- home
- Surgery
- Fibroma removal
KDS Clinic offers its clients operations to remove skin fibroids in an outpatient setting. The best doctors in the field of surgery and dermatology will conduct a full examination and help you get rid of the tumor quickly and safely.
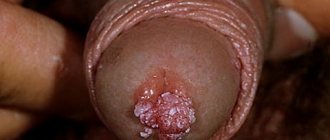
Skin fibroma is a benign tumor that forms from mature connective tissue cells. It can be localized on any part of the body, but mainly affects the face and neck.
Why does fibroma appear?
Fibroids can develop as a result of a hereditary predisposition. In addition, poor diet, smoking and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages lead to the development of fibroids.
The causes of fibroids also include:
- hormonal imbalance;
- overweight;
- metabolic disease;
- frequent skin damage (scratches, bruises, cuts);
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease).
Abortions in late pregnancy, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system and ovarian dysfunction can lead to the development of uterine fibroids. Breast fibroids can be triggered by prolonged breastfeeding or refusal of lactation.
Causes and symptoms
Cutaneous fibroma is most often diagnosed in women. The disease practically does not occur in children and adolescents. The exact cause of the development of dermatofibroma has not been established. The following factors can trigger its development:
- microtraumas;
- dermatological diseases of an infectious nature;
- insect bites;
- acne;
- age-related changes in the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- liver pathologies.
Symptoms of the disease are accompanied by the appearance of a small convex formation in the shape of a hemisphere. It has a dense consistency and a smooth surface. Most often the growths are located on the feet.
Symptoms of fibroma development
Fibroids can be single or multiple. The main symptom of the development of skin fibromas is the presence of a lump under the skin ranging in size from one to several centimeters. Signs of breast fibroids include nipple discharge, breast asymmetry, and the presence of dense lumps in the breast area.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids include:
- pain in the pelvic area;
- pain in the back and legs;
- menstrual irregularities;
- frequent or difficulty urinating.
At the first signs of fibroid development, you must make an appointment with a dermatologist, gynecologist or mammologist, depending on where the tumor develops (on the skin, in the uterus or in the mammary glands). Only a doctor can diagnose a neoplasm and prescribe a treatment regimen.
Preparatory stage
Laser removal of skin tumors does not require special preparation. The only thing is that you cannot get into the procedure without a preliminary examination of the fibroid.
You need an in-person consultation, where a cosmetologist:
- conduct a visual examination and dermatoscopy;
- clarifies the contraindications;
- will prescribe tests to clarify the diagnosis.
The presence of any diseases or medications can seriously affect the quality of the procedure. Equally important is the identification of the fibroma itself, including testing the tumor for benignity. It is impossible to confirm this without biopsy results. The patient may also be asked to take a general blood test and go for an ultrasound.
Types of fibroids
Fibroids can be soft or hard. A soft fibroma is a small, slowly growing growth on a stalk. Solid fibroma has a wide base without a stalk.
Based on location and symptoms, the following types of fibromas are distinguished:
- a single cervical fibroma is a benign formation that reaches small sizes and, as a rule, does not interfere with pregnancy;
- nodular fibroid (fibromyoma) of the uterus - characterized by the development of nodes in the tumor, which can increase in size, cause severe pain and put pressure on other internal organs;
- submucous fibroids of the uterus - a benign formation of fibrous fibers of the muscle layer, which grows inside the uterine cavity;
- mammary fibroma (mammary fibroma, breast fibroma) is a benign tumor of the mammary gland in the form of nodules consisting of fibrous and glandular tissue;
- fibroadenoma of the mammary gland is a benign formation of glandular nature, fibroadenoma resolves extremely rarely, in most cases it must be removed surgically;
- soft tissue fibroma is a benign formation that develops in soft tissues (muscle tissue, tendons, subcutaneous fat, intramuscular layer, lymph nodes); upon palpation, the fibroma can move;
- Ovarian fibroma is a benign ovarian tumor of a round or oval shape. The risk of developing ovarian fibroids increases after menopause.
Only a doctor can determine the type of fibroma. Depending on the type of tumor, its size and stage of development, an individual treatment regimen is prescribed.
Diagnostics
Initially, experienced specialists - oncologists or multidisciplinary surgeons - conduct a detailed examination of the patient, record all the complaints that exist, palpate the formation and make a preliminary diagnosis.
Then you need to determine the nature of the tumor. After this, you need to conduct an ultrasound examination of the tissues where the tumor is located to determine its size, nature, and changes in the tissues. If necessary, an X-ray examination is performed. If questions remain, a biopsy of the suspicious area should be performed to rule out a malignant process. Fibroids can be detected by palpation (feeling with fingers or hands) performed as part of a pelvic examination, or diagnosed through imaging procedures such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Contraindications for fibroids
For single fibroids of small size, there are no contraindications to physical and sexual activity. But if fibroids are multiple or are characterized by clear signs (heavy bleeding after sexual intercourse, severe pain in the pelvic area and back), you need to consult a doctor who will conduct a diagnosis, prescribe a treatment regimen and determine individual contraindications.
With large fibroids and fibroids at advanced stages of their development, there may be contraindications to intense physical activity and sexual life. In addition, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation (sunbathing, solarium), as well as visiting baths and saunas, may be contraindicated.
Prices for radio wave removal of skin lesions on a wide base
| Removal of 1 milia (grass, wen) in the eye area | 950 rub. |
| Removal of 1 wide-based skin lesion (digital dermatoscopy 750, removal 2150, anesthesia 550, histology 1500, free consultation on the day of treatment) | 4950 rub. |
| Removal of 2 wide-based skin lesions (digital dermatoscopy 750, removal 4300, anesthesia 1100, histology 3000, free consultation on the day of treatment) | 9900 rub. 9150 rub. ( 8% discount |
| Removal of 3 broad-based skin lesions (digital dermatoscopy 750, removal 6450, anesthesia 1650, histology 4500, free consultation on the day of treatment) | 14850 rub. 13350 rub. ( 11% discount |
If you are reading these lines, then you probably have a formation (or several) on your skin and you want to get rid of them. keratoma pigment nevus fibroma milia (also called millet or wen)
hemangioma (angioma) dermatofibroma
- Do you think that keratomas or milia
on your face make you less attractive? - Because of a nevus
in your armpit, are you now wielding a razor like a professional hairdresser? - Are fibroids on your back
making it difficult to wear a bra? - Instead of playing sports and active recreation, are you thinking about accidentally damaging the hemangioma
? - At the beach, do you cover dermatofibromas
on your skin with a band-aid and are afraid to sunbathe? - Tired of touching the wart with your hand
or clothes, and are you thinking about getting rid of it for the hundredth time?
Read this text to the end and you will learn how to get rid of unwanted formations on the skin in one visit without scars and 100% safely.
Removal of uterine and ovarian fibroids
Removal of uterine and ovarian fibroids is carried out after their diagnosis. A gynecologist or surgeon conducts an examination, studies the medical history and, if necessary, prescribes additional tests (ultrasound of the pelvic organs, laboratory tests).
After diagnosis, the gynecologist prescribes an individual treatment regimen for fibroids of the uterus and ovary, which includes drug therapy (anti-inflammatory and hormonal drugs) and surgical removal of fibroids. Methods for surgical removal of uterine and ovarian fibroids include:
- hysteroscopic surgery for fibroids of the uterus and ovary - performed through the vagina using a long thin probe with a built-in backlit video camera, the image from which is transmitted to the monitor;
- laparoscopy of fibroids of the uterus and ovary - a minimally invasive intervention during which the fibroid is removed through several small punctures in the lower abdomen;
- open surgery - access to the uterus is provided through an incision in the lower abdomen along a natural fold of skin; it is performed in the presence of large fibroids.
The duration of the operation to remove fibroids of the uterus and ovary is 1-2 hours. The evening before the operation and on the day of the intervention, you should not eat, and two hours before the start of the operation you should not drink.
Treatment methods
Dermatofibromas are harmless and treatment is not required unless there are warning signs or cosmetic concerns. If the patient wishes to remove dermatofibroma, surgical treatment is possible - surgery .
It is important to evaluate its consequences: the scarring and tissue changes that occur after surgical excision may look worse than the original lump. For plantar fibroids, non-surgical treatment options are preferred because the surgical procedure requires a long recovery period and can lead to complications that may be worse than the plantar fibroids themselves. Non-invasive treatments for plantar fibroids include:
- extreme cold or cryodestruction to reduce fibroids.
- pads or insoles to relieve discomfort when wearing shoes.
- stretching.
Most doctors agree that for severe cases of plantar fibroma, the smartest option is to resort to invasive treatments and surgery. Invasive treatments for plantar fibroids include:
- injections of corticosteroids into fibroids.
- surgical removal of the entire plantar fascia (which is associated with a long recovery period and a high risk of developing other foot problems).
- surgical removal of fibroids (with a high recurrence rate).
Treatment is indicated when dermatofibromas are bothersome or persistently irritated. In these cases, surgical removal and freezing with liquid nitrogen can be performed.
Treatment for uterine fibroids depends on the size, symptoms, and other factors. Asymptomatic fibroids may not require treatment. A myomectomy (surgical removal of uterine fibroids) may be performed to remove fibroids that are interfering with fertility in women who want to become pregnant. Hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) is also commonly performed on patients with severe symptoms of uterine fibroids, but is not an option for women planning a pregnancy. Non-surgical treatment for uterine fibroids includes medications, uterine artery embolization and targeted ultrasound treatment.
Removal of breast fibroadenoma
Preparation for removal of breast fibroadenoma includes a consultation with a mammologist and undergoing diagnostic tests. Methods for diagnosing breast fibroadenoma include:
- breast biopsy;
- ECG of the heart and consultation with a therapist;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- blood test for pathogens of hepatitis B and C, HIV and syphilis;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands.
After diagnosing fibroadenoma, the doctor prescribes surgical treatment. At the initial stage of fibroadenoma, sectoral resection (partial removal) is performed. Removal of breast fibroids is performed under local anesthesia. After removing the formation, the surgeon applies a cosmetic suture using self-absorbing threads.
For large breast fibroadenoma, total resection of the tumor and the affected gland is performed. Typically, the operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts from one to two hours.
How does the procedure work?
The doctor works in a treatment room. All manipulations are carried out using disposable gloves. Disinfection of a wound with an ultraviolet ray does not eliminate the requirements for sterile conditions.
The cost of removing fibroids on the face with a laser is around 1000 rubles. In other areas of the body, you will have to pay for the size and number of tumors. Most clinics indicate an area of 1 cm2 in the price list. The average price depends on the area:
- Intimate - 1000 rub.
- Heads - 1000 rub.
- Eye - 2000 rub.
- Mouth and mucous membranes - 2500 rub.
- Bodies - 700 rub.
Anesthesia and doctor's consultation are not included in the cost of the procedure.
Recovery after fibroid removal
The recovery period after fibroid removal is usually up to seven to ten days. After removal of breast fibroids, you must visit a doctor or nurse every day or every other day to apply dressings. In addition, you should minimize physical activity, wear bandages, and eat a healthy and balanced diet. After removal of fibroids of the uterus and ovaries, it is also necessary to wear a postoperative bandage and lead a healthy lifestyle (eat properly, avoid overwork, stress, and maintain a sleep schedule).
Causes of soft skin fibroids
Scientists have not yet established the exact causes of soft skin fibromas. It is believed that the appearance of acrochordon is provoked by the following factors:
- Endocrine disorders . It has been established that soft fibromas are more common in pregnant women (with increased levels of progesterone and estrogen), with diabetes mellitus, as well as with acromegaly (a disease caused by dysfunction of the pituitary gland).
- Irritating factor . Often soft fibroids form in places where mechanical friction occurs with jewelry (for example, a chain on the neck), clothing straps, belts, as well as in skin folds.
- Aging processes . The appearance of acrochordons is often associated with the natural processes of skin aging, since cases of soft fibroids are more common among older people.
- Human papillomavirus infection . Some scientists believe that soft fibroma is caused by human papillomavirus infection, but there is not enough research to confirm this fact at the moment.