a pregnant woman at risk of having a child with atopic dermatitis also does not provide any prevention.
Another thing is that breastfeeding and the mother’s adherence to a hypoallergenic diet during lactation can delay or alleviate the course of atopic dermatitis in the child.
Allergic
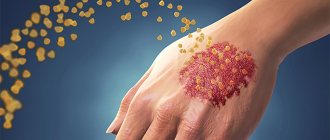
Allergic dermatitis is the body’s reaction to a specific allergen: food product, household detergent. Knowing what exactly caused the reaction, you can cope with an outbreak of the disease: it is enough to eliminate the irritant. In the case of food products, everything is simple: the allergen must be removed from the diet and avoided in the future. If the cause was external irritants (aggressive chemicals, alkalis, acids, UV radiation), it will be more difficult to identify, let alone avoid contact. In this case, you will have to seek medical help.
Help the baby
Remember that atopic dermatitis can go away with age, and your task is to make the course of this unpleasant disease as easy as possible for your baby and help him learn to cope with it.
How to treat atopic dermatitis and how to properly care for such skin?
– Treatment is prescribed by the attending dermatologist, pediatrician, or general practitioner. The basis is specialized skin care that will moisturize it and restore the barrier.
You always need to take care. During exacerbations, external hormonal (GCS) creams and ointments, calcineurin inhibitors, and oral antihistamines are prescribed. It is also necessary to carry out symptomatic therapy in the form of soothing, drying, antibacterial (for weeping rashes) and wound-healing drugs. In severe forms, systemic therapy may be prescribed.
Reasons why contact dermatitis occurs
Contact dermatitis always develops “in the presence” of some chemical, biological or physical environmental irritant. All unfavorable factors that cause a skin reaction in the form of inflammation are conventionally divided into two large groups - obligate and facultative.
To obligate
include factors that irritate the skin of absolutely any person:
- alkaline and acidic compounds;
- poisonous plants, animals, insects;
- ionizing radiation;
- temperatures too low or too high.
Optional
These are the factors that provoke inflammation of the skin only when there is increased sensitivity in a particular person:
- turpentine;
- metal salts;
- some local drugs;
- cleaning and detergents;
- cosmetics;
- synthetic underwear;
- wool clothing;
- formalin;
- machine oil and others.
In addition to the obligatory contact skin irritant, relapses can be caused by the following factors:
- decreased immunity;
- increased sweating;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- hormonal disorders;
- frequent trauma to the skin;
- chronic skin diseases.
For example, a woman experiences dry and tight skin after using a detergent. But she doesn’t pay attention to this and continues to wash the dishes without household gloves. And one day, dryness and tightness quickly turn into inflammation with itching.
Most likely, in such cases, in addition to an external contact irritant, something else turns on - spring has come, immunity has decreased due to vitamin deficiency, or the day before you cut your finger.
The following point of view is also widespread among specialists: the cause of contact dermatitis should be sought in a violation of autoimmune processes. Due to an autoimmune failure, the body begins to produce antibodies to its own cells. And then any aggressive substance provokes an inflammatory reaction.
Is dermatitis contagious?
The appearance of simple pimples on the skin is not always characteristic of acne. Under the guise of these seemingly familiar rashes for many people, a disease such as dermatitis can be hidden.
The skin in such affected areas loses its attractiveness, and the inflammatory process occurring in the epidermis causes a person a lot of inconvenience. In addition to its unpleasant appearance, this disease is accompanied by many unpleasant sensations, including itching or flaking.
As a result, many people, not understanding whether dermatitis is contagious, still try to avoid contact with such a patient.
The appearance of dermatitis is explained by the influence of various factors, which are usually divided into 2 groups: internal and external.
Internal reasons:
- Hormonal surges;
- Vitamin deficiency;
- Scleroderma;
- Heredity;
- Decreased immunity.
- Stress;
- Metabolic disorder.
External factors are characterized by the influence of such stimuli as:
- Mechanical;
- Biological;
- Physical;
- Chemical.
Common external causes include:
- Wrong lifestyle;
- Solar radiation;
- Food irritants;
- Household chemicals;
- Ionizing radiation;
- Construction Materials;
- Temperature difference;
- Poor quality cosmetics.
Types of dermatitis
The skin's response to any damaging factor may be the development of dermatitis.
The disease has several types:
- Allergic (toxic) dermatitis. The disease manifests itself after exposure to a specific allergen, which enters the body through the respiratory tract and stomach. Most often, a food product acts as such an irritant, so unpleasant symptoms can be easily eliminated by eliminating such food from the diet. If the provoking factor for dermatitis is a chemical irritant or a household allergen, then medications must be used to get rid of skin problems.
- Seborrheic. The cause of this type of skin disease is mainly endocrine or trophic changes that disrupt the functions of the sebaceous glands. This pathology often becomes chronic. The location of inflammation is the face, part of the head with hair, and neck. According to many experts, the source of the disease can also be a fungus, which under favorable conditions begins to multiply intensively.
- Atopic. This type of dermatitis is often a manifestation of a hereditary predisposition. The rapid spread of atopic disease is considered to be a consequence of incorrect treatment tactics, as well as a complete lack of therapy.
- Contact. This type of dermatitis develops upon contact with a specific irritant. As a result of this interaction of a negative factor with the surface of the skin, an inflammatory process begins.
- Medication. This dermatitis is a consequence of taking certain medications (antibiotics, drugs with novocaine), which cause a similar reaction in the body. As a rule, the disease recedes almost immediately after discontinuation of therapy with these medications.
Symptoms
Manifestations of dermatitis depend on factors such as:
- Type of stimulus;
- Skin Features;
- The duration of the negative impact of a specific stimulus.
Main symptoms:
- Itching;
- Peeling;
- Intertrigo;
- Attrition;
- Allergic reactions;
- Chills;
- Ulcerative lesions;
- Red spots;
- Loss of sensitivity in damaged areas of the skin.
Symptoms of the disease may vary depending on the type, area of distribution or stage of dermatitis.
Stages of development:
- Spicy. This period is characterized by the formation of bubbles on the skin, of different sizes and filled with liquid inside.
- Subacute. At this stage, dermatitis is accompanied by the formation of crusts and scales on the affected areas.
- Chronic. During this period, the disease has already become advanced, so the skin thickens, and areas with redness become darker (sometimes even purple).
A simple form of contact dermatitis is accompanied by slight redness of the skin with a feeling of itching, hyperthermia, and tingling.
Long and close contact of the irritant with the surface of the skin often leads to the appearance of ulcerative necrotic formations characteristic of dermatitis, erosion with a possible risk of infection after their opening.
In such situations, the itching sensation becomes stronger, and pain also appears in the affected areas of the skin.
In most cases, dermatitis is characterized only by external manifestations; only with the toxic form of the disease may there be feelings of weakness, pain in the joints and head. Purulent formations and nodular rashes that form during the oral form of the disease most often affect the wings of the nose, cheeks, and bridge of the nose.
Only a doctor can confirm dermatitis in a person. Usually a dermatologist deals with skin problems. He may prescribe a blood test to the patient and take material from the affected skin surface to determine a possible allergic reaction. If necessary, the patient may need to consult a therapist, allergist, and gastroenterologist.
Inflammation of the skin inherent in dermatitis is always caused by a certain irritant (inappropriate food, household chemicals, internal pathologies in the body, and others).
This fact allows us to safely say that contact with a person who has areas of the body affected by dermatitis is not a way of transmitting such a disease. You should not be afraid or avoid shaking hands with a patient in every possible way, or completely refuse to communicate with him.
A carrier of dermatitis should not be considered a spreader, since the disease is not transmitted even by airborne droplets.
Even a hereditary factor does not transmit the disease itself, but only increases the likelihood of predisposition to it.
The occurrence of dermatitis will depend not only on the characteristics of the body, but also on lifestyle, diet and many external factors that create favorable conditions for the development of pathology.
The rapid spread of inflammation to healthy areas of the skin is also not a sign of contagiousness of the disease. This can only signal the lack of proper therapy, attempts to eliminate the allergen, as well as non-compliance with the diet.
Dermatitis therapy
To treat dermatitis, traditional therapy can be prescribed, which involves the use of medications, as well as folk methods. The main goal of treatment is to get rid of the main irritant that provoked the disease.
Treatment tactics include the following recommendations:
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet. This diet can minimize the manifestations of the disease on the skin.
- Application of enzyme therapy. It is necessary for dysfunction of an organ such as the pancreas, as well as dysbacteriosis. Restoring the functioning of the digestive system allows in many cases to eliminate the external symptoms of dermatitis. At the time of enzymatic therapy, chocolate, citrus fruits, nuts, fish products, strong tea, mayonnaise and various sauces are excluded. When compiling a diet, the emphasis is on the consumption of fermented milk products, light soups, and vegetables.
- Use of antihistamines. They help relieve swelling, reduce the number of infiltrates and reduce the feeling of itching.
- Carrying out detoxification therapy if the need is identified.
- Applying hormonal ointments, antiseptics, using soothing compresses or bandages.
- It is recommended to open pustules or vesicles that occur against the background of dermatitis and immediately treat them with aniline dyes.
- Taking drugs that have a sedative effect on the body. Such drugs prevent the development of severe neurological disorder.
- Use of plants with anti-inflammatory properties. It is recommended to prepare decoctions and tinctures from them for treating affected skin.
- Urine therapy. This method is often used to combat skin inflammation, since urine has the necessary antibacterial effect.
It is recommended to select a suitable method that can cope with the manifestations of dermatitis only with a doctor.
Traditional therapy
The most effective home recipes are:
- Dilute celandine juice with water in a ratio of 2:1 (respectively). The resulting solution should be applied to the skin using gauze pads. Application of the lotion should not exceed 10 minutes in duration to prevent skin irritation. It is prohibited to use alcohol tinctures with celandine for the treatment of dermatitis.
- Mix a tablespoon (tablespoon) of string powder with 200 ml of water. Pour boiling water over the resulting solution and wait until it turns dark. The product is used to apply bandages to areas of skin with dermatitis. It is allowed to carry out 4 such procedures per day.
- Mix 100 g of baby soap, water with two tablespoons (tablespoons) of vegetable oil and the same amount of tar. To treat the skin with the resulting product, three procedures per day will be enough.
Although dermatitis is not an infectious disease, its symptoms should not be ignored. Timely measures taken to eliminate unpleasant manifestations prevent further spread of inflammation throughout the body and quickly return the skin to a healthy appearance.
Seborrheic
Seborrheic dermatitis is localized in areas with a large number of sebaceous glands: on the neck, scalp.
Under conditions of increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, the number of fungal organisms increases greatly, which causes inflammation, accompanied by the accelerated death of epidermal particles (peeling) and itching.
A variety of factors can lead to disruption of the functioning of the sebaceous glands: severe nervous tension, stress, hormonal imbalance, decreased immune defense, low physical activity (associated, for example, with obesity or impaired motor function).
Three reasons to treat contact dermatitis at El.En.
Rapid improvement.
If you follow medical recommendations, improvement occurs in a matter of days. The doctor tries to choose a treatment tactic that will give the fastest maximum effect.
Individual approach.
All symptoms and complaints of the patient must be taken into account - sometimes the causes of diseases are found where no one had thought to look for them before...
Stable result.
All our patients note long remissions and rare deterioration (in case of accidental contact with an irritant). Of course, you will have to strictly follow the proposed rules and change your habits a little.