In this article we will tell you:
- Causes of chalazion
- Symptoms and diagnosis of chalazion
- Chalazion treatment
- Contraindications
- Complications
- Prevention of chalazion
- Chalazion in children
- Conclusion
A chalazion (or chalazion) is a chronic inflammation of the eyelid margin around the meibomian gland, resulting from a blockage. Externally, chalazion is very similar to stye; both diseases manifest themselves in the form of a small nodule. Unlike styes, chalazions rarely resolve on their own. It has its own signs, symptoms, stages and treatment regimen. There are several types of chalazion. It can be internal (located inside the eyelid) and external. There is a chalazion of the upper eyelid and a chalazion of the lower eyelid. When we are healthy, our sebaceous glands produce fatty secretions. It moisturizes the mucous membrane of the eye, facilitates the movement of the eyelids during blinking. When the meibomian gland ducts are blocked, a chalazion can develop. Most often, the pathology occurs in people over 30 years of age. Chalazion does not threaten human life. In addition to pain, it most often causes only cosmetic discomfort.
Causes of chalazion
- Chalazion on the eyelids develops as a pathological process. It can be triggered by various factors:
- Unsanitary conditions in the premises, poor hygiene;
- Weakened immune system;
- Incorrect use of contact lenses;
- Stress, depression, disturbed psycho-emotional state;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Vitamin deficiency as a consequence of improper diet;
- Untreated barley;
- Excess cosmetics on eyelids and eyelashes. For example, upper eyelid chalazion can occur in women who wear false eyelashes;
- Chronic forms of blepharitis;
- Skin diseases;
- Oncology;
- Hormonal imbalances and metabolic disorders, including diabetes;
- Blockage of the excretory ducts of the meibomian glands
Symptoms and diagnosis of chalazion
Typically, the inflammatory process begins smoothly and gradually becomes chronic. A person discovers lumps by accident. Both diseases present in the same way with redness and swelling of the eyelid. Barley occurs due to purulent inflammation of the gland tissue, while chalazion is the result of a blocked duct. It affects the inside of the eyelid and is in close contact with the conjunctiva of the eye. But pathology can develop precisely because of untreated barley.
Styes, as a precursor to chalazion, can be caused by a bacterial infection. In most cases it is Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteria begin to multiply due to weakened immunity and colds. It is important to catch the onset of the inflammatory process at an early stage in order to prevent its development.
The following diagnostic procedures may be required:
- General blood analysis;
- Bacteriological blood culture;
- Screening immunogram;
- Stool analysis;
- Staphylococcus culture;
- Analysis of sexually transmitted infections.
Inflammation can develop due to:
- Bacteria;
- Gribov;
- Parasites;
- Chlamydia;
- Viruses.
There are a number of signs that will help determine that barley is developing into a chalazion:
- After a week of treatment for stye, it does not decrease and the redness does not subside;
- Increases in size, begins to bleed and affects vision;
- The eyelid area becomes red and swollen;
- Redness may appear on the cheeks or other parts of the face.
If any of the signs occur, consult a doctor immediately. You may have a chalazion.
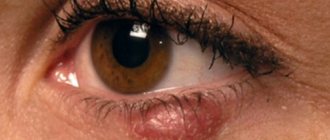
The clinical picture of chalazion formation is as follows:
- A lump grows on the eyelid;
- There is slight pain, swelling, and the mucous membrane of the eye turns red;
- The tumor becomes mobile and looks like a small pea.
If you let the process take its course, then:
- Visual acuity is impaired;
- The cone increases to 1 cm in diameter;
- The temperature may rise, lacrimation may increase, and itching in the eyelid area may appear.
When the formation develops into a cyst, it accumulates pus and spontaneously opens. If you do not seek help from a specialist, pus remaining under the eyelid can cause new lumps to appear. Inflammation can be easily avoided if chalazion treatment is started in the early stages.
Typically, an ophthalmologist recognizes the disease by external examination of the inflamed eyelid. If the disease affects the upper eyelid, the doctor turns it inside out to see the lump. As a rule, local swelling of the conjunctiva is observed. When a lesion is present, blink rate may decrease. If there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor, the ophthalmologist prescribes a histological examination. Often additional examination methods are required when a diagnosis has already been established. These include blood, urine and stool tests, cultures for staphylococcal infections, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and screening immunograms, and tests for sexually transmitted infections. The ophthalmologist may additionally prescribe a consultation with an immunologist, dermatologist and parasitologist.
Are wen dangerous if left untreated?
Wen, being a benign phenomenon, poses only an indirect danger (subject to degeneration into a malignant tumor).
Know! In some cases, encapsulation of the compaction is possible - this is the cessation of its interaction with other nearby structures and with immunoglobulins.
As a result, pathogenic microorganisms will begin to multiply in the cone over time. As a consequence, the development of inflammatory processes and suppuration in the wen.
Chalazion treatment
In the early stages of the disease, the doctor will tell you how to treat chalazion and prescribe conservative treatment. It includes the use of antibacterial drops, ointments, and dry warm compresses on the eyelid area. To remove viscous lipid secretions, you can use eyelid massage.
Massage is effective only at the initial stage of the disease. It must be performed exclusively in circular movements and with extreme caution. Contact your doctor to go through the procedure with you several times. He will demonstrate the force of pressure to massage the inflamed area. Do not resort to traditional methods of treatment. The eyes react sharply to any irritants. When the mucous membrane is irritated, it can cause multiple inflammations, and it will be difficult to cure the disease without surgery.
If the size of a pea does not exceed 4 mm, the doctor prescribes herbal medicine and physiotherapy: electrophoresis, laser heating, UHF. When such treatment does not help, the doctor uses steroid hormonal drugs to promote the resorption of the chalazion.
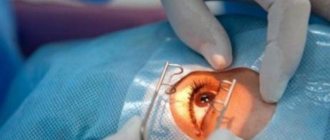
If the pathological process has gone far, visual function is impaired or relapses occur, you will have to consult a surgeon for treatment of chalazion. Eyelid surgery is indicated for nodule sizes greater than 5 mm. The surgeon opens the nodule and scrapes out its cavity. To reduce pain and avoid relapses, the doctor often operates with a laser. Removing a chalazion of the upper or lower eyelid takes about half an hour and is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. In the postoperative period, it is recommended to put an eye ointment with an antibiotic behind the eyelid. It is advisable to visit a doctor in a week for a re-examination. In the first days after surgery, the skin around the operated eye may be swollen and hyperemic, however, soon all unpleasant symptoms disappear.
The treatment time depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the course of the disease. If there are no complications, 1 or 2 weeks will be enough. If the process is started, therapy can last up to 8 weeks.
The application of cosmetics, especially to the mucous membrane of the eyes, will have to be limited to up to 1 month. Creams, lotions, masks, patches and tonics should also be put aside. If you apply cosmetics during the treatment period, this will aggravate the inflammation, increase the redness of the area around the chalazion, and it will increase in size. Exposure to the eyes should be kept to a minimum in the future to prevent recurrence of the disease.
How to get rid of it?
Medicines
Drug treatment is an auxiliary method that will help get rid of small bumps (up to three centimeters).
In such cases, for external treatment you can use dimexide ointment, ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky ointment.
Important! As a result of the action of the active components of such products, self-opening of the seal may occur.
The drugs also have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and analgesic effects.
The method of injecting into the cones that promote resorption more
The procedure is performed only once in a hospital setting to avoid infection.
Complications
By delaying treatment, you risk developing a chalazion. A secondary infection may occur, and the disease progresses to the stage of abscess chalazion. Swelling appears on the skin around the entire area of inflammation. A situation may arise in which a channel connecting them (fistula) is formed between the cavity of the chalazion capsule and the skin of the eyelid. After which the chalazion spontaneously opens and the purulent contents flow out through the fistula. With this development of events, the patient will certainly require surgical intervention, since the abscess can renew in the remaining dense pyogenic capsule (otherwise known as the purulent membrane). Another complication is that chalazion puts constant pressure on the eyeball, thereby irritating it and leading to the development of conjunctivitis in the patient.
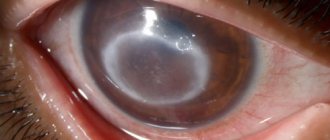
There is a possibility of complications after surgery to remove a chalazion. If the capsule is not completely removed or the wound is not thoroughly inspected, the blockage may occur again. If the specialist’s recommendations are ignored, the level of vision may sharply decrease, resulting in astigmatism. In rare cases, keratitis occurs - inflammation of the cornea of the eye, in which it becomes cloudy and the eye turns red, pain also appears, or a cyst with purulent fluid forms.
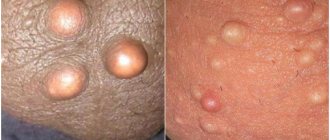
What are wen on the eyelids?
A fatty tissue (lipoma) is a benign formation in which adipose tissue is formed.
As a result of such processes, protruding seals of different sizes are formed under the skin.
These formations are yellowish in color and are usually lighter than the base color of the skin.
Lipomas can range in size from a few millimeters to one and a half centimeters.
Seals are divided into two types: milia and xanthelasma.
Milia are yellowish formations in the form of small pinpoint compactions.
It is worth noting! Xanthelasmas are flatter and larger than milia; moreover, unlike them, such formations necessarily grow over time.
Prevention of chalazion
Prevention of chalazion includes:
- Proper nutrition;
- Maintaining personal hygiene;
- Strengthening immunity;
- Compliance with the terms of wearing lenses and timely replacement of the solution for their storage;
- Timely treatment of tonsillitis and caries;
- Maintaining a sleep schedule;
- Getting rid of bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- Eyelid massage.
Also, to prevent chalazion, girls should pay special attention to cosmetic procedures. Before getting eyelash extensions or eyelid tattooing, consult an ophthalmologist.
Chalazion in children
Chalazion is rare in children unless there is a congenital predisposition. The composition of fat secretion is different for everyone, as are the properties of the skin. If you have a predisposition to eye diseases and gland blockage, then there is a high probability that your child may inherit this feature.
Children aged 5 to 10 years are at risk. The difficulty is that the child is inattentive to eye hygiene. Pay attention if your child rubs his eyes frequently. Find out if he is bothered by itching or burning.
Treatment of chalazion in children is no different from treatment in adults. The only difference is that surgery cannot be performed using a laser if the child is under 14 years old.
Bags, hernias or swelling?
First, let's list all the formations that can be found in an older patient.
The formations under the eyes can be swelling, they can be sagging skin of the lower eyelid, or they can be fatty hernias.
Fig.1. 1 - swelling under the eyes; 2 - ridge of the lower eyelid during facial activity; 3 - lower eyelid hernia; 4.5 — manifestations of the nasolacrimal groove; 6 - sagging skin of the lower eyelid, facial wrinkles.
Patients often refer to swelling of the lower eyelid area as bags. Their origin has nothing to do with the redistribution of fat packets; usually it is fluid stagnation and problems with the lymphatic drainage system.