A peritonsillar abscess is an inflammatory process in the tissue around the tonsils. Usually the cause of its appearance is a sore throat, when inflammation moves from the palatine tonsils to nearby tissues. An abscess can also form as a complication of purulent or streptococcal pharyngitis.
An oral cavity weakened by infectious lesions, injuries to the gums, palate and tongue, smoking and caries, as well as reduced immunity are factors that contribute to the development of the disease. The accumulation of pus provokes pain and prevents the patient from swallowing food, talking, and even moving his head normally.
Paratonsillitis: etiology and danger of its development
Acute inflammation of the peritoneal tissue feels like a huge lump in the back of the throat, filled with pus. It can be unilateral, or affect the right and left tonsils simultaneously.
The development of the disease occurs against the background of acute tonsillitis, streptococcal pharyngitis and general weakening of the body. When the infection enters the tissue around the tonsils from the festering follicles and lacunae, purulent contents begin to accumulate in it.
The concept of “peritonsillar abscess” characterizes an already formed process of a cavity with pus. In this case, the patient feels a strong, increasing pain in the throat, notes difficulty swallowing, weakness, chills, and a strong increase in temperature. He has swollen lymph nodes and bad breath.
Content:
- Paratonsillitis: etiology and danger of its development
- Methods for identifying and treating pathology
- Indications for opening an abscess
- How is an abscess removed?
- Mandatory hospitalization for peritonsillar abscess
- Recovery measures after surgery
Painful sensations radiate to the ear and jaw, causing trismus of the masticatory muscles to develop, and the patient cannot open his mouth normally.
The danger of the pathology is that if pus continues to accumulate in the throat, it can enter the deeper tissues of the neck and cause the development of sepsis, acute laryngeal stenosis, neck phlegmon and mediastinitis. In severe cases, death is possible. The presence of these complications is an indication for hospitalization of the patient.
Depending on the location of the cavity with pus, paratonsillitis is classified into several forms.
The posterior abscess is localized between the velopharyngeal arch and the tonsil, with a high probability of inflammation spreading to the larynx area.
The anterior form is located between the upper part of the tonsil and the palatoglossus arch. Such an abscess often opens on its own, after which the pus ends up in the throat.
Some inflammatory dental conditions cause the formation of lower paratonsillitis - an abscess behind the lower edge of the tonsil.
External paratonsillar abscess is diagnosed quite rarely - it is localized outside the tonsil. In this case, rupture of the abscess is dangerous because pus gets into the soft tissues of the neck.
The differences in pathological changes in the pharynx that paratonsillitis causes allow us to distinguish the following types of pathology:
- edematous;
- infiltration;
- abscess.
The first type of pathology develops without pronounced inflammation, and is characterized by severe swelling of the tissues, while the symptoms manifest themselves at this stage in the form of moderate sore throat.
Further, symptoms of progression of inflammation appear, pain increases and an increase in temperature is noted. At this stage, the disease can already be diagnosed.
The abscess form occurs 2-4 days after the onset of inflammation. At this time, a massive formation filled with pus is formed, which leads to deformation of the pharynx.
Services
Opening of abscesses - a puncture, an incision of the abscess with a scalpel, followed by cleaning the wound.
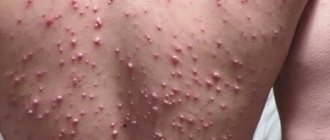
An abscess is a formation on the skin and mucous membranes of various sizes and shapes with purulent contents.
At the “My Doctor” medical center, the following types of ulcers are opened:
- carbuncles
- boils
- acne
- abscesses
- hidradenitis
- panaritiums
- paronychia
- phlegmon
EXAMINATION BEFORE OPENING UPSURES
Express test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B, C (blood test is performed in our laboratory within 30 minutes).
Carbuncle is an acute purulent inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue around several adjacent hair follicles and sebaceous glands. The opening of the carbuncle is carried out in case of necrosis (death) of tissue.
HOW IS THE CARBUNCLE OPENED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the carbuncle. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, a cross-shaped incision is made with a scalpel at the site of the formation, dead tissue is removed, and the leaks are opened. The wound is cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
After the procedure, an aseptic bandage is applied for 2 days. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes.
A furuncle or boil is an acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and surrounding tissue with the formation of a rod. A furuncle, unlike a carbuncle, develops within the boundaries of one hair follicle. The boil is opened if the abscess grows in the subcutaneous tissue and prevents the rod from being rejected.
HOW IS THE OPENING OF A BOIL PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the boil. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, the wall of the boil is pierced with a scalpel, and the rod is removed. The wound is cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
After the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied. Dressings are required daily until the wound is completely healed.
The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes.
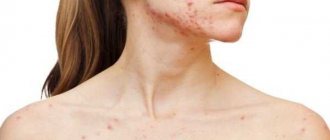
Acne is a purulent pimple that occurs due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. Autopsy of the acne is performed for severe acne.
HOW IS THE OPTION OF AN EAL PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the acne. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, the wall of the acne is pierced with a scalpel. The wound is cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
After the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes.
An abscess is a purulent inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue with the formation of an abscess.
HOW IS AN ABSCESS OPENED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, an incision is made over the abscess with a scalpel, the surgeon inserts a finger into the cavity of the abscess and destroys the walls of the chambers. A strip of gauze soaked in a special solution is inserted into the incision to drain the pus, and an aseptic bandage is applied.
The drainage is removed after 2 days. Repeated drainage is carried out as necessary until the pus is completely removed. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
Hidradenitis is a purulent inflammation of the sweat glands.
HOW IS HYDRADENITIS OPENED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, a wide incision is made with a scalpel through the abscess to healthy tissue. The surgeon cleans out the pus and removes all infected fatty tissue. The wound is treated with an antiseptic.
After the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
Panaritium is a purulent inflammation of the soft tissues and bones of the finger around the nail.
HOW IS THE OPTION OF A PANARICIUM PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. after anesthesia, the subcutaneous tissue of the finger is dissected with a scalpel. The wound is cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
The affected nail may need to be removed.
If necessary, drainage of the abscess is carried out - a strip of gauze soaked in a special solution is placed under the nail fold to drain the pus. The gauze is removed after 4-5 days.
After the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes.
Paronychia is a purulent inflammation of the skin and tissues of the finger around the nail.
HOW IS THE OPTION OF PARONYCHIA PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. after anesthesia, the detached part of the nail is removed using surgical scissors - the nail fold is lifted from the nail, the scissors are inserted under the edge of the root and the detached part is removed. A strip of gauze soaked in a special solution is placed under the nail fold to drain the pus, and an aseptic bandage is applied.
The drainage is removed after 2-3 days. Repeated drainage is carried out as necessary until the pus is completely removed. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
Cellulitis is an acute purulent inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue with the formation of an abscess that does not have clear boundaries.
HOW TO OPEN PHLEGMON WITH A SCALPEL
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, an incision is made over the abscess using a scalpel, the cavity with pus is emptied and washed with an antiseptic solution. If necessary, a drainage is inserted into the incision to drain pus. An aseptic bandage is applied on top. The drainage is removed after the cavity is completely cleared of pus. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
HOW IS RADIOSURGICAL OPENING OF PHLEGMON PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, a non-contact incision is made over the abscess of the damaged tissue and cauterization of the vessels using the Surgitron apparatus. Using a special electrode resembling a thin wire, a beam of radio waves penetrates deep into the damaged area of tissue and evaporates it. The cavity with pus is emptied and washed with an antiseptic solution. If necessary, a drainage is inserted into the incision to drain pus. An aseptic bandage is applied on top. The drainage is removed after the cavity is completely cleared of pus. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
During the operation, the Surgitron radiosurgical device simultaneously cuts, eliminates bleeding and disinfects the incision site, which is almost invisible.
TREATING UPRESSURES INDEPENDENTLY IS PROHIBITED
- the use of absorbable ointments without a surgeon’s prescription can provoke the spread of inflammation to neighboring tissues, lead to damage to internal organs and even sepsis - blood poisoning
- squeezing out the abscess also leads to the spread of inflammation to neighboring tissues, causing the disease to become chronic. And squeezing out acne in the nasolabial area can lead to meningitis, encephalitis, neuritis of the cranial nerves
Therefore, when an abscess passes into the stage of abscess and necrosis, it is important to contact a surgeon in a timely manner.
Methods for identifying and treating pathology
Considering that an abscess, especially at the abscess stage, has characteristic manifestations, the doctor usually does not have any problems making a preliminary diagnosis.
After examining and collecting anamnesis, the doctor will refer the patient for pharyngoscopy and some tests - a general analysis and blood biochemistry, a smear for bacterial culture and a diphtheria pathogen from the pharynx.
To determine the depth of the lesion, ultrasound and computed tomography of the neck may additionally be prescribed. It is important to differentiate the disease from other lesions - scarlet fever, diphtheria, carotid artery aneurysm.
Treatment of paratonsillitis includes drug therapy and surgery - opening of the paratonsillar abscess.
Antibiotics are mandatory prescribed as etiotropic therapy. In addition, the patient must be prescribed antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and painkillers. To have a local effect on the inflammatory process, you need to rinse the mouth and throat with antiseptic solutions.
Surgery is the most effective method of eliminating an abscess. It can be performed on patients according to indications, regardless of gender and age.
Is it necessary to open a boil?
In the case of an abscess, that is, when there is an accumulation of pus in the inflamed area, the boils are opened. Purulent formation does not respond to any conservative treatment; in this case, only surgical intervention will help.
You need to understand that the surgical procedure for opening the boil itself does not cause any complications, and its duration is minutes. It is extremely important to start treatment as early as possible to avoid causing serious adverse effects.
Abscesses on the face are very dangerous, there is a risk of infection through the anastomoses into the vascular system of the brain, diseases such as sepsis, meningitis, phlegmon, osteomyelitis can develop.
Content:
- Is it necessary to open a boil?
- Algorithm for opening a boil
- Prevention of boils
If the infection is not removed in a timely manner, it can spread throughout the body, capturing more and more areas of healthy skin.
Sometimes the inflammation extends beyond the hair follicle, and phlegmon develops, which, unlike a local lesion, will have to be treated in a hospital setting.
At the initial stage of the development of an abscess, it is possible to do without surgical intervention. After the formation of a purulent abscess, it must be removed in a hospital setting, after which therapy with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antiseptic drugs is mandatory.
Indications for surgery are the presence of high fever; severe pain; pronounced swelling of the tissue around the purulent formation; loss of strength; lethargy and weakness.
Indications for opening an abscess
The possibility of developing this kind of complications can be assumed if the following symptoms are present:
- tonsillitis, the duration of which exceeds 5-6 days: during this time an abscess may form;
- severe, severe pain in the throat that is felt when swallowing or moving the head;
- temperature increase over 39 degrees;
- significant enlargement of one or two tonsils;
- signs of intoxication and fever (weakness, malaise, muscle pain, apathy and drowsiness);
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- increased heart rate and breathing.
The development of an abscess, which is accompanied by such symptoms, is a direct indication for opening the abscess.
Usually the operation is performed 4-5 days from the onset of the inflammatory process - by this time the abscess is already fully formed. To check the readiness of the cavity for removal, the doctor may prescribe a diagnostic puncture - puncturing the cavity with a thick needle in the place that protrudes the most above the tonsil. The progress of the procedure is most often monitored by endoscopic or ultrasound monitoring. If pus is found in the cavity of the syringe used for puncture, it means that an abscess has formed and is ready for removal.
The autopsy is performed on an outpatient basis, that is, to perform it, the patient does not need to go to the ENT department of a medical institution.
Reasons for formation
Due to their development, there are two types of perimaxillary abscesses:
- Odontogenic. The cause of development is damaged dental elements.
- Non-odontogenic. Not caused by the condition of the dentofacial apparatus.
The most common causes of anomalies are dental diseases:
- Advanced carious lesions of units, pulpitis.
- Deep periodontal pockets.
- Periodontitis.
- Pericoronitis.
- Infected and impacted molars and premolars.
- Root cyst.
The development of a lesion can be triggered by penetration of infection under the periosteum from a diseased unit.
Reasons for the development of non-odontogenic foci of pus:
- Traumatic lesions of the jaws, elements or soft membranes of the oral cavity with infection.
- Nasopharyngeal and ear infections.
- Complications of unqualified dental treatment.
- Spread of infection to the jaw from other organs and systems.
The development of an abscess depends critically on the general health and immunity of the patient.
How is an abscess removed?
A few days before the planned surgery, the patient needs to start taking antibiotics.
Before the autopsy begins, the patient is given an anesthetic for local anesthesia. In the place where the wall of the pharynx protrudes most and has the smallest thickness, the doctor makes an incision into the purulent formation. Its depth does not exceed 10-15 millimeters - this way it is possible to prevent damage to adjacent vessels and nerves. Using a special suction, the surgeon removes purulent contents from the cavity, after which he inserts a blunt instrument into the incision and destroys the partitions of the cavity from the inside to improve the outflow of pus. Next, an antiseptic is injected into the cavity, the doctor stops the bleeding and sutures the edges of the wound.
If during the process it is discovered that the pus does not have a clear localization, but has spread between the fascia of the neck, the surgeon decides to take the necessary therapeutic measures. The scope of the operation is expanding, since this condition is deadly for the person being operated on. If necessary, a drainage tube can be inserted into the patient through incisions in the neck. Each specific situation requires different surgical procedures.
Clinical symptoms
Manifestations of the disease are determined by the location and severity. The pathology clinic is similar to periodontitis. The patient experiences intense pain that increases with palpation or biting on the affected area.
The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
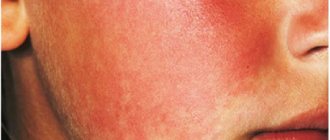
- Dense swelling and severe hyperemia.
- Protrusion of a pathological focus from the mucous membrane of the cheeks or periodontium.
- Facial asymmetry, jaw deformation.
- The flow of pus from the fistulous passages.
- Hyperthermia during intoxication.
- Dizziness, lack of appetite, deterioration in general health.
- Allergic reactions.
Some symptoms may be absent or mild. Clinical manifestations depend on the location.
Diagnostic techniques
Initially, the doctor conducts a patient interview and a clinical examination of the oral cavity. The time of onset and nature of the symptoms are clarified. Complaints of deterioration in health, loss of appetite and other manifestations of intoxication are heard.
During the examination, the doctor visually and palpably assesses the condition of the mucous membrane in the affected area. The pain of touch, the presence of carious units, the condition of the skin in projection, the symmetry of facial features, and lymph nodes are recorded. Body temperature and pressure are measured.
If necessary, additional diagnostic measures are carried out: X-ray, ultrasound, EDI, CBC.
Based on the data received, the doctor confirms the diagnosis and draws up a treatment plan.
Schemes for eliminating the disease
An integrated approach to treating the disease is used. Surgery allows you to open and drain the source of infection. Symptomatic therapy, antibiotics, vitamins, anti-inflammatory drugs, and detoxification drugs are prescribed as additional methods. Drug therapy is limited to 1-2 weeks.
When choosing a treatment regimen, the following are taken into account:
- Features of the pathology: stage, localization, prevalence, etc.
- Age and immune status of the patient, concomitant diseases.
The main task of the dentist is to prevent the spread of infection to other organs and systems of the patient’s body.
Surgical autopsy
It is performed under local anesthesia. The operation consists of several stages:
- Opening and removing pus.
- Antiseptic wound treatment.
- Drainage, dressing.
- Daily dressings with antiseptic treatment.
After surgery, the oral cavity must undergo sanitation, treatment or extraction of the affected unit.
Potential Complications
A maxillary abscess is actually a complication of infectious diseases, trauma or caries-affected units. In the absence of timely treatment, the pathology can take dangerous and life-threatening forms: meningitis, phlegmon, mediastinitis, thrombophlebitis of the sinuses of the brain, sepsis.
Mandatory hospitalization for peritonsillar abscess
The development of a purulent cavity in the tissues of the tonsils in some cases can pose a real danger to the patient’s life. The attending physician decides to place the following categories of patients in the hospital:
- children;
- pregnant women;
- people with a pronounced decrease in immunity;
- those who have severe concomitant diseases;
- patients at risk of developing complications;
- if you have a drug allergy;
- patients with the absence of a localized location of pus, when it is distributed in the tissues of the neck.