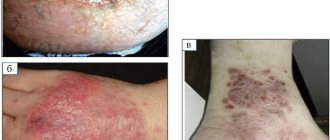
Scarring
Healing of a granulating wound occurs through scarring and epithelization. At the final stage of healing, collagen fibers appear among the cells of the granulating tissue, the number of granules decreases, and the number of fibers increases. Ultimately, the fibrous substance passes into the connective tissue and forms a scar.
When wounds heal by primary intention, delicate scar tissue is formed, which tends to resolve.
In case of healing by secondary intention, a rough scar is formed, which will not be easy to get rid of.
Trophic ulcer on the leg: how to treat
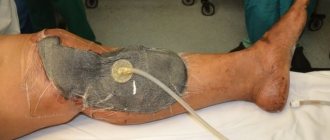
Treatment of a trophic ulcer includes two important components: treatment of the wound itself, which can last several weeks or months, and treatment of varicose veins, which leads to the formation of ulcers and can cause their reappearance. When there is an open wound on the skin, it is impossible to treat varicose veins: neither surgery nor the use of injection techniques is indicated. That is why you first need to achieve closure of the ulcer.
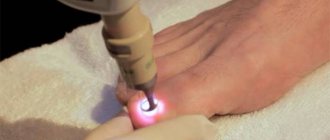
To do this, doctors carry out cleansing, as well as medicinal treatment of trophic ulcers on the legs. To disinfect a wound, both drugs and laser or ultraviolet irradiation can be used. Drugs are prescribed that improve tissue trophism and normalize blood circulation.
Ointments are used to improve wound healing. The appearance of trophic ulcers is usually accompanied by severe itching, but scratching the skin around the ulcer only worsens the situation. To relieve itching, your doctor may prescribe antihistamines. But it is better not to use folk remedies (herbal preparations, decoctions), as they can cause an allergic reaction.
The healing of a trophic ulcer is facilitated by compression, which improves blood circulation and helps avoid venous stagnation. Studies show that when using compression stockings or elastic bandages, ulcers heal in almost 80% of patients, and the area of unhealed wounds is halved.
Patients faced with the problem of complications of varicose veins should definitely consult a specialist and not self-medicate. Often, trophic ulcers heal poorly, increase in size, and if drug treatment is not started on time, skin graft surgery may eventually be required. To prevent this, you need to prevent and treat varicose veins at the earliest stages and regularly see a phlebologist. This will help keep your feet healthy and beautiful for many years.
Types of wound healing
According to the classification of I.V. Davydkovsky, the following types of wound healing are distinguished:
- closing the defect of the epithelial cover, which occurs when the upper epithelial layer is damaged;
- healing under a scab, or healing without a scar. Observed on mucous membranes in case of minor defects.
- healing by primary intention, or healing without suppuration. Characteristic of wounds with damage to the skin and tissue underneath.
- healing by secondary intention, or healing through suppuration and granulation. Occurs with extensive wounds, accompanied by foreign objects entering the wound, tissue necrosis, microbes and infections.
Why do ulcers appear on the gums, and is it always dangerous?
There are many possible reasons. To understand how dangerous the appearance of certain lesions on the gums is, you need to look at additional accompanying symptoms:
- in case it is trivial mechanical damage. The gums can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush, or a foreign object. These lesions may resolve in 3-5 days. If a person does not brush his teeth, then infection is added to these damages, and healing may take several weeks.
- Sometimes ulcers can appear as a result of wearing orthodontic structures, braces or removable dentures.
Stages of healing
The wound healing process goes through three main stages: inflammation, regeneration, and restoration of the epithelium.
The inflammation phase begins immediately after injury and in an uncomplicated state lasts for 4–5 days. During the hemostasis stage, platelets attach to sites of injury and cause a chemical reaction that activates fibrin, which forms a matrix network and binds platelets to each other. This is how blood clots form, blocking damaged blood vessels and stopping bleeding.
At the stage of proliferation and regeneration, the process of angiogenesis, collagen deposition, and the formation of granulation tissue (young connective tissue formed in places of defects) occurs. The regeneration stage can last 2–4 weeks depending on the size of the defect.
The final stage is the formation of the epithelium. Depending on the severity of the injury, the process can last from several weeks to a year or more.
The most common diseases of the oral cavity in which ulcers appear
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis. The cause of this disease is bacteria that multiply when immunity decreases. Extensive ulcers appear on the gums, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Up to 4-5 white spots first appear in the mouth, which later turn into ulcers. There is no temperature or other problems related to well-being. If such symptoms appear 1-2 times a year in small quantities, then there should be no cause for concern. Frequent occurrence is associated with weakened immunity and possible intestinal diseases, as well as allergies.
- acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis occurs in a child when he first encounters the herpes virus. Many bubbles appear on the gums, which, after bursting, turn into ulcers that merge with each other. The gums are always bright red, and the ulcers themselves are very painful, the temperature may rise
Wound treatment
The choice of wound treatment method largely depends on their type (infected or necrotic, wet exuding or fibrous granulating, trophic ulcers or bedsores). Only a doctor can choose the optimal solution for treating each type of wound.
In addition, at each stage of wound healing, it is necessary to use a different agent: one that promotes the removal of exudate, the formation of granulation tissue, accelerating epithelization, etc.
When treating wounds, you need to remember that the wound does not heal on its own, but thanks to the body’s resources aimed at healing it. The immune, endocrine, and circulatory systems are involved in this process. A qualified doctor, along with treating the wound itself, will definitely prescribe a vitamin complex to maintain the body.
Features of the course of the disease
Experts identify the following stages of development and treatment of trophic ulcers:
- damage (exudation). This stage is characterized by severe inflammation, the appearance of foci of necrosis, and a large amount of pus can be separated from the wound. In the damaged stage, the ulcer must be actively treated by cleaning it and using anti-inflammatory therapy.
- granulation (purification). At this stage, topical medications should be used to improve healing. Then the ulcer gradually clears, becomes covered with new pink tissue (granulation tissue), purulent discharge disappears, the total amount of discharge and inflammation decrease.
- epithelization (healing). At this time, new skin appears on the ulcer, usually along the edges, but there may also be island epithelialization, when the skin appears in islands throughout the ulcer. During the active healing stage, it is necessary to maintain a moist environment in the ulcer through the use of ointments, use wound healing agents, and moisturize the skin so that it does not dry out or crack.
Scarring and healing of the ulcer occurs only if the trophic ulcer is treated. Ulcers do not heal on their own.
How to speed up healing
The speed of wound healing varies. It depends on the nature of the injury and the individual characteristics of the patient, such as age, nutrition, and medications taken.
To speed up healing, it is necessary to provide optimal conditions for tissue regeneration at each stage. This role is fulfilled by therapeutic dressings designed for each stage of healing.
The method of hydrotherapy has a positive effect. Its essence consists in the sequential use of two dressings HydroClean and HydroTac. Using the first, the wound is cleaned, and then a second is applied, creating optimal conditions for granulation and epithelization.
First aid
If the temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic drug. In the future, before visiting a doctor, nothing should be done. Do not take antibiotics yourself or try to get into the ulcer with any object.
How to relieve symptoms of ulcers
- do not eat sour and salty foods
- food should be warm, no hot dishes or drinks
- Care should be taken to ensure that the child does not put dirty hands in his mouth
- teeth should be brushed, but make sure that the bristles do not touch the gums with ulcers
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal solutions (oak bark, chamomile) 3-4 times a day
You should be careful when using antibacterial solutions. They must be prescribed by a doctor. If such solutions are used incorrectly, they can provoke the development of thrush. The antibacterial agent will “kill” the beneficial microflora, which can result in a fungal infection.
Prevention of ulcers
- professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year
- Regularly replacing your toothbrush
- Proper brushing of teeth at least 2 times a day
- using additional hygiene techniques such as irrigators, dental floss, and tongue scrapers
- Children should be monitored for bad habits such as putting dirty fingers and other objects into their mouths
- It is important to treat your teeth in a timely manner. Microbes that are found in carious teeth and rotten roots can serve as a source of infection for ulcers
If you have problems in the oral cavity, contact the specialists of the Center for Family Dentistry!
What to do if the wound does not heal
Non-healing or chronic are wounds that do not respond adequately to therapy despite prolonged treatment. Such wounds are usually caused not by external factors, but by reasons hidden inside the body, leading to disruption of metabolic processes and, as a consequence, disruption of the wound healing process. This category includes trophic ulcers, bedsores, and diabetic foot ulcers. Before using any dressings, consult a doctor: therapy and treatment of wounds can only be prescribed to you by a doctor!
For the treatment of chronic wounds, HARTMANN has developed a two-bandage system - HydroClean Plus and HydroTac.
The HydroClean Plus cleansing dressing can be used at all stages of wound healing, effectively removing necrotic tissue and pathogenic bacteria from the wound surface. They get caught in the absorbent layer and die under the influence of the antiseptic. The HydroTac dressing has absorbent and moisturizing properties and also protects the wound from secondary infection.
With the help of the hydrotherapy system, many patients have been able to significantly alleviate suffering and improve their quality of life.
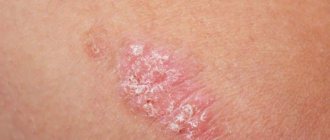
Causes of trophic ulcers
In the vast majority of cases, leg ulcers are caused by varicose veins. After all, if a vein is stretched and the valves inside it do not close tightly, so-called reflux occurs - reverse blood flow. As a result, the blood stagnates, which means the harmonious blood flow in the limb is disrupted.
This means a violation of tissue nutrition (from the Greek trophe - food, nutrition). As a result, the swelling characteristic of varicose veins intensifies, the skin becomes thinner, a darker pigment spot appears on it, and then a wound that does not heal for a long time.
Most often, ulcers appear on the inner surface of the lower third of the leg; the fingers are rarely, almost never, involved. From a venous ulcer, inflammation rarely spreads to the tendons and bones. This is why trophic ulcers cannot be ignored and must be treated.