He underwent a routine examination. I was unpleasantly upset and amazed because the doctor discovered a tumor in the mediastinum. A detailed study revealed the type of tumor - lipoma.
One thing is good. This tumor is benign. But you still have to remove it from the body. What is mediastinal lipomatosis? What are the treatment options for the disease and the prognosis for the patient?
Types of lipomas
There are several main classifications of lipomas that are actively used in medical practice. Depending on the type of tissue that is involved in the pathological process, the following types of neoplasms are distinguished:
- perineural - localized around nerve trunks;
- intermuscular – located between the muscles of the body;
- lumbosacral - grow near the vertebrae or in the spinal canal;
- soft tissues - located on the surface of the skin, less often subcutaneous;
- joints - are located in the synovial membrane or vagina of the joints.
The formation can appear in almost any part of the body and internal organs. Depending on the location of the compaction , the following types of lipomas are most often diagnosed:
- mammary gland - forms in the glandular tissue and deforms the shape of the breast as it grows;
- breasts - a soft and mobile formation that appears in the subcutaneous fatty tissues;
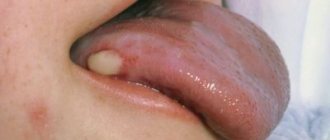
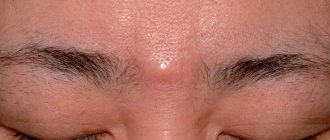
- head - a frequently occurring pathology, which is mainly formed as a result of insufficient hygiene;
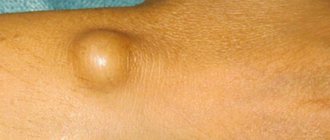
- back - one of the most common neoplasms, characterized by extremely slow development;
- neck is a hereditary disease that, during development, can impair the airways, cause weakness and angina.
There are also other, less common places where pathology forms, which include the brain, limbs, skin, peritoneum, eyes, lips and face.
Also, these compactions are divided into two large groups: single and multiple. The first represent a single formation in any part of the body. The latter, accordingly, are characterized by multiple manifestations in different areas of the body and are much less common.
What are the possible consequences of pulmonary mediastinal lipomatosis?
Lipomas grow slowly, do not metastasize, and do not penetrate healthy cells. In the area of the anterior mediastinum, the organs of the respiratory system are located, and fatty growths begin to compress the lung tissue and bronchi.
Consequences of lipomatosis in this area of the body:
- disruption of the outflow of mucus from the bronchi;
- lung ventilation is difficult;
- shortness of breath;
- the appearance of sputum with blood due to compression of the vessels of the respiratory organs;
- stenosis – narrowing – of the lumen of the bronchi;
- Inflammatory processes develop in the trachea, lungs, and bronchi. Bronchial bleeding is possible.
In severe cases, atelectasis may develop. This is the collapse of an area or lung in its entirety.
Important! Lipomas themselves do not pose a threat to human life. They do not degenerate into malignant neoplasms. The danger is the size of the tumor and the possibility of compression and injury to nearby organs and tissues!
Causes of lipomas
Experts identify a set of prerequisites that can provoke the formation of lipomas. Among the most common:
- genetic factors, hereditary predisposition;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body and fatty tissues;
- insufficient level of personal hygiene;
- malfunctions of the thyroid and pancreas;
- chronic pathologies that significantly affect the body’s immune forces (diabetes, hepatitis, HIV, etc.);
- dependence on alcohol, tobacco, drugs;
- poor nutrition;
- obesity, excess fatty tissue;
- injuries, damage;
- sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity.
Despite the fact that lipoma is a benign formation, there is always a risk of developing its malignant form. This probability is especially high for people who are included in the relevant risk groups: they have precancerous diseases (polyps, dysplasia), have already suffered from oncological pathologies, have a hereditary predisposition to the formation of tumors, and are under the constant influence of carcinogens, radiation and other harmful environmental factors.
Features of diffuse mediastinal lipomatosis
A distinctive feature of this type of fatty tumors is the absence of clear boundaries of the tumor. Wen tissues are distributed around the organs, do not have a clearly defined capsule, and can be intertwined with healthy muscle fibers.
Diagnosis of such growth is possible only with the help of x-ray examination. Fat tissue in the images is defined as a uniform expansion of the median shadow.
Diffuse nodular lipomas are distinguished separately. These neoplasms are characterized by the presence of an extensive vascular network connecting individual fat capsules.
Symptoms of lipomas
The clinical picture of the pathology is quite sparse and is characterized by:
- the presence of a palpable formation, which is distinguished by its soft consistency, mobility, and elasticity;
- the appearance of pain due to compression of nerve trunks or growth in internal organs;
- stability of the compact size or its increase with weight loss;
- swelling of the limbs and disruption of their function (if the formation compresses nerves and blood vessels).
If a malignant process develops, general malaise and headaches appear, blood pressure rises and other characteristic symptoms of intoxication of the body appear.
In this case, depending on the exact location of the compaction, other, more pronounced symptoms and signs may occur:
- neoplasms in the esophagus cause nausea and cough;
- seals on the trachea and bronchi cause a painful dry cough that does not subside after taking antitussive drugs;
- a fatty tumor on cartilage and tendons causes pain in the joints and impedes movement;
- formation in the mammary gland provokes pain in this area;
- compaction in the kidney area causes increased blood pressure, colic and lower back pain;
- a formation in the head causes neurological symptoms – headaches, dizziness;
- lipoma of the neck is accompanied by hoarseness, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing;
- a neoplasm in the heart area causes the development of cardiac pathologies: arrhythmia, heart failure, etc.
What is mediastinal lipomatosis and its symptoms
In order to clearly understand what kind of pathology this is, you need to understand the medical terminology.
Lipoma is a benign neoplasm formed from mature fat cells separated from each other by connective tissue. Tumors of this type can be encapsulated - that is, they have clear boundaries, and the contents are enclosed in a capsule of connective tissue - and diffuse - that is, the fatty growth does not have clear boundaries and the cords can intertwine with muscle fibers.
The mediastinum is the area of the body bounded by the spine at the back and the sternum at the front. This cavity contains the lungs, heart, aorta, trachea, bronchi, large nerve nodes, and esophagus.
That is, if the diagnosis is mediastinal lipomatosis, this means that a benign fatty tumor was discovered in the retrosternal space. Wen.
The symptoms of this pathological process at the initial stage do not bother the patient. When fatty strands grow, syndromes associated with compression of internal organs develop.
Symptoms of mediastinal lipomatosis:
- the appearance of shortness of breath after minor exertion;
- cyanosis of lips and nails;
- swelling on the face;
- chest pain;
- heart rhythm disturbances, both increased and decreased contraction speed;
- pleurisy;
- weakness;
- weight loss without changing eating habits;
- decreased performance;
- signs of cerebral vasospasm - migraines, headaches;
- cough, wheezing breathing due to compression of the trachea or bronchi;
- when nerve nodes are damaged, hyperemia of the skin, ptosis of the eyelids, impaired sweating, and pathological constriction of the pupil appear;
- feeling of a lump in the throat.
The causes of this pathology have not yet been identified. Hereditary factors, diseases of the endocrine system, and cases of toxic damage to the body play a certain role. Excess weight does not provoke the development of this disease, just as losing weight does not contribute to the resorption of these tumors.
Lipomas in the chest space are somewhat more common in women than in representatives of the stronger sex.
Diagnosis of lipomas
Since the development of a neoplasm in the body practically does not cause symptoms, the patient may not be aware of its presence for a long time.
Therefore, in most cases it is diagnosed accidentally during a preventive examination or treatment of other pathologies. If the localization of the formation allows the doctor to palpate, the specialist can determine the lipoma even during a standard physical examination. However, the placement of a node does not always allow it to be detected by superficial palpation. At the same time, quite a few dangerous diseases have symptoms similar to lipoma. Therefore, diagnostics are carried out not only to identify a neoplasm, but also to exclude other diseases and clarify the benign quality of the process.
A comprehensive examination includes a number of laboratory and instrumental examinations, the need for which is determined individually by the attending physician in each medical case:
- Blood tests. The most accessible method of primary assessment of the body’s condition. The results of the study allow us to identify the presence of pathological changes, inflammation, viruses or bacteria.
- X-ray examination. Depending on the location of the compaction, an X-ray of the chest, abdominal cavity, and extremities is prescribed. Allows you to diagnose a formation, identify its exact location, and also analyze the condition of bone tissue and structures.
- Ultrasonography. Scanning soft tissues and organs allows you to determine the size of the node, identify the clarity of its contours, and analyze the contents. Not the most informative examination method for suspected lipoma, since even in the presence of a capsule, the compaction is often difficult to visualize using ultrasound waves.
- CT scan. Allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis and distinguish lipoma from malignant neoplasms if there is suspicion.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It is prescribed, if necessary, to evaluate the signs of compaction and distinguish it from malignant liposarcoma. Using this method, the diagnosis is established with maximum accuracy.
- Biopsy. Tissue collection from the compaction and their further cytological and histological analysis. Allows you to exclude the possible oncological nature of the pathology.
The examination also reveals the reasons that caused the formation of a compaction in the body. If other chronic diseases are a prerequisite for the development of pathology, additional diagnostics are also carried out for an accurate diagnosis and further effective treatment.
Lipoma treatment
The only medical treatment for lipoma is surgical removal. Clinic specialists prescribe surgery if the tumor:
- grows rapidly, involving surrounding tissues and organs in the pathological process;
- affects appearance, causes aesthetic defects;
- causes pain;
- disrupts the functioning of internal organs.
Only surgical intervention can avoid future complications and prevent the transformation of pathology into malignancy.
Depending on the characteristics of the tumor and taking into account the individual characteristics of the body, SM-Clinic doctors choose one of the most effective methods for removing the lump:
- endoscopic method - the advantage is a small incision, but relapses are possible;
- excision of the lipoma – the likelihood of relapse is almost completely absent;
- liposuction is a gentle method with a good cosmetic effect and very frequent recurrence.
SM-Clinic specialists initially conduct a comprehensive examination, after which they establish an accurate diagnosis and provide consultation regarding surgical excision of the tumor. Before removing a lipoma, specialists must provide detailed information about the possible risks of the operation, as well as the consequences of non-intervention. Interventions are performed exclusively by experienced surgeons with many years of experience.
Doctors warn that, despite the apparent harmlessness of the pathology and its benign course, it is not worth delaying its treatment. It is important to remember that along with the increase in neoplasm, the risk of developing malignant processes and the occurrence of concomitant pathologies of internal organs significantly increases.
Sources:
- Congenital lipomas of the brain and spinal cord: clinical and MRI diagnostics. Bein B.N., Syrchin E.F., Yakushev K.B. Medical almanac, 2013
- Accidental detection of cardiac lipoma. Alekseeva I.V., Gordova V.S. Bulletin of the Baltic Federal University. I. Kant. Series: Natural and medical sciences, 2022.
- A rare congenital anomaly: a cerebral lipoma connecting to a subcutaneous lipoma through a defect in the frontal bone. Miloserdov M.A., Korneva Yu.S., Gelt T.D., Rudenko Y.A. Difficult patient, 2022.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.