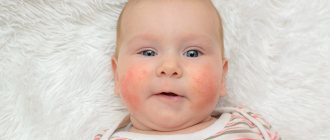
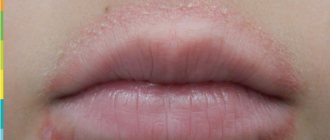
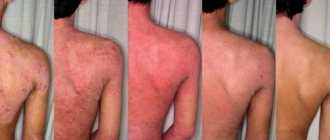
One of the most common skin pathologies in children is dermatitis. The nature of the disease is due to widespread or local inflammation of the skin, provoked by direct or indirect exposure to various factors - chemical, physical or biological. According to selective data from pediatric dermatologists and pediatricians, dermatitis in children is diagnosed in more than 40% of cases among all childhood skin diseases.
The disease usually manifests itself in the first years of a child’s life. It is quite rare for preschoolers and schoolchildren to develop for the first time.
Children are susceptible to diaper, contact, seborrheic dermatitis, but most often - atopic and allergic. At their core, these two dermatitis are a type of one disease of allergic origin. The only difference is in etiology - the cause and condition of development.
Types of dermatitis
Dermatitis appears in children and adults. Inflammation in the skin can be an independent disease or a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Regardless of the causes, dermatitis can occur in acute and chronic forms. The following types of dermatitis exist:
- atopic dermatitis;
- contact dermatitis;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- exfoliative dermatitis;
- nummular dermatitis;
- dermatitis of the hands and feet;
- simple chronic lichen;
- congestive dermatitis;
- blistering dermatitis.
A separate group of allergic dermatitis can be distinguished. Atopic and contact dermatitis, as well as cold dermatitis can be of an allergic nature. An allergic reaction to sunlight leads to the development of solar dermatitis (rashes appear on exposed areas of the skin not protected by clothing or light filters).
Insidious cosmetics
In some people, an allergic reaction occurs after using cream, ointment, deodorant, perfume, followed by prolonged exposure to the sun. Certain substances in cosmetics and perfumes react with UV rays and cause allergies. Photodermatitis can even be triggered by... sun protection cream. The danger may be:
- eosin (found in some lipsticks);
- PAVA acid (found in many sun creams);
- retinoids (found in acne and acne products);
- salicylic acid (in antiseptic ointments);
- phenol (may be present in some perfumes);
- rose, musk, sandalwood, bergamot, St. John's wort oil;
- dill juice.
What does dermatitis look like?
Cutaneous dermatitis is manifested by changes in the skin, which are usually accompanied by itching or pain. Inflammation on the skin can be local or spread over the entire surface of the body.
Inflamed skin not only changes its appearance, but also ceases to perform its functions (protective, thermoregulatory). Dermatitis is accompanied by the following skin manifestations:
- redness;
- swelling;
- getting wet;
- the formation of crusts on the surface of inflamed areas of the skin;
- peeling;
- rash (in the form of blisters or bumps).
Redness, swelling and rash are more typical of acute dermatitis, while flaking and itching more often accompany chronic skin inflammation. Each type of dermatitis has its own manifestations. The initial stage of atopic dermatitis is accompanied by the appearance of redness and rash; in the acute period, the skin may become weeping. When the inflammatory process becomes chronic, atopic dermatitis becomes dry and manifests itself as peeling and thickening of the skin. Atopic dermatitis refers to itchy dermatitis, which may leave marks on the skin from scratching. An example of skin with atopic dermatitis is shown in the photo.
Atopic dermatitis on the neck.
Contact dermatitis is manifested by redness at the site of contact with the provoking irritant, which may be accompanied by pain. Contact dermatitis is shown in the photo.
Contact dermatitis on the body.
Seborrheic dermatitis is manifested by the appearance of dandruff and dry yellowish crusts on the affected areas of the skin. Seborrheic dermatitis is shown in the photo.
Seborrheic dermatitis.
Allergic dermatitis is manifested by urticaria - a rash in the form of red spots, which is accompanied by itching. An example of allergic dermatitis is shown in the photo.
Manifestation of allergic dermatitis.
Allergy to the sun - photodermatitis (photodermatosis) and its prevention
The sun's rays not only warm us with their warmth in spring and summer and make us happy in winter, but also help strengthen our immune system. But, unfortunately, exposure to the open sun can cause an allergic reaction in some people.
Sun allergy, photodermatitis (photodermatosis) are diseases caused by increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight. This is not at all a rare occurrence. Statistics show that about 20% of people worldwide experience this disease.
Sun allergy actually refers to photodermatitis or photodermatosis. The toxic or allergic effect of the sun occurs when the sun's (ultraviolet) rays interact with any substance located on the skin (exogenous photodermatitis) or in the skin (endogenous photodermatitis).
Allergy to the sun in the form of exogenous photodermatitis
The most striking example of exogenous photodermatitis is the so-called meadow dermatitis. In summer, during the flowering period, many meadow plants secrete special substances - furocoumarins, which settle on the skin when a person is in these places. With simultaneous exposure to ultraviolet radiation, some sensitive people may experience skin redness and blisters (erythema, vesicles, bullae). The rash is accompanied by severe itching. Subsequently, long-term pigmentation remains on the affected areas of the skin.
An allergy to the sun or photodermatitis can also occur if, before going out into the sun, a person sensitive to it applied cream or ointment, or used perfume and deodorant. Substances contained in various cosmetics or perfumes can react with ultraviolet rays and cause an allergic reaction. Such properties are possessed, for example, by eosin, which can be contained in lipstick, and para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), which is part of some sunscreens. In addition, polyunsaturated fatty acids, retinoids, bergamot oil, St. John's wort, rose, musk, sandalwood, dill juice, parsley, boric acid, salicylic acid, phenol, and mercury preparations have a similar effect.
More often than others, people with fair skin and young children, whose skin defense mechanisms are much weaker, suffer from sun allergies.
Photodermatitis is often caused by many medications. This effect is exerted, in particular, by sulfonamides, barbiturates, aminazine, some antibiotics (doxycycline, tetracycline), antihistamines, some cardiovascular drugs (amiodarone, Trazicor), cytostatics, some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, aspirin), and oral contraceptives.
In addition, an increased reaction of the skin to the sun's rays appears when the skin is “weakened” by some additional influence - peeling, tattooing using cadmium salts.
Allergy to the sun in the form of endogenous photodermatitis
This group of photodermatitis includes quite rare diseases, in the development of which disturbances in the functioning of the body’s immune system, as well as various metabolic disorders (metabolic disorders), play an important role. Endogenous photodermatitis includes, in particular, porphyria, xeroderma pigmentosum, solar eczema, solar prurigo, Hydroa vacciniformia, polymorphic photodermatosis.
Typically, these reactions can occur by two mechanisms: 1) a phototoxic reaction and 2) a photoallergic reaction. Phototoxic reactions are much more common than photoallergic reactions.
How does sun allergy or photodermatitis usually manifest?
The main symptoms of photodermatosis:
- redness and inflammation of the skin,
- peeling of the skin,
- often accompanied by intense itching and burning,
- rashes can be in the form of folliculitis (pustules) or papules.
Often this condition does not develop immediately. Unlike a burn, it can occur several hours after you leave the beach, and in some cases even after returning from the resort. A phototoxic reaction can occur within a few hours of sun exposure, while a photoallergic reaction can occur even days after sun exposure.
Increased risk of developing sun allergies:
- in people with naturally light skin;
- in pregnant women;
- in young children;
- a number of medications can make skin burns faster - these include tetracycline antibiotics, sulfa drugs, painkillers, etc.;
- who has relatives with sun allergies. There is a greater chance of having a sun allergy if you have a sibling or parent with a sun allergy;
- also, the presence of atopic dermatitis or another type of dermatitis increases the risk of developing an allergy to the sun;
- Some skin allergy symptoms are triggered when your skin is exposed to a certain substance and then sunlight. Some common substances responsible for this type of reaction include fragrances, disinfectants, bleach, and even some chemicals used in sunscreens;
- those who abuse tanning beds;
- In addition, an allergic reaction from exposure to the sun can also develop in those who the day before performed cosmetic procedures using cadmium salts (tattooing, chemical peeling).
Photosensitizers are the cause of sun allergies
Some vegetables and plants can cause sun sensitivity when they come into contact with the skin. Mango peels, lime juice, parsnips, and celery may cause temporary discoloration (darkening) of the area of skin exposed to the sun. The main phototoxic fruits and vegetables: celery, carrots, rice, parsley, parsnips, and all types of citrus fruits. Therefore, before going to the beach, you should not eat oranges, tangerines or grapefruits. Swelling, redness and itching may occur on the surface of the skin where drops of juice from these fruits remain. And the more active the sun is, the more acute the body’s reaction will be.
Prevention of sun allergies (photodermatitis and photodermatosis)
Unfortunately, there are not many methods for preventing such allergies.
If you have very sensitive skin, make it a rule to sunbathe under a tent or umbrella. Avoid exposure to the sun during peak sun hours (11:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m.). Protect yourself with a hat and loose clothing made from natural fabrics: linen, cotton. Children have a very weak protective skin reaction, so children under three years old are generally not recommended to be in direct sunlight.
Use sunscreens with high photoprotection from well-known brands, and regularly, at least every two hours. Please note that the cream contains protection against UVB rays (SPF) and UVA rays (PPD) - they are the ones that affect the occurrence of photodermatosis.
It should be noted that wavelength plays an important role. Try not to go to resorts where the sun is especially active.
Recommendations for preventing photoallergy on the beach:
- Before going to the beach, you should not use cologne, perfume or regular moisturizers. They contain alcohol, which can cause sunburn in the sun.
- In your case, you need to use sunscreen as often as possible. Just pay attention to its composition. Fat-based products can cause allergies. It is better to choose a hypoallergenic spray with a protective SPF factor.
- It is better not to use waterproof sunscreen - it clogs the pores, as a result of which ulcers may appear on the skin. When going to the beach, you should opt for a water-soluble product.
If it is not possible to see a doctor, how to relieve acute manifestations of sun allergy?
No way. Only a doctor will be able to understand: the manifestations on the skin relate to phototoxic reactions or are they a manifestation of another disease. Often, “folk” methods only aggravate the course of toxic and allergic reactions.
Where can dermatitis occur?
Dermatitis can occur on any part of the skin: on the face, on the body, on the arms and legs, on the scalp. Each type of dermatitis has its own localization.
Atopic dermatitis in newborns and children of the first two years of life, as a rule, manifests itself as rashes on the face, neck, as well as on the skin of the arms and legs (shins, forearms). Atopic dermatitis in children over 2-3 years of age and adults, as a rule, manifests itself on the neck and on the flexor surfaces of the arms and legs (in the elbow and popliteal fossae).
Contact dermatitis can appear on any part of the skin, but most often develops on the hands.
Seborrheic dermatitis can appear on the scalp, behind the ears, on the face, chest and between the shoulder blades. Seborrheic dermatitis on the face usually appears on the eyebrows, along the hairline and on the sides of the nose.
Varicose dermatitis appears on the skin located above varicose veins (usually on the lateral surfaces of the legs). Dermatitis with varicose veins has the appearance of an itchy rash, which, if traumatized, can become infected with the formation of poorly healing ulcers. The cause of dermatitis in varicose veins is fluid stagnation and deterioration of skin nutrition in the area of varicose veins.
Perioral dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that occurs around the mouth. Perioral dermatitis usually manifests as pustular rashes or rosacea-like dermatitis (redness) and is a consequence of acne.
Dermatitis on the penis in men and in the labia area in women can be a consequence of sexually transmitted infections, and therefore requires consultation with a urologist (for men) or a gynecologist (for women). Dermatitis in the anus and anus can occur with proctological diseases: anal fissure, anal fistula, hemorrhoids. If inflammation occurs in the anus, you should consult a proctologist.
Dermatitis on hands photo
Photo 1. Dermatitis of the palms.
Photo 2. Dermatitis on the back of the hand.
Photo 3. Dermatitis on the hands.
Photo 4. Dermatitis on the hands.
Causes of dermatitis: contact with an aggressive chemical environment.
Prolonged exposure to low temperatures.
Dermatitis on the hands is not only a physical problem, but also a cosmetic one. Most of the time, hands are seen by strangers, who may react to rashes, papules and scratching in completely different ways. The patient’s experiences and psychological discomfort aggravate the course of the disease. According to statistics, the risk group consists of women living in big cities, but dermatitis on the hands can appear in anyone, regardless of gender, age, and lifestyle.
In addition to mental factors, the treatment of dermatitis on the hands is complicated even by hygiene and contact with the environment: with air (which can be dusty, dry, etc.), cleaning products, water, and various surfaces, sometimes contaminated. That is why dermatitis is called a disease of civilization: the development of industry and the emergence of new household chemicals have led to the fact that people are constantly faced with new types of cleaning, washing, dyeing, and adhesive products. Even the rules of hygiene, so necessary in a modern city, can do a disservice to a patient with dermatitis on the hands. Public and home toilets, money, door handles and handrails - contact with these objects, firstly, increases the risk of infection of diseased skin, and secondly, makes frequent hand washing necessary, which leads to drying, peeling, and cracking of the skin.
Through wounds formed at the site of scratching or bursting dry skin, infection can enter the bloodstream. In turn, this can lead to serious consequences for the body, including a general decline in immunity and the spread of dermatitis to other parts of the body.
Causes of dermatitis
The causes of dermatitis can be allergies, contact with irritants, skin infections or diseases of internal organs. Each type of dermatitis has its own causes and mechanisms of development.
A single cause for the development of atopic dermatitis is unknown. The appearance of atopic dermatitis is promoted by:
- genetic predisposition;
- presence of allergies;
- decreased protective properties of the skin;
- environmental factors.
A special form of atopic dermatitis is neurodermatitis - nervous dermatitis. Rashes with neurodermatitis appear against the background of stress, neuropsychic tension. An example of neurological dermatitis is shown in the photo.
Neurological dermatitis.
The cause of allergic dermatitis is individual sensitivity to foreign protein molecules (allergens). Allergens can enter the human body through food, inhaled air, animal bites or direct contact with human skin. Flea dermatitis is one of the types of allergic reactions to flea bites.
Dermatitis of the hands and feet is not an independent disease, but occurs as a symptom of other diseases. Dermatitis herpetiformis (with a rash in the form of blisters) on the palms and soles, as a rule, develops as a result of an enterovirus infection. Dermatitis on the hands and feet can also appear with psoriasis.
Foot dermatitis can also be caused by a fungal infection. An example of fungal dermatitis is shown in the photo.
Fungal dermatitis.
Bullous (blistering) dermatitis can be caused by a bacterial skin infection or sunburn. Bullous dermatitis also develops with a severe allergic reaction - toxicoderma. Infectious bullous dermatitis is shown in the photo.
Manifestation of infectious dermatitis.
Relative photodermatitis
This group includes photomicrobial and photofungal (mycotic) eczema, as well as solar exudative erythema multiforme. Sunlight activates the body's defense response when bacteria and fungi come into contact with the skin. As a result, pustules (impetigo), crusts (ecthyma), and acne appear.
Scientists (in particular, M.A. Steinberg, V.P. Fedotov7) include lupus erythematosus, a disease of southern countries with a humid climate. The reasons are autoimmune disorders that manifest themselves as persistent rashes. There are acute and subacute forms.
The sun is not an allergen, but can become a catalyst for an allergic reaction. Photo: Wolfness72 / Depositphotos
Dermatitis in children
Dermatitis can appear not only in adults, but also in children. Children are susceptible to different types of skin inflammation: atopic, seborrheic, allergic, contact dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis in children is the most common skin disease.
Children may also experience seborrheic dermatitis. Seborrheic dermatitis on the head of a child can occur immediately after birth in the form of yellowish crusts on the scalp. Special medicated shampoos can be used as prescribed by the pediatrician.
A special form of skin inflammation in children is diaper dermatitis. Diaper dermatitis develops in children in the first year of life and is an inguinal dermatitis in the form of weeping, redness and rashes in the area of the groin folds and buttocks, caused by increased skin moisture in this area.
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms of allergic dermatitis in children depends on:
- depending on age - the younger the child, the brighter the symptoms;
- duration of allergenic exposure;
- the current state of the immune system.
As a rule, dermatitis in children of an allergic nature affects the skin of the face, the skin of natural folds, the outer surface of the legs and arms, manifesting itself:
- swelling and hyperemia in places of contact with the irritant;
- burning and itching sensation;
- a rash of small, exudate-filled blisters (opening forms weeping lesions and ulcers);
- peeling of the skin (if you are allergic to certain injectable drugs).
In severe cases (Lyell's syndrome), the following are possible:
- chills and fever;
- headache accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- dehydration;
- hyperemia of the skin of the groin area, buttock and axillary folds with subsequent formation of blisters and erosions;
- epithelial detachment.
An exacerbation of the disease occurs against the background of stressful situations, severe fatigue, poor nutrition, or prolonged exposure to chemical factors.
How to cure dermatitis?
Dermatitis is treated by a dermatologist. Therapy for skin inflammation is complex and includes not only medications, but also the selection of proper skin care, diet and cosmetic methods of influencing the skin.
Skin care for dermatitis includes the selection of medicinal cosmetics to cleanse and moisturize the skin. Skincare products are selected during consultation with a dermatologist in accordance with the diagnosis.
For dermatitis, a diet may be recommended. The diet for allergic dermatitis excludes the consumption of fish, eggs, seafood, nuts, as well as those foods to which individual sensitivity has been identified. A diet for atopic dermatitis is also necessary if a food allergy has been identified.
Plasmolifting may be recommended as a cosmetic procedure to improve skin condition. Plasmolifting is the introduction of your own blood plasma into the skin. Plasmolifting for dermatitis allows you to moisturize the skin and restore its natural protective properties.
Zinc-based preparations
To eliminate the external manifestations of atopic dermatitis, doctors often recommend preparations based on activated zinc pyrithione - preparations from the Skin-cap line, which do not contain hormonal components.
Skin cap has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal effects. Skin-cap cream helps eliminate inflammation, fights fungi of the genus Malassezia, which can trigger inflammation on the skin in atopic dermatitis, and also helps reduce the risk of secondary infection and has an additional moisturizing effect.
The anti-inflammatory effect of Skin-cap is due to the inhibition of excessive production of inflammatory mediators. Thus, the mechanism of action of the drug Skin-cap contributes to the rapid resolution of rashes and elimination of itching, and the absence of a hormonal component in the composition of the drug determines the possibility of its long-term use (up to 6 weeks).
Skin-cap preparations can be used both in the active stage of inflammation for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults and children in order to reduce skin irritation, and as maintenance therapy after discontinuation of external hormonal agents.
Drug treatment of dermatitis
Drug treatment of dermatitis includes the prescription of antiallergic drugs, local hormonal ointments with anti-inflammatory activity, and keratolytic agents. Antifungal ointments may also be recommended to treat seborrheic dermatitis.
In some cases, vitamins (A, B, D) may be recommended for dermatitis. Indications for taking nutritional supplements with vitamins are determined by your doctor. Vitamin A (retinol) for dermatitis can be used both internally in the form of tablets and topically in the form of creams, serums and emulsions.
Sources
- Bolotnaya L.A. Photodermatoses // Dermatovenereology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology. —2009. — No. 1-2 (12). — pp. 188-197.
- Princely N. And there are spots from the sun // Asthma and allergies. - 2010. - No. 2. - P. 6-7.
- Macharadze D.Sh., Tsintsadze N.N. Solar urticaria and other photodermatoses // Medical advice. - 2011. - 5-6. — P. 30-34.
- Osipova V.V. Photodermatoses: photoallergic reactions // Asthma and allergy. - 2014. - No. 2. - P. 3-5.
- Polymorphic photodermatosis. Clinical recommendations. - M., 2015. - 15 p.
- Sidorovich O.I., Tsyvkina E.A. Photodermatoses: prevention and treatment // Medical advice. - 2022. - No. 18. - P. 132-134.
- Fedotov V.P. Photodermatoses (clinical lecture) // Dermatovenerology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology. - 2015. - No. 3-4. — pp. 143-157.
- Yarovaya N.F. Photodermatoses // Attending physician. - 2009. - No. 6. - P. 61-66.
Differences between dermatitis and seborrhea
Seborrhea is the excess production of sebum, which is the basis of acne. Seborrheic dermatitis is a type of dermatitis that is caused by a fungal infection and affects areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands. The manifestations of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis also vary. While seborrheic dermatitis is manifested by the appearance of yellowish crusts on the skin, seborrhea leads to oily skin and pustular rashes.
What to do?
For a treatment regimen, you should contact an allergist or dermatologist. Before treating sun allergies, you need to find out the cause of increased photosensitivity. To do this, the doctor needs to know:
- what are your working and living conditions?
- how much time do you spend in the sun;
- what medications are you taking;
- what you eat;
- Is there enough vitamin B in the body?
Diagnostic measures mainly consist of application tests with photoallergens. A specific allergen is applied to the skin and irradiated with UV light. If a reaction occurs, then the allergen has been identified.
In more complex cases, a comprehensive diagnosis is prescribed, primarily including a blood test.
Skin care for atopic dermatitis
Patients are recommended to systematically moisturize and lubricate the dry epidermis, and use dermocosmetics with a neutral pH. The use of emollients that create an occlusive layer is recommended to prevent water loss from the epidermis.
Hypoallergenic powders should be used for washing. It is better to avoid using softeners.
Skin prone to allergies and severe itching should be dried with a soft towel. Rubbing the epidermis should be avoided. The duration of bathing is no more than 10-15 minutes.
Diet for people with atopic dermatitis
People with dermatological problems need to exclude allergens from their food: gluten, cow's milk, eggs, peanuts, soy, wheat and citrus fruits. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, which have an anti-inflammatory effect, should be included in the daily menu.
Sources of healthy fats:
- fatty sea fish (mackerel, salmon, tuna, sardines);
- oils (linseed, rapeseed, hemp);
- flax-seed;
- walnuts and almonds.
Fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants have anti-inflammatory effects.
It is important to avoid fast food, limit the consumption of sugar, hot spices, animal fats, coffee and tea. Drinks can be replaced with herbal decoctions of nettle, chamomile, and plantain. Vitamin D3 supplements, probiotics and prebiotics are helpful.