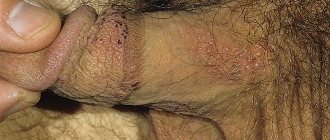
In recent years, the incidence of human papillomavirus infection has been increasing. According to WHO, every year around the world, about 250,000 women with HPV infection die from cervical cancer. Against this background, the search for effective treatments for this infection becomes extremely important. The problem of its diagnosis and treatment attracts the attention of doctors of various specialties: dermatologists, gynecologists, urologists, oncologists, immunologists, virologists, pathomorphologists. At the moment, most scientists have come to a consensus - the manifestations of the human papillomavirus can be combated using immunomodulators with antiviral activity.
- What are immunomodulators
- List of drugs
- Antiviral for HPV
- Is it possible to use VIFERON Suppositories vaginally?
- Treatment of mucous membranes in men
- Alternative Treatments
What is papillomavirus
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of small viruses that contain DNA. These viruses cause pathologies of epithelial tissue. The main method of transmission of infection is unprotected sexual contact. Scientists have discovered more than 200 strains of HPV, of which 29 strains are oncogenic. Dangerous strains cause malignant degeneration of epithelial cells.
The relationship between HPV infection and the development of malignant tumors has been scientifically proven. The papillomavirus is integrated into the human genome, which leads to a failure of the program embedded in the DNA. When epithelial cells divide, the affected gene is transferred to new cells. This is how the virus penetrates into the deep layers of tissue.
The infection is asymptomatic until cells with an altered genome begin to reproduce cancer cells. HPV causes cancer:
- cervix;
- vulva and vagina;
- penis;
- anal canal;
- throat and larynx;
- neck and scalp;
- stomach and esophagus.
The growth of benign tumors is also possible: papillomas, condylomas, anogenital warts. Complications include recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (in adults and children). This disease leads to difficulty breathing and obstruction of the airways.
Classification of viral strains
All HPV strains are divided into cutaneous and mucosotropic. Skin viruses lead to the formation of benign tumors on the skin. Mucosotropic provoke the appearance of neoplasms on the mucous membranes.
Skin strains provoke the development of different types of papillomas:
- Flat. Round nodules with a diameter of up to 10 mm. They do not turn into cancer.
- Pointed. Shaped like a cockscomb. These are pink formations covered with horny cells.
- Thread-like. Round papillomas on a thin stalk. Diameter up to 7 mm.
Mucosotropic strains cause the following diseases:
- Bowenoid papulosis. The appearance of spots and plaques on the genitals.
- Dysplasia. Pathological degeneration of cervical tissue.
- Inguinal condylomas. Ball-shaped tumors on a stalk.
If benign tumors appear, you should consult a doctor. A dermatovenerologist will determine the type of papillomavirus and the degree of its danger, and prescribe a treatment regimen for the infection.
Removal of papillomas
The treatment regimen also includes removal of papillomatous lesions. Large and/or inflamed tumors are removed surgically. Electrocoagulation is considered an effective method of getting rid of papillomas. The procedure does not require special preparation and is practically painless (surface anesthetics are used). The method is safe and there are no scars left after its use. After electrocoagulation, a crust forms, and when it peels off, a depigmented spot remains on the skin for some time.
A modern gentle method, after which no traces remain, is laser removal of papilloma. During the session, in parallel with the cauterization of the benign neoplasm, the blood vessels are sealed, so the procedure is bloodless. It is performed using a local anesthetic. The risk of damage to adjacent tissues is reduced to zero. A red mark remains at the site of the removed papilloma for some time, disappearing on its own or after using gels/ointments prescribed by the doctor. The removal procedure should be performed not in a beauty salon, but in a specialized medical institution and only after consultation with a dermatologist or dermatologist-oncologist.
Stages of HPV development
After infection, the latent stage of the disease begins. The virus is already present in the body and is localized in epithelial cells. But so far there are no symptoms that would suggest a human papillomavirus infection. When the virus is dormant, laboratory tests may show a negative result. The latent stage lasts from a couple of weeks to tens of years.
Papillomavirus multiplies in epithelial cells. The number of affected cells increases, and the disease enters the subclinical stage. The first small tissue pathologies appear, not yet visible to the naked eye. The presence of papillomavirus can be determined in a laboratory. The affected epithelium becomes more sensitive to bacterial and chemical influences.
At the clinical stage, formations appear on the skin. To stop the spread of infection and prevent complications, you should consult a doctor in time.
Degrees of oncogenicity of strains
- Non-oncogenic. Provoke the development of benign tumors. The DNA of these viruses is not prone to mutations that cause cancer.
- Low degree of oncogenicity. They can lead to the formation of a cancerous tumor in combination with other risk factors (heredity, weak immunity, bad habits).
- High degree of oncogenicity. Directly provoke the growth of malignant tumors.
Is it possible to use VIFERON Suppositories for HPV vaginally?
Antiviral suppositories VIFERON are produced only for rectal use. Vaginal use is not provided for in the instructions for the medicine. The use of the drug in complex therapy is aimed at increasing the level of immune defense of the body as a whole. Therefore, inserting suppositories directly into the site of infection is not required.
There are many blood vessels in the rectum that absorb the medicine directly injected into the rectal cavity. Blood from the rectum, bypassing the liver, directly enters the systemic circulation. This ensures the systemic effect of the drug. Moreover, the liver does not undergo additional stress, which is an undeniable advantage of drugs with rectal administration.
Symptoms of virus infection
At the clinical stage, visible signs of infection appear. The symptom complex depends on the strain of the virus and the location of the affected area. Possible symptoms include:
- the appearance of warts and papillomas on various parts of the body;
- in women: a feeling of discomfort in the vagina, painful sexual intercourse, bleeding from the cervix outside the menstrual cycle;
- copious discharge with an uncharacteristic odor;
- the formation of benign tumors on the genitals, in the anus, in the urethra;
- associated diseases: inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis), bacterial vaginosis, dysplasia of the cervical epithelium.
Indirect symptoms of the disease are chronic fatigue, problems with concentration, physical weakness, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Types and symptoms
Neoplasms caused by HPV infection can form on the skin and mucous membranes of various parts of the body, including the face, neck and décolleté. They can also form on the arms, legs, back, genitals, including the perineum, labia minora and majora, vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, especially along the coronary sulcus and frenulum. Damage to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, esophagus, bladder, conjunctiva of the eye, trachea and other internal organs is possible.
The human papillomavirus can lead to the appearance of neoplasms of various types. In general, they can be divided into 3 groups, although in all cases the cause of their appearance is the same - infection with the human papillomavirus.
- Papillomas are benign neoplasms of pink, white, pearl or light brown color, most often forming on the eyelids, lips, chest, armpits, and neck. They are located singly and usually do not tend to merge even with multiple lesions. Papillomas are usually round or lumpy, resemble the head of a cauliflower, and often have a stalk.
- Condylomas are benign formations of a dirty brown or paler color in the form of a cock's comb or many villi united by a common base. They are most often found in the genital area, anus and near the mouth. They tend to merge with each other and, as a result, cover large areas of the body. Their appearance is caused by infection with HPV types 6 and 11. There are pointed, flat and intraepithelial condylomas.
- Warts are uneven, light, benign tumor-like formations in the form of a plaque or small nodule on the surface of the skin of the hands, near the nails, feet, face, and front of the body. Warts can be similar to papillomas, but differ from them in that they have a wide base. They usually occur when infected with HPV types 1-5, 7-10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-24.
Such tumor-like formations can vary in size from a few millimeters to large growths covering large areas of the skin or mucous membranes.
Also, neoplasms may differ in appearance, which directly depends on the type of HPV that entered the body. The most common ones are:
- Vulgar or ordinary - protrusions of dense consistency with a diameter of more than 1 mm. They tend to merge and be located in groups.
- Plantar warts are protruding above the surface of the skin, often painful bumps with a shiny surface and rim. A characteristic feature is the absence of a skin pattern. They provoke the formation of HPV types 1, 2, 4.
- Flat papillomas are soft, smooth, flat, usually round growths that have a normal skin color or slightly yellowish, pinkish. They can provoke itching, so they are often injured, painful and inflamed. The reason for their formation is HPV strains 3 and 10.
- Filiform (acrochordas) are one of the most common papillomas, especially among elderly patients. Most often they are found on the face, around the eyes, in the groin, armpits, and neck. They are yellowish in color and tend to gradually enlarge, turning into bumps with a dense but elastic consistency.
- Genital warts in the perineal area, genitals.
Papillomas can be visible to the naked eye or located deep in the skin or mucous membranes. In the latter case, they are called endophytic and one of their manifestations is cervical dysplasia. Damage to the female internal genital organs by papillomatosis may be indicated by:
- itching, burning, weeping in the perineal area;
- profuse leucorrhoea;
- spotting, particularly after sexual intercourse;
- discomfort during intimacy.
Sometimes papillomatosis can provoke pain in the back and pelvis, weakness, swelling of the legs and causeless weight loss. Such signs are among the most alarming, as they may indicate the development of complications of HPV infection.
Causes of HPV infection and development of the disease
Infection with papillomavirus can occur at the stage of birth of a child, while he is passing through the birth canal. The virus can be transmitted through contact and household contact in the first years of life. In adults, most cases of infection occur through sexual contact.
Risk factors include:
- Illness of one of the parents or family members.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, unprotected contacts.
- Gynecological manipulations: installation of a spiral, abortion.
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptive pills.
- Hormonal imbalance caused by other reasons.
- Pregnancy and the postpartum period in women.
- Various diseases of the reproductive system.
- Hypothermia of the pelvic organs.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs.
- Chronic stress, diseases of the nervous system.
Infection with a virus does not always lead to the development of disease. Human papillomavirus infection can be suppressed by a strong human immune system. Therefore, the HPV treatment regimen sometimes includes taking immunomodulator pills.
How papillomavirus is transmitted, risks
Papillomavirus enters the human body in different ways, the probability of infection is 60%. You can get an infection in the following ways:
- Sexually, regardless of the type of sexual relations - oral, genital and anal. The presence of genital warts in a partner guarantees infection by 98-100%.
- Contact household - in the case of using a shared towel, washcloths, etc. The virus can also be transmitted through saliva during a kiss.
- Through wounds - a violation of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes - an open gateway to the body.
- Infection of a child during the passage of the birth canal - children suffer from rare forms, papillomas grow in the nasopharynx and sinuses. Recent studies have shown that children born by cesarean section also become infected - this may indicate that the virus is able to penetrate the placenta.
Infection does not always guarantee the development of the disease. HPV causes disease in the body in 50% of cases, the rest are limited to carriage of the infection: a strong immune system can keep the virus in numbers that are not dangerous to the body. The incubation period ranges from a year to 20 years, with an average of 3-5 years.
The development of the disease is provoked by hormonal imbalances, immunodeficiency states, and sexually transmitted infections (STDs, STIs). Any condition that reduces immunity increases the risk - pregnancy, bad habits, chronic diseases, stress, etc.
It should be understood that infection of epithelial cells is a necessary but not sufficient factor for the development of oncology. According to Professor V.A. Molochkov, a well-known and respected scientist in the world of medicine, a number of other factors are necessary for the development of irreversible neoplasia:
- active expression of genes E6, E7 of highly oncogenic types hpv16 and hpv18;
- induction of estradiol metabolism to 16-OH;
- multiple damage to chromosomal DNA in an infected cell.
The first stage of CIN I neoplasia is expressed by active copying of the virus and its asymptomatic course. Tumor development is stimulated by the interaction of papillomavirus with cytomegaloviruses, trachomatis, mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, and herpes simplex virus type 2.
Diagnosis of infection at the Private Practice clinic
Several tests are required to make a diagnosis of HPV. Analyzes in our modern laboratory are done quickly using highly accurate methods. You will find out the result on the day of the smear test.
Polymerase chain reaction
PCR determines the presence or absence of viral DNA in a biomaterial. For analysis, a smear is taken from the mucous membranes and directly from the neoplasms themselves, papillomas, condylomas and erosions. The location of the smear depends on the location of the skin tumors. PCR identifies the types of viral strains in the body. The cost of analysis starts from 300 rubles.
Cytological analysis. PAP diagnostics
Papanicolaou test - examination of a smear under a microscope. A smear is taken from the affected area and applied in a thin layer to laboratory glass. The preparation is stained to improve the visibility of cells.
Examining the drug under a microscope, the diagnostician pays attention to the size and shape of the cells. Cytological examination reveals the presence of atypical cells, dysplasia, and malignant mutations. The detected virus is assigned a Pap class.
Colposcopy in women
Examination and examination of the cervix. The procedure is performed in a gynecological chair. For diagnosis, the cervix is stained with safe Lugol's solution. If it is affected by a virus, the area with infected cells is different in color. After a positive colposcopy, a biopsy is performed. It is necessary to clarify the degree of oncogenicity of the virus. A survey colposcopy in our clinic is included in the cost of an appointment with a gynecologist.
Biopsy
A biopsy is used to accurately determine the cellular composition of tissue. This is a reliable method for diagnosing cancer. A biopsy is prescribed when the doctor suspects that malignant degeneration of epithelial tissue has already begun. The cost of diagnostics starts from 1500 rubles.
HPV: can it be treated or not?
It happens that papillomavirus is cleared from the body within two years after infection. But this is typical mainly for children and young people. However, since the prevalence of the virus is high, there is a risk of re-infection (relapse). Immunity after an illness is not formed for life, but for 1–3 years. It is this fact that underlies the statement that HPV cannot be cured.
In most cases, in adults, the papillomavirus does not leave the body on its own, but is integrated into the genome, provoking the development of tumors, including cancer. We advise you not to rely on luck, but to start treatment at the first symptoms of the disease. Human papillomavirus infection is successfully treated with modern medicine. New growths on the skin are removed using destructive methods.
Effective treatment is possible only according to the regimen proposed by the attending physician. When prescribing therapy, the dermatovenerologist takes into account the HPV strain, the degree of oncogenicity, and the patient’s immune system. Self-selection of medications will most likely not give the desired result. After therapy, you need to get tested for HPV every 2 years to avoid relapse of the disease.
Immunomodulators for HPV: list of drugs
Drugs that are synthetic complex purine derivatives
This group of immunomodulators, used in the treatment of manifestations of the human papillomavirus, have immunostimulating activity and a nonspecific antiviral effect. They restore the activity of lymphocytes, which are the main cells of the immune system. It has been clinically proven that low lymphocyte activity is a predisposing factor to the pronounced development of clinical manifestations of HPV. Also, this type of drug increases the functioning of natural killer cells and the so-called T-helpers - T-lymphocytes, the main function of which is to coordinate the immune response.
Some of the drugs in this group have an extensive list of side effects, including problems with the gastrointestinal tract, liver and biliary tract. Adverse reactions such as headache, drowsiness, insomnia, itching and joint pain are also possible. Contraindications include children under 3 years of age, pregnancy, kidney disease and hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Preparations with the active ingredient glucosaminylmuramyl dipeptide (GMDP)
GMDP is a fragment of the shell of pathogenic bacteria that cause infectious and inflammatory diseases of various organs and systems. When this fragment enters the body, the immune system perceives it as a foreign pathogenic agent and immediately begins producing antibodies. Thanks to this, there is a general activation of the entire immune system, which promotes recovery or reduces the frequency of relapses of viral infections, including HPV.
Side effects include an increase in body temperature to subfebrile and febrile levels, and diarrhea is also possible. Drugs in this group are contraindicated for metabolic disorders and for women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Preparations containing natural plant materials as active ingredients
This group of drugs was created based on the discovery of Nobel Prize laureate N.N. Semenov about the powerful immunostimulating properties of biologically active substances contained in plant cells. Plant extracts and auxiliary components strengthen the nonspecific part of the immune system, which increases the human body’s resistance to various viral and some bacterial infections. The immunomodulatory effect activates leukocytes, which is especially important in the fight against chronic and protracted inflammatory processes.
Allergic reactions are possible when using these drugs. Contraindications for use include diseases of the excretory system, pregnancy, lactation and children under 18 years of age.
Drug treatment of HPV at the Private Practice clinic
To treat human papillomavirus infection, doctors at our Private Practice clinic prescribe complex therapy. Medications reduce the concentration of the virus in tissues and strengthen the body’s immunity. Medicines eliminate the symptoms of the disease and improve a person’s well-being.
Attention! Self-medication can be dangerous to your health. Drugs for the treatment of HPV in women and men should be selected by a dermatovenerologist.
Antiviral tablets
Lavomax has a combined effect. This medicine suppresses the virus, stops its reproduction and stimulates the immune system. Take one tablet containing 125 grams of active ingredient, once a day, every other day. Do not reduce the interval between taking the medicine so as not to harm your health. The treatment course includes twenty tablets.
Isoprinosine is a universal drug. Prescribed to combat tumors on the skin, larynx, and genitals. This medicine suppresses the activity of the virus and stimulates the development of immunity. The dosage regimen is prescribed individually. The treatment regimen may include taking six to eight tablets per day. The course lasts from five days to several months.
Lykopid strengthens the body's defense against infections. Activates hereditary immunity, helps form an acquired immune response. Take one tablet (10 mg) once a day (half an hour before meals). The treatment course lasts from ten days.
Gepon is an immunomodulator. The drug activates the body's immune responses. Has anti-inflammatory and antiviral effect. Take one tablet (10 mg) per day. The duration of treatment depends on the individual response to the drug.
Unfortunately, all of the listed tablet drugs have very low effectiveness for the treatment of HPV. We have observed in many cases where patients undergoing treatment for human papillomavirus infection only with tablets experienced an increase in papillomas and condylomas while taking these medications.
Vaginal suppositories
Suppositories (candles) are prescribed by gynecologists at our clinic for the treatment of the vagina and cervix. Medicines for the treatment of human papillomavirus infection in women:
- Genferon. Double action drug. It contains interferon, which suppresses the development of the virus. Candles eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease: pain and burning. For treatment, administer two suppositories per day: morning and evening. The treatment course lasts ten days;
- Viferon. Combined candles. Inhibits the reproduction of the virus, eliminates the symptoms of the disease, stimulates the immune system. Use suppositories twice a day, morning and evening, for five days.
Intramuscular injections
To treat papillomavirus, a dermatovenerologist may prescribe intramuscular injections. A popular injection drug is Ferrovir. 5 milliliters of medication should be administered twice a day. Duration of treatment course: two weeks.
Cycloferon is used for both intramuscular and intravenous administration using a special technique. Enhances the production of interferon in virus-affected and immune cells, which prevents its active reproduction.
Intravenous injections
The most effective drugs are administered intravenously in drip courses. Typically, polyoxidonium, panavir, and cycloferon are used, which suppress viral replication by activating the appropriate antiviral defense mechanisms.
The courses of treatment are long and combine well with general intravenous ozone therapy.
Cytostatic drugs
To combat skin defects, cytostatics and coagulants are used. These are topical medications. They do not suppress the development of the virus, but eliminate the external symptoms of infection. They are prescribed as an element of complex therapy. Medicinal substances are contained in a solution that is applied to the skin.
Podophyllin. It removes genital warts well. Burns through the cells of skin formations, causing necrosis. The solution is applied to the condyloma twice a day, with an interval of 12 hours. The duration of the treatment course is three days. The drug should not come into contact with healthy skin.
Solcoderm. Used to remove benign tumors. This is a powerful drug. We do not recommend using it without medical supervision. To remove papilloma, warts or condyloma, it is enough to apply it once. The skin lesion will become necrotic and darken, and then fall off.
Antibiotics
HPV is not treated with antibiotics. They act on bacteria, not viruses. Antibiotics are prescribed if diagnostic results reveal concomitant diseases (for example, bacterial vaginosis).
Antiviral drugs against HPV
After infecting a cell, the virus can remain free or penetrate the cell’s genome. In either case, the virus alters normal cellular processes. And instead of producing everything necessary for its life, the cell provides mechanisms for the synthesis of viral DNA molecules, which will later be used to create new viral particles. But viruses are not always capable of causing disease. With an adequate immune response, the body gets rid of the virus on its own. If the body's immune response is ineffective, long-term carriage of the virus is possible, which can lead to benign or malignant, depending on the type of virus, manifestations of the disease.
In order to break the chain of endless reproduction of the virus and subsequent development of the disease, the need to treat HPV infection with immunomodulators with antiviral activity has been recognized, because To date, not a single antiviral drug against HPV has been developed that specifically targets the human papillomavirus.
VIFERON for HPV
Are there drugs that fight viruses and at the same time help restore the immune system? Of course, such drugs exist. One of these drugs that helps restore the immune system and has a wide spectrum of antiviral activity is the drug VIFERON.
Recombinant interferon alpha-2b, which is part of this drug, prevents the synthesis of viral DNA and blocks the reproduction of the virus, helps restore the immune system, and also has antiproliferative properties. It is identical to human interferon alpha-2b, but is produced using modern technology without the use of donor blood.
The drug, which is available in the form of suppositories, gel and ointment, was developed as a result of fundamental research in the field of immunology, which has proven that in the presence of antioxidants (vitamins C, E), the antiviral effect of interferon is enhanced.
Method of use and dosage of VIFERON suppositories for HPV
VIFERON Suppositories are produced in the form of bullet-shaped rectal suppositories of white-yellow or yellow color. During the treatment process, the drug suppresses the activity of viruses and increases the effectiveness of the body's own immune response to pathogenic microorganisms.
The drug in the form of suppositories can be used during pregnancy (from the 14th week), as well as during breastfeeding and when treating children.
The recommended dose for adults is VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5-10 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued.
Pregnant women from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from the 14th week of gestation) are prescribed VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours daily for 10 days, then for 9 days 3 times with an interval of 3 days (on the fourth day) 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours. Then every 4 weeks until delivery - the drug in a dosage of 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, the drug is prescribed before delivery (from the 38th week of gestation) at a dosage of 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days.
Destructive and surgical treatment methods
To quickly eliminate warts, condylomas, and papillomas, destructive techniques are used. Unlike conservative treatment, they do not allow you to wait until the tumor necrotizes and falls off on its own. In the office of a dermatovenerologist, skin defects can be eliminated in one visit. Removal of pathologies in hard-to-reach places is carried out only by surgical methods.
Electrocoagulation
During electrocoagulation, defects are removed with an electric knife. It generates electrical waves that cut off skin growths and destroy pathological tissues. Electric waves cauterize small vessels, there is no bleeding after surgery. Removing one defect takes from a few seconds to five minutes. Removal of small papillomas on the skin with an amount of more than 20 pcs. costs 200 rubles. for 1 unit. Large tumors are removed under local anesthesia at a cost of 1000–1500 rubles.
Cryodestruction
Liquid nitrogen is used for cryodestruction. The temperature of the substance is -190 degrees. When liquid nitrogen gets into the defects, necrosis occurs. Extremely low temperatures cause cell destruction, blockage of oxygen, and blockage of blood vessels. A thermal burn is formed and the tissues die. The operation is carried out under the supervision of an experienced doctor, who ensures that the substance does not come into contact with healthy skin. The effect of the procedure does not occur immediately, but after 5–10 days, when the necrotic papilloma tissue is completely rejected. The cost of cryodestruction usually ranges from 500 to 1500 rubles. per element.
Radio wave surgery
The operation uses a device that emits radio waves at high frequencies. Radio waves destroy skin defects using thermal energy. The device is operated by an experienced doctor. It directs radio waves, focusing the flow on the growth, avoiding touching healthy skin. This is the most effective and cost effective method for removing papillomavirus tumors on the skin and mucous membranes. The cost of the procedure is from 300 rubles. for the destruction of multiple small papillomas, up to 1500 -2000 rubles, for the removal of large tumors.
Laser defect removal
A directed beam of laser beams removes skin defects. Under the influence of the laser, the cells evaporate. A protective crust is formed at the site of the removed growth. Destruction of the defect takes from 5 seconds to two minutes. Healthy skin forms under the horny crust. About a week after the intervention, the crust disappears. The cost of laser removal of large papillomas is from 1000 rubles.
Removal of affected tissue
Invasive intervention techniques are used for deep tissue damage, when the process of malignant degeneration has already begun. Knife conization is used to remove pathological areas of the epithelium. When HPV is advanced and oncology begins to develop, they resort to removing the cervix with a scalpel.
Our doctors use an integrated approach to the treatment of HPV, which provides close to 100% effect from the therapy. It includes a combination of injectable, tableted immune, antiviral and topical medications. Removal of tumors is carried out using the chosen method against the background of drug treatment, which allows you to completely get rid of papillomas and condylomas and other manifestations of HPV, and prevent recurrence of the infection.
Modern approaches to the treatment of human papillomavirus infection of the urogenital tract
In recent years, in Russia, as in many countries of the world, the incidence of human papillomavirus infection has been increasing. The problem of its diagnosis and treatment attracts the attention of doctors of various specialties: dermatologists, gynecologists, urologists, oncologists, pathomorphologists, immunologists, virologists. This is explained by the high contagiousness and tendency to increase the frequency of this disease, as well as the ability of some varieties of human papillomavirus (HPV) to initiate malignant processes. The latter mostly concerns the genital manifestations of human papillomavirus infection.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is epitheliotropic and is found in the skin, oral mucosa, conjunctiva, esophagus, bronchi, and rectum.
There is information in the literature that the introduction of HPV infection occurs at the level of immature epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes (basal layer). The result of this invasion is cell proliferation, but without the production of viral particles, since proliferating epithelial cells are not able to support the life cycle of viruses. Complete replication of HPV occurs only in highly specialized cells of stratified squamous epithelium: granular, spinous cells of the skin, superficial epithelial cells of the cervical mucosa. Currently, about 100 types of papillomaviruses have been described. Their tissue and species specificity should be noted. Different types of HPV are associated with different types of lesions. It has been established that certain types of HPV are associated with the urogenital area. There are varieties:
- low cancer risk;
- average cancer risk;
- high cancer risk.
Viral genome structure
Papilloma viruses belong to the papovavirus family (Papovaviridae), which infect cattle, birds, and humans and can infect basal cells of the skin and squamous epithelium. Papillomaviruses are one of the most heterogeneous groups of viruses, the differentiation criterion of which is the degree of genetic relatedness of the viruses according to molecular hybridization: it ranges from 10 to 85%. The diameter of viral particles is 55 nm. The virus does not have an outer shell. The virus capsid consists of 72 capsomeres. A detailed analysis of the HPV DNA molecule became possible after the development of a technique for DNA cleavage using endonucleases and analysis of these fragments using gel electrophoresis.
When studying preparations stained by Papanicolaou, a specific set of signs was identified that characterizes the nucleus and cytoplasm of epithelial cells (koilocytic cell atypia), caused by the cytopathic effect of papilloma viruses.
A specific cell for this infection is the koilocyte, which is an oxyphilt-stained epithelial cell with clear boundaries and a clearly defined perinuclear clearing zone and numerous vacuoles in the cytoplasm.
The term “koilocytic dysplasia” was introduced by HS Stegner in 1981. It is assumed that these changes are a consequence of the reproduction of a virus that causes disruption of cell metabolism, leading to their partial necrosis with the formation of balloon-like cells.
Cytological examination of lesions caused by HPV infection showed that the cellular material contains mostly anucleate, or orthokeratotic, cells. About 20% of scales contain nuclei - the so-called. "parakeratotic cells".
It should be remembered that morphology alone is not enough to identify HPV. In this regard, it is advisable to use the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method and in situ hybridization. Increasingly, there are reports in the literature about the determination of HPV infection in urine using PCR as an alternative method for testing samples from the cervix. Along with this, nested PCR in one tube and type-specific nucleotide hybridization are used.
The PCR method is used for low-symptomatic or asymptomatic forms of the disease caused by HPV infection.
Using immunochemical methods, it is possible to detect HPV antigens in the tissues of genital warts in 71.4% of cases, by hybridization in 96.5%, and by PCR in 10% of cases.
The effectiveness of DNA hybridization does not exceed the effectiveness of histological examination, but it allows identifying patients with a high degree of this infection.
HPV infection clinic
The clinical manifestations of genital HPV infection are highly variable. Currently, they are divided into genital condylomas, papillary varieties of condylomas (with pronounced exophytic growth), as well as flat and inverted (intraepithelial) with endophytic growth. The last option, also known as “subclinical HPV infection,” is the most difficult in diagnostic terms, since there are no clear microscopic changes in the epithelium. In this case, special screening techniques are required to determine clear boundaries of the lesion.
A peculiar variant of genital warts is bowenoid papulosis and giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma. Condylomas acuminata (AC) are fibroepithelial formations on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes, with a thin stalk or a wide base in the form of a single nodule or multiple epithelial outgrowths, resembling cockscombs or cauliflower in appearance. Diagnosis of large condylomas does not cause difficulties. Genital condylomas are localized mainly in places of maceration: labia minora, vagina, cervix, urethral orifice, anal area, skin. In men, OCs are located in the foreskin, on the glans penis, in the perinatal area, and less commonly in the endurethral region. The incubation period ranges from one to 12 months (average 3-6 months).
Studies of recent decades indicate that 85% of patients with typical OC of the vulva and perineum have additional foci of HPV infection in the vagina or cervix, and almost every fourth of them has diseases associated with HPV infection - cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CVN) of various types. degree of severity. One of the clinical types of diseases caused by HPV infection are bowenoid papules associated with HPV 16, sometimes pigmented on the skin and mucous membranes of both sexes, more often resembling common warts or seborrheic keratosis. In contrast to Bowen's disease, Bowenoid papules are benign and regress spontaneously, although they can occasionally become malignant. The course is asymptomatic.
Some authors include Lewandowski-Lutz epidermodysplasia verruciformis in this group of diseases. This disease is based on local and genetic disorders associated with chronic HPV infection.
JM Handley and WJ Dinsmore (1994), based on literature data, as well as their own studies, proposed a classification of clinical forms of HPV infection and associated diseases (Table 1).
In the vast majority of cases, manifest forms of HPV infection are combined with other sexually transmitted diseases. According to Bernard K. and Mugi K. (1996), manifest forms of HPV infection usually arise as a result of a number of factors:
- social;
- infectious, associated with associations of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs);
- associated with changes in immune status.
The most significant is the influence of urogenital tract infections associated with HPV lesions: urogenital chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections, dysbiotic conditions. The result of their influence on the course of HPV infection is the chronicization of the process, the formation of persistent, usually nonspecific inflammatory changes in the genitourinary area and significant difficulties in carrying out therapeutic measures.
The significance of the presence of concomitant infection for the treatment of condylomatosis is explained by the following circumstances.
- The presence of STDs associated with HPV infection prolongs the treatment period for the latter by an average of three times.
- In most cases, relapses are associated with the above reason.
- Epithelization of cervical erosions after destruction of condylomas can be achieved only if there is a preliminary scan for concomitant STDs and bacterial vaginosis.
The possibility of a relationship between cervical neoplasia and sexually transmitted diseases has been discussed for many years. In the group of women suffering from invasive cervical cancer (CC), a higher frequency of detection of nonspecific microflora, including Trichomonas and Gardnerella infections, was noted. Examples of such effects have been discussed in relation to Treponema pallidum, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, herpes simplex virus type 2, cytomegalovirus, and human papillomavirus. Epidemiological studies have convincingly shown that genital HPV infection is an undeniable risk factor for the occurrence of precancerous changes and cervical cancer.
Principles of treatment of HPV infection
Considering the fact that specific antiviral drugs and vaccines that act on HPV are not yet available, it is generally accepted that complete elimination of the virus from the body cannot be achieved. The goal of therapy is to eliminate clinical and subclinical forms of HPV infection.
Today, practitioners have many methods for removing anogenital warts in their arsenal. Their effectiveness varies from 30 to 90%, but none of the methods is a panacea, since the relapse rate is quite high with any method of treatment. Treatment must be strictly individual: it is necessary to select the most optimal solution in each specific case, sometimes taking into account the wishes of the patient himself. The problem of relapse does not depend on the choice of therapy. Recurrences of anogenital warts are most often associated not with reinfection from a sexual partner, but with reactivation of the infection. There are three ways that events can develop in the absence of treatment:
- warts may resolve on their own;
- remain unchanged;
- progress.
At the same time, one must always take into account the possibility of persistence of the virus in the absence of any clinical manifestations.
When choosing the most optimal method in each specific case, you must be guided by four main characteristics:
- effectiveness for this pathology;
- relapse rate after treatment;
- tolerability (minimal side effects);
- ease of performing procedures.
In addition to removing anogenital warts, it is necessary to solve the following important problems:
1. Identify and treat other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in patients with anogenital warts (and their sexual partners).
2. Screen all women with anogenital warts for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CVN) using cytology and colposcopy.
3. Maintain further monitoring of CVN lesions in the early stages for timely detection of their progression or development of microinvasive carcinoma.
4. Conduct active treatment of anogenital warts, neoplasia in the early stages, occurring with a detailed clinical picture, neoplasia in the later stages and squamous cell carcinoma.
5. Provide patients with recommendations on the use of condoms and limiting casual sexual contact to prevent infection (and reinfection) with HPV infection and other STDs.
In fact, treatment of anogenital HPV lesions is aimed either at destroying papillomatous lesions by one method or another, or at stimulating an antiviral immune response; a combination of these approaches is possible.
Destructive methods
Physical destructive methods
Surgical excision. Currently used infrequently, it is mainly used in the treatment of malignant neoplasms when wide excision is necessary. This method may require hospitalization due to the fact that quite severe bleeding may occur during excision, and a long postoperative period will require special therapy.
Electrosurgical methods. These include electrocoagulation, electroacoustics, fulgation, electrosurgical excision (electroexcision) using an electric knife. Not so long ago, plasma began to be used in medicine. Our scientists have developed an original plasma coagulator (plasmaskin) EKH-1, which has no foreign analogues. Temperature measurements in plasma showed that it can reach 2000-2500°C. Such high temperature values, in turn, provide the ability to work in a non-contact mode, the operation time is significantly reduced and thereby the necrosis zone is reduced. In addition, with this effect in most cases the pain threshold is not exceeded. This temperature regime ensures almost complete combustion of tumors.
Advantages of this method:
- availability;
- cheapness;
- fairly high efficiency;
- possibility of use in outpatient settings;
- the risk of bleeding is reduced.
Flaws:
- need for pain relief
- When using this method, infectious HPV DNA is released along with the resulting smoke, so it is necessary to create adequate working conditions - vacuum extraction of smoke, the use of protective masks.
Laser excision. A fairly effective and safe method is excision of warts using a laser. Neodymium and CO lasers are used in practice. When using a CO laser, surrounding tissues are less damaged, and a neodymium laser provides a better hemostatic effect. In addition to the laser physically removing lesions, studies have shown that laser radiation has a toxic effect on HPV. The procedures require well-trained personnel. When using lasers, anesthesia is necessary - often local or local anesthesia is sufficient, which allows the procedures to be performed on an outpatient basis. Laser excision and surgical methods are approximately equally effective. Laser therapy can be successfully used to treat common condylomas that are resistant to other treatments. It allows you to stop recurrence in approximately 40% of patients. Studies have shown that such an ineffective result is due to the fact that the CO laser is ineffective when it comes to eliminating the genome from lesions that are resistant to treatment (according to the PCR method, a molecular biological cure occurs in 26% of patients).
The use of a CO laser is the method of choice in the treatment of CVI. Laser conization of the cervix is used. Relapses occur in 2% of patients. A mild method of laser therapy is vaporization, which does not cause virtually any complications. Laser vaporization has been successfully used in the treatment of low-grade CVN. Relapses are observed in 4% of patients.
Laser therapy has been successfully used to treat genital warts in pregnant women. There are reports of treatment in pregnant women at 28–35 weeks of pregnancy. In most patients, healing occurred after the first session. There were no complications during childbirth or in newborns.
Side effects include ulceration, bleeding, secondary infection, and scarring. As with electrosurgical methods, HPV DNA is released through smoke, which also requires precautions.
Laser therapy is not widely used due to the high cost of equipment and the need to train experienced personnel.
Cryotherapy. A fairly effective and safe method that involves the use of liquid nitrogen, nitrogen oxide and carbon dioxide as a refrigerant. In this case, rapid freezing of both intra- and extracellular fluid occurs, leading to lysis and death of cells upon thawing. Cryotherapy does not usually require pain relief, although local anesthetics can be used if necessary. Cryotherapy can be used to treat small warts of various locations. If the warts are multiple, then removal should be carried out in several stages. This method is characterized by the following side effects: the development of local redness, swelling, followed by the formation of blisters and their ulceration. To reduce damage to surrounding tissues, before the procedure, the surface of the warts is treated with KY-gel, which, when frozen, makes it possible to carefully lift and separate the lesion from the underlying epithelium.
The method can be used in gynecological practice.
We think the combined use of cryodestruction and plasma coagulation is extremely promising, allowing us to avoid the disadvantages inherent in the above methods separately.
Chemical destructive methods. This group of products includes solutions of acids, alkalis, and salts. Among them we can mention Feresol, hydrogen peroxide, solutions of quinacrine and hingamine, preparations of mercury and arsenic, bismuth, preparations based on salicylic and lactic acids, acetic and nitric acids, thuja and celandine juices. All these drugs are easily available, but have low, poorly predictable effectiveness, and produce numerous side effects.
Isoprinosine should be used in combination with locally destructive methods of treatment.
The effectiveness of combination treatment for PV, according to the literature, ranges from 38 to 96%.
Combined treatment methods. To treat the manifestations of HPV infection, various methods are proposed, based on the use of immune drugs in combination with laser, electrosurgical and cryodestructive effects.
The combined use of the above methods can reduce the number of relapses and thereby increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Good results have been obtained using a combined method of treating condylomas, including destruction of lesions using cryodestruction (exposure temperature from –160 to –180°C, exposure 40–120 s, twice) in combination with immune stimulation. To stimulate local immunity, the affected area was treated with an emulsion containing interferon (IF), and to stimulate the immune system of the whole body, the drug Kemantan was prescribed at a dose of 0.2 g three times a day orally for 10 days.
A combination of various destructive methods is possible. If there are manifestations of HPV infection on the skin and mucous membranes, cryospraying is first performed for 10–30 s, which makes it possible to clearly identify the boundaries of the lesion due to the characteristic papillary surface of the lesions, which turns white. Then the affected area is exposed to plasma (using the plasmaskin device).
A number of researchers recognize the best method of treating anogenital warts as surgical removal of all visible lesions followed by local administration of IF. In some cases, it is advisable to use general and local IF before surgical excision of extensive condylomas.
There is no therapeutic effect from the use of IF if the disease lasts more than one year, as well as with immunodeficiency.
Currently, there are not many remedies that can be used after using destructive methods. In particular, the drug impran has now appeared for local use in the area of lesions after destructive effects.
Specific antiviral therapy
Currently, there are no drugs that have a specific effect on HPV. Known drugs that suppress the replication of the herpes simplex virus (acyclovir, ganciclovir) turned out to be ineffective in the treatment of anogenital HPV infection.
Theoretically, vaccination is an ideal method for the treatment and prevention of anogenital warts.
There are reports of the effective use of IF inductors. Of interest is the local use of a low molecular weight derivative of imiquidaquinolamine, imiquimod, which is an inducer of cytokines and, in particular, L-IF. It is used in the form of a 5% cream three times a week or daily at night until the rash completely disappears (but not more than 4 months). Complete disappearance of condylomas is observed in 13–56% of cases. With daily use, local side effects more often developed: redness, swelling, erosion. The cream is especially indicated for the treatment of subclinical HPV infection. It is possible to use virazole.
The effect of using IF monotherapy has not been sufficiently studied and is not very high; in addition, it is necessary to take into account the high cost of such treatment. In this regard, this method is not widely used in practice.
Isoprinosine. In recent years, the new immunomodulator isoprinosine, which is a complex of inosine and the salt of N,N-dimethylamine-2-propanol and P-acetaminobenzoic acid, has attracted the close attention of immunologists. The drug can be used in the form of tablets or a solution for parenteral injection. The active substance in this complex appears to be inosine, and the amino alcohol salt stimulates its penetration through the membrane of lymphocytes and other cells.
Isoprinosine has a powerful and broad immunomodulatory effect. Numerous data and extensive literature indicate that in vitro the drug significantly enhances the proliferation of T lymphocytes induced by mitogens or specific antigens, as well as the differentiation of pre-T lymphocytes into more mature T lymphocytes, accompanied by the appearance of corresponding antigens on their surface. PI also stimulates mitogen-induced B cell proliferation. The stimulating effect of isoprinoline on the activity of natural killer cells (NK cells) in healthy people and the functional ability of cytotoxic T lymphocytes has been proven. The drug improves the CD4+/CD8+ ratio; increases the production of IL-2 by T lymphocytes; promotes the maturation and proliferation of T cells; activates the synthesis of IL-1 by macrophages. PI has an antiviral effect and prevents the use of ribosomal RNA for virus replication. It should be noted that when isoprinoline was used with other immunocorrectors, it significantly enhanced the antiviral effect of the latter.
Various treatment regimens using isoprinoline have been adopted depending on the size of condylomas, their location and the degree of malignancy.
Scheme 1: treatment of small, multiple genital warts with a low degree of malignancy.
The drug is taken in 2 tablets. three times a day for 14–28 days.
Scheme 2: treatment of multiple condylomas with individual large condylomas or flat condyloma of the cervix.
Among the chemicals used in our country and abroad that have a destructive effect are TCA and nitric acid, as well as a combined acid preparation - solcoderm.
TCA and nitric acid. TCA is used in 80-90% concentration and causes the formation of local coagulative necrosis. A solution of nitric acid has a similar effect. Due to their cheapness and availability, both methods are quite widespread to this day. Acids are effective for the treatment of condylomas of the vulva, preputial sac, coronary sulcus, glans penis, especially in cases where the use of PF and PFG is contraindicated. Cauterization is carried out once a week for 5-6 weeks. The effectiveness of using TCA and nitric acid is approximately 70-80%. In some cases, a local reaction may develop in the form of weeping and ulceration.
Solcoderm. Solcoderm is an aqueous solution, the active component of which is the interaction products of organic acids (acetic, oxalic and lactic) and metal ions with nitric acid.
acid. The solution contains nitrites in an amount of 0.02 mg/ml.
Listed below are the properties and mechanism of action of Solcoderm, which distinguish it from other drugs in this group used as part of destructive methods:
- when applied topically, solcoderm causes immediate intravital fixation of the tissue to which it is applied;
- the effect of the drug is strictly limited to the place of application;
- a sign of an immediate effect is a change in the color of the treated area;
- devitalized tissue dries out and darkens (mummification effect);
- The “mummified” scab is rejected on its own;
- The healing process is short and complications (secondary infection or scarring) are rare.
General characteristics of treatment with Solcoderm:
- the drug has a precisely limited local effect on the pathologically altered tissue to which it is applied, while the surrounding tissue is not damaged;
- the method is suitable for the treatment of various skin tumors;
- the treatment is painless;
- rapid healing, no complications;
- treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis and does not require special equipment;
- absence of any restrictions for the patient.
Indications for the use of Solcoderm: simple warts, plantar warts, anogenital warts (genital warts), seborrheic keratoses, actinokeratoses, basal cell epitheliomas (basaliomas).
Solcoderm is very easy to use and quite effective for the treatment of condylomas of any location. In most cases, a single application is sufficient.
Cytotoxic drugs
Podophyllin (PF). Pophylline is a resin obtained from the plants P.pelatum and P.emodi, which grow in North America and the Himalayas. To treat warts of the anogenital area, a 10-25% solution of PF in ethanol or benzoin tincture is used. It binds to the microtubule apparatus of the cell and inhibits mitosis, and also inhibits the transport of nucleic acids, resulting in inhibition of DNA synthesis and cell division.
The use of PF is a simple, affordable, fairly safe treatment method that can be used in an outpatient setting, as well as by patients independently. The drug is applied once or twice a week for a maximum of 5 weeks in an amount of no more than 0.5 ml per procedure. The patient must ensure that water does not enter the treated area for 4-6 hours after the procedure. PF is not recommended for use on vaginal, cervical and intraepithelial warts. According to some authors, the recurrence rate varies from 0 to 67%.
Approximately 10-15% of patients develop local adverse reactions in the form of weeping contact dermatitis. Particularly severe complications in the form of multiple ulcerations occur when used incorrectly. As a result of long-term or improper use of PF, patients may experience various adverse reactions, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, symptoms of damage to the kidneys, myocardium, liver, central nervous system and bone marrow.
The use of PF is contraindicated during pregnancy, since cases of teratogenic effects on the fetus and intrauterine fetal death have been reported.
Many researchers consider PF to be an insufficiently studied and crudely purified plant extract, and therefore recommend using only highly purified podophyllotoxins, and independent use of the drug by patients themselves is undesirable due to the above-mentioned complications.
Podophyllotoxin (PFT) (condylin). PFT is the most therapeutically active fraction of PF. Available in the form of solutions of 0.25, 0.3 and 0.5%, as well as in the form of cream 0.15, 0.3 and 0.5%.
It is usually prescribed twice a day for three days a week in a row for 4-5 weeks.
Although PFT is better purified than PF, a high incidence of side effects has been reported with the use of PFT, especially its 0.5% solution. The following side effects are most often observed as a result of the use of PFT: local inflammatory reactions (erythema, burning, soreness, itching, weeping and erosion in the area of application). Although systemic side effects have not been reported in the literature, it is recommended to limit the use of PFT to a dose of 0.2 ml per treatment.
The disadvantages of PFT are its high cost and long duration of treatment.
5-fluorouracil (5-FU). 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is a pyrimidine antagonist and has the ability to disrupt the synthesis of both cellular and viral DNA. For the treatment of warts of the anogenital area, it is prescribed in the form of a 5% cream. When treating intravaginal warts, the drug is prescribed once at night for a week or once a week for 10 weeks. The degree of effectiveness of the drug, according to various researchers, is 85-90%. When using 5-FU, weeping erosions on the vaginal mucosa may occur, up to the development of severe weeping contact dermatitis. When treating warts of the terminal part of the urethra, the cream is administered immediately after urination at night for 3-8 days. Complete cure of intraurethral warts is observed in 90-95% of men. However, during treatment there are many side effects: stenosis and stricture of the urethra, dysuria, ulceration. The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Immunological methods
Interferon. Since the human papillomavirus persists in epithelial cells and the use of destructive methods does not guarantee against relapses, the use of IF is promising in this regard, both as monotherapy and in combination with other treatment methods.
IFs are endogenous cytokines with antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory properties. There are three main classes of IF: leukocyte (L-IF), fibroblast (F-IF) and T-lymphocyte (T-IF). IF can be used locally, intralesional and systemically (subcutaneous, IM or IV). It has been established that when using IF in patients, the amount of viral DNA in the lesions decreases (according to PCR data), which correlates with clinical improvement or disappearance of the lesion.
There is data regarding the use of domestic IF, human leukocyte interferon (HLI), for the treatment of condylomas. It was used intralesional (under papilloma) at a dose of 100,000-500,000 IU, for a course of 3-6 procedures in combination with the application of interferon ointment with an activity of 40 IU to the lesions. PLI can be prescribed systemically and in the treatment of widespread lesions in combination with destructive methods.
L-IF can be considered the most effective drug for various methods, schedules and doses of administration. With systemic use of L-IF, complete disappearance of warts was observed in 11–100% of patients. The effectiveness of using F-IF was 45–82%. The effectiveness of T-IF, shown in different studies, is much lower than that of L-IF and F-IF, and varies from 7 to 57%.
It should be remembered that the unsystematic use of various treatment methods leads to a high percentage of relapses, however, the development of certain algorithms that take into account the gender of patients, the location and number of rashes can significantly reduce the number of relapses.
Table 1. Anogenital HPV infection and HPV-associated diseases
HPV infection
Detailed clinical forms (visible to the naked eye or invisible, but determined in the presence of appropriate symptoms):
- warts (genital condylomas, flat condylomas, vulgar warts)
- symptomatic intraepithelial neoplasia in the early stages - koilocytosis, dyskeratosis in the absence of dysplasia (flat condylomas)
Subclinical forms (not visible to the naked eye and asymptomatic, detected only by colposcopy and/or cytological or histological examination
- asymptomatic intraepithelial neoplasia (IN) in the early stages - koilocytosis, dyskeratosis in the absence of dysplasia (flat warts)
Latent forms (no morphological or histological changes when HPV DNA is detected)
back
Table 2. Diseases associated with HPV
Clinical and subclinical forms:
- VN in the early stages - mild dysplasia, /+-/ koilocytosis, dyskeratosis (VN stage 1)
- VN in late stages - severe dysplasia, /+-/ koilocytosis, dyskeratosis (VN stage 2)
- Late stage LN - severe dysplasia or carcinoma in situ /+-/ koilocytosis, dyskeratosis (stage 3 LN, or CIS)
Microinvasive squamous cell carcinoma:
- clinically visible or invisible, but in the presence of appropriate symptoms
- subclinical, not visible to the naked eye and asymptomatic, revealed only by cytological and histological examination
- latent - absence of morphological and histological changes when detecting DNA HPV infection by molecular hybridization
- intraepithelial neoplasia
Table 3. Classification of treatment methods for anogenital warts
Destructive methods
- physical
- surgical excision
- electrosurgical methods
- cryotherapy
- laser therapy
- chemical
- Nitric acid
- trichloroacetic acid (TCA)
- solcoderm
Cytotoxic methods
- podophyllin (PF)
- podophyllotoxin (PFT)
- 5-fluorouracil
Immunological methods
- interferons
- isoprinosine
Combined methods
- combined use of various methods
Treatment of HPV with folk remedies
Is it possible to cure HPV only with folk remedies? From the point of view of official medicine, it is impossible. Traditional recipes help strengthen the immune system and eliminate external symptoms of the disease. But they do not suppress the development of the virus, like medications.
Recipes for clear skin
Do not apply active ingredients with bare hands. Use gloves and cotton swabs to treat the affected area.
- Lubricate the wart, papilloma, condyloma with 70% vinegar essence. Repeat the treatment two to three times a day. The tumor will become covered with a white crust and then fall off. Often there are complications in the form of deep non-healing ulcers.
- Treat skin defects with iodine solution. Apply iodine twice daily for two weeks. During this time, the defect should dry out and fall off.
- Grind the celandine and mix it with medical alcohol in a 2:1 ratio or buy a ready-made tincture at the pharmacy. Treat the defect three times a day. Celandine does not act immediately. The course of treatment can last up to three weeks.
- Essential oils of sea buckthorn, thuja, and tea tree help cleanse the skin. They soften tumor cells, which promotes its death. Mix one of the listed oils with castor oil 1:1. Treat defects twice a day. The duration of the course is not limited.
Using folk remedies only on the recommendation and under the supervision of a doctor, wait until the defect is completely necrotic. Do not tear off the tumor until it falls off on its own, otherwise you may provoke bleeding or introduce an infection into the wound. The active substance should burn the wart, papilloma, condyloma to the roots. Otherwise, the tumor may grow again in the same place.
Recipes to boost your immune system
Prepare or buy herbs: horsetail, nettle, plantain and lemon balm. If you harvest your own herbs, dry them and grind them into powder. For the recipe you will need a tablespoon of each herb. Mix the herbs in a saucepan and pour 200 ml of boiling water (about three glasses) over them. The decoction should be infused for three hours. Take the decoction for a week, 50 ml per day.
For the second recipe you will need two tablespoons of spruce or pine needles. Add 100 ml of water (about a glass and a quarter). Bring the mixture to a boil. When the water boils, reduce the heat. Keep the broth on low heat for half an hour. It needs to be insisted for the same amount of time. Drink two tablespoons of decoction three times a day. You should drink it for one to two weeks.
Attention! We do not recommend treatment with traditional methods without first consulting a doctor in order to avoid possible undesirable consequences.
HPV prevention methods
For the development of the disease, it is enough for several small viruses to enter the body. Prevention methods will help prevent infection or recurrence of the disease:
- Use barrier contraception during sexual intercourse.
- Avoid public swimming pools, baths, saunas.
- Strengthen the body's immune system.
- Avoid stress and nervous overload.
- Dress warmly and avoid hypothermia.
We advise women to undergo a gynecological examination and tests for infections at least once a year. This will help maintain the health of the reproductive system.
Possible complications
Human papillomavirus infection can cause severe or mild complications. The most severe possible complication is the development of malignant tumors. Oncogenic strains of the virus cause cellular mutations that contribute to the transformation of benign tumors into malignant ones.
Cervical dysplasia precedes the development of cancer. Papillomas on the larynx grow and cause attacks of suffocation. HPV increases the likelihood of cancer of the stomach, intestines, and respiratory system.
Benign formations on the skin seem less dangerous than cancer. But we do not recommend delaying their treatment. Condylomas, papillomas and warts can accidentally come off. In their place, a bleeding wound forms, into which pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate. Large defects can leave unsightly scars if the removal is not carried out in the office of a dermatovenerologist.
Intraurethral condylomas may be accompanied by inflammation and bleeding from the urethra.
How dangerous are papillomas on the body: why they need to be removed
Papillomas are harmless only in appearance. These neoplasms, in the absence of timely and adequate treatment, quickly spread throughout the body to healthy tissue. This process is called autoinaculation. The result of the proliferation of neoplasms is at least multiple warts.
Of course, warts - papillomas on the body - are very ugly, but this is not the only problem. A good dermatologist will tell you why papillomas on the body are dangerous - such neoplasms are susceptible to melanization - malignant degeneration of the tumor. How quickly the process will proceed and whether it will begin at all depends on the location of the papilloma and the type of HPV. Genital warts growing on the cervix are especially dangerous. The degeneration of such formations into cancer occurs in every second case.
The structures that form on the skin as a result of damage by the papilloma virus are usually not accompanied by pain, itching or burning, which often causes negligence on the part of the patient. But since papillomas almost always come into contact with clothing, there is a high risk of damage. The result will be severe bleeding, infection and the formation of unsightly scars on the skin. From all this follows the answer to the question of whether it is necessary to remove papillomas on the body - of course it is necessary!
When to see a doctor
There is no universal way to get rid of the papilloma virus in the body. The treatment regimen is prescribed by a dermatovenerologist after reviewing the test results and the patient’s medical history. When should you visit a dermatovenerologist:
- Since childhood, your skin has had many warts, papillomas, and condylomas;
- skin defects have begun to appear en masse recently;
- you notice strange discharge from the genitals;
- you began to feel itching and burning in the perineum;
- unpleasant sensations appeared during sexual intercourse;
- you started self-treatment for HPV, but did not get results;
- you are planning to have a child (then both partners should be checked);
- you have not been tested for sexually transmitted infections for more than a year.
We recommend getting tested regularly for HPV, even if you have no symptoms and are not planning a pregnancy. Sometimes the latent stage of the disease can last for years. The virus may be present in the body, but not manifest itself in any way. Early diagnosis will help avoid the development of complications.
Diagnostics
If papillomas form on the body, face or genitals, you should consult a dermatologist. This will allow not only to diagnose human papillomavirus infection at an early stage, but also to take measures to prevent the formation of new elements, as well as monitor changes in existing ones.
It is especially important not to delay visiting a doctor if there are signs of growth, change in color of the papilloma, unpleasant odor or pain in the area where it is located.
First of all, the doctor will perform a dermatoscopy, i.e., an examination of the tumors using a special magnifying device. This will make it possible to determine their nature, as well as to notice dangerous signs indicating a high probability of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one, not to mention the formation of a cancerous tumor. When detected at an early stage of development, they can be successfully treated and have a favorable prognosis in the future.
Patients are recommended to be tested for the presence of STDs, especially if condylomas are detected in the genital area. Also in such situations, women are advised to consult a gynecologist, and men - a urologist. This is important for diagnosing the presence of human papillomavirus infection of the cervix, urethra, etc. and, if necessary, prescribing appropriate treatment.
To confirm papillomatous infection, patients are usually prescribed a PCR test. With its help, it is possible not only to confirm or refute infection with the human papillomavirus, but also to accurately determine the strains.
Advantages of the Private Practice Clinic
- Certification in all areas of work.
- The consultation is conducted by experienced dermatovenerologists and gynecologists.
- The latest methods of treating diseases.
- Possibility of removing papillomas and condylomas using all currently known modern methods without pain and serious scars.
- Results of express tests on the day of treatment.
- Individual approach to each patient.
- Polite and friendly staff.
- You can undergo diagnosis and treatment anonymously.
- Convenient location of the clinic in the center of Moscow and Southern Administrative District.
- Parking for visitors to the medical center.