All people have moles on their bodies.
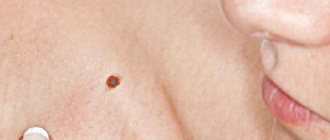
Among them there may be a birthmark that looks like a wart, called a warty nevus.
The danger of such a neoplasm is that it is capable of degeneration into a malignant form.
A warty (verrucous) nevus can be recognized by the presence of a bumpy surface.
The mole looks like a head of cabbage or has the appearance of a garland.
Nevus is dangerous, since such neoplasms often degenerate into a cancerous tumor.
A mole may appear some time after the baby is born, and sometimes it forms much later.
- Initially, a convex formation appears on the surface of the child’s skin. As it grows, the formation darkens and becomes brown or yellowish.
- As the child grows, the mole also becomes more noticeable, but there is no growth in width. The size of the nevus increases due to the proliferation of epithelial tissue that it affects.
- Over time, the surface of the neoplasm becomes keratinized and the mole becomes convex. As a result of injury to the upper layer, the neoplasm becomes larger.
In most cases, moles are not dangerous, but sometimes they become so as a result of degeneration into a malignant form.
Why does a warty nevus appear?
Scientists have come to the conclusion that the formation of moles begins at the embryonic stage of development.
Factors that provoke their formation in humans are:
- imbalance of female sex hormones in a woman during pregnancy
- the presence of infectious pathologies during pregnancy
- the influence of unfavorable environmental factors on a woman’s body during pregnancy
- hereditary factors
As a result of these reasons, the development process of melanoblasts, from which melanocytes are formed, is disrupted.
Melanocytes, concentrating in certain areas of the skin, turn into nevocytes.
Their difference from melanocytes is that they do not have processes that contribute to the spread of pigment.
Can a nevus turn into cancer?
A birthmark that forms in the upper layer of the skin poses a risk of degeneration.
Malignancy of a warty nevus can occur with repeated damage.
Please note the following changes:
- mole color change
- hair loss on a mole
- change in size towards larger tumors
- appearance of asymmetry
- presence of discharge from the nevus
- uneven edges
If at least one of the signs appears, you should immediately visit a doctor.
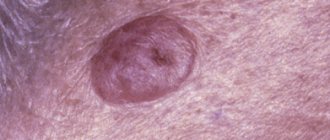
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a benign tumor of blood vessels. It is a spot on the skin of red, raspberry or cherry color. May rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Sizes - from a pinhead to quite large (see photo).
Types of warty nevus
There are localized forms of nevus manifestation or systemic (verrucous).
Localized - most moles are found in this form.
Signs of its manifestation:
- The diameter of the neoplasm does not exceed 1 cm.
- elements appear separately or are located so close that they can merge
- localization zone is clearly limited
- the keratinized surface of the nevus often has cracks
- moles are dark brown or maroon in color. In very rare cases, nevi are light brown or light pink in color.
- the area affected by moles is often devoid of hair
Systemic form of the disease - the incidence of pathology is approximately 20% of cases.
A distinctive feature of a nevus is the presence of a “garland” of neoplasms.
Such elements are located at close distances relative to each other and “stretch” along the surface of the skin along the entire body.
This form of nevus has a number of features:
- the elements spread along large vessels, and they can also be in different places of the body
- The surface layer of moles may differ in shade. Elements may have different color intensities
- the length of one garland can reach up to 20 cm.
- When feeling the moles, it is noted that they have a dense structure
- the surface of each mole is lumpy and tortuous. As a person ages, these symptoms become more pronounced.
Each type of warty mole can be frequently injured.
Melanoma
If you have pigmented tumors on your skin, our clinic is pleased to offer modern ultrasound diagnostics to prevent or timely detect melanoma.
Melanoma (from the Greek melas - “black”) is a malignant tumor of melanocytic origin.
Melanoma is one of the most aggressive and unpredictable tumors, often relapsing and metastasizing both lymphogenously and hematogenously to almost all organs. The etiology of skin melanoma, like most neoplasms, is multifactorial. However, numerous studies show that the most important role is played by ultraviolet (UV) radiation with a certain UVB range (from 280 to 315 nm). UVA rays from the solar spectrum enhance the damaging effects of UVB rays. Unlike other malignant skin tumors , the occurrence of which is associated with a cumulative UV radiation dose, the development and progression of melanoma is provoked by exposure to uncertain doses of UV radiation on the body with individual characteristics of the genotype and phenotype.
The second common cause of tumor development is chronic irritation and traumatic damage to nevi, including self-medication and non-radical cosmetic interventions.
Glasgow 7-point system of signs of malignancy of skin formations
- Changing sizes, volume
- Changing shape, outline
- Color change
- Inflammation
- Crusting or bleeding
- Changes in sensations, sensitivity
- Diameter more than 7 mm
Hardware diagnostic methods
DUB-TPM
Ultrasound diagnostics of skin.
Ultrasound diagnostic scanning is a well-known and proven technique, which currently accounts for more than 1/3 of all diagnostic procedures in medical practice. Modern devices are already quite easy to use and are available to many clinics.
However, these studies have not previously been used in dermatology, which was due to the difficulty of technically solving this problem. In conventional devices, the sensors have a frequency of 3-10 MHz, at which it was impossible to image the structures of the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis.
The German company TPM has created unique devices with sensor frequencies of 20-100 MHz. This technique is called high-resolution digital ultrasound imaging with the ability to study the most superficial layers of the skin.
Based on research materials conducted using the DUB TPM apparatus (the list is attached separately), many articles and 2 monographs have been published.
Until now, the main method for studying skin morphology has been histological and pathomorphological examination. This technique is quite labor-intensive and expensive; in addition, a biopsy sample is examined that has already been treated with various chemical reagents.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the skin fills the gap that previously existed between external research methods and histology, since this non-invasive method allows the study of the skin in vivo.
The importance of ultrasound scanning for skin diagnosis cannot be overestimated. This method has a number of undeniable advantages - non-invasiveness, painlessness, safety and high measurement accuracy. All studies are carried out without damaging tissue and can be repeated on the same area of skin many times.
The new tool allows you to see a section of the skin and subcutaneous fat down to the muscle fascia. We can examine the skin at various time intervals, documenting all the features. The data is digitized and placed in a database. It is easy to carry out a comparative analysis of images obtained over time, the images are saved on any digital media and the data is transmitted in publicly accessible formats via the Internet.
Ultrasound examination of the skin should become the “gold standard” in skin diagnostics, as in obstetrics, gynecology and cardiology.
Distinctive features of the DUB system
- TPM was the first to develop and commercialize skin ultrasound and set the standard for skin ultrasound throughout the world.
- Only DUB devices are equipped with sensors with a maximum frequency of up to 100 MHz and a resolution of up to 8-10 microns.
- Scan modes A,B,C.
- Three-dimensional scanning.
- Cinema loop without limitation of shooting duration.
- Digitization of the signal means the image is more detailed and clear.
- Digital data processing.
- View multiple images taken at different times.
- Innovative image processing algorithms.
- Saving raw data.
- Advanced software package.
- The use of an open system with water allows you to obtain 10-20% more information than using a system with film.
- At the moment, the device has no analogues throughout the world.
Device capabilities:
- 1) Study of the condition, structure and size of all layers of skin and skin formations.
- 2) In-depth diagnosis of morphological and functional changes in acute and chronic skin diseases, including scar changes and lipodystrophies.
- 3) Assessment of the dynamics of skin condition in normal and pathological conditions.
- 4) Facilitation of diagnosis of small skin rashes.
- 5) Timely early diagnosis, since with the help of ultrasound scanning it is possible not only to identify characteristic signs of skin manifestations at the earliest stages, but also to carry out preclinical diagnosis, prevention or timely treatment.
- 6) Diagnosis of skin conditions in the case of any manifestations difficult to detect with the naked eye.
- 7) Visualization, determination of size, volume and depth of invasion, as well as assessment of skin tumors and skin metastases, selection of treatment methods, setting parameters and monitoring effectiveness.
- Preoperative measurement of the depth of spread and volume of tumors during surgical interventions, including electrosurgery, cryosurgery, laser or radiation therapy.
- 9) Study of age-related skin changes.
- 10) Determination of the depth, intensity and duration of the therapeutic effect, choice of method.
- 11) Evaluating the effectiveness and monitoring of therapeutic, physiotherapeutic and surgical treatment methods, including cosmetic procedures (for example, mesotherapy, peelings, plastic surgery, tattoo removal, hardware procedures, etc.).
- 12) Preliminary diagnosis and evaluation of the results of the introduction of fillers, hyaluronic acid, collagen, synthetic or semi-synthetic gels, etc.
- 13) Early diagnosis of osteoporosis.
- 14) Study of skin elasticity.
- 15) Study of mucous membranes.
Advantages of using this method:
- 1) A non-invasive technique for visualizing the internal structures of the skin in vivo, which allows you to obtain important information that is not available with other research methods.
- 2) The method is indispensable for assessing the dynamics of skin condition in dermatology, cosmetology and dermato-oncology. Allows you to monitor the condition of skin manifestations and use the data in the primary diagnosis, prevention and treatment of most skin diseases.
- 3) The ability to save data in computer memory and on any electronic media, print out photographs for medical records, send via the Internet for consultations with colleagues.
- 4) An objective assessment of the dynamics of the patient’s skin condition is an important legal aspect in resolving conflict situations.
- 5) Visual visualization of the state of the internal structures of the skin and its relief is a strong psychological factor in explaining to patients the need for therapeutic measures.
- 6) With the help of DUB, it is easy to prove the effectiveness of treatment in a form accessible to the client. This is a powerful marketing tool to attract new customers.
- 7) The presence of this method increases the rating of the institution and indicates high equipment and the use of advanced technologies.
- In addition to the histological picture, it increases the accuracy of the pathological diagnosis.
- 9) Conducting scientific and educational programs.
- 10) Conducting consultations and consulting and diagnostic activities.
A new aspect of using this method for manufacturers is to assess the effects on the skin of various products, including cosmetics, medications, and devices.
VIVASCOPE® 1500 MULTILASER
The most accurate diagnostic device in dermatology, dermato-oncology and cosmetology.
Confocal laser scanning microscope for in vivo histological examination of skin by fluorescence using lasers of 3 wavelengths (785 nm, 658 nm, 445 nm)
- Combining reflected laser and fluorescence detection technology
- Optical non-invasive biopsy
- Real time display
The VivaScope 1500 Multilaser system combines reflected laser acquisition technology with fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy. Similar to the standard VivaScope 1500, skin areas can be viewed in vivo using infrared light. The wavelengths used are 785 nm (near infrared), 658 nm (red) or 445 nm (blue). All three lasers are integrated in one device.
Before using VivaScope, a fluorescent dye (non-toxic to the body) is applied to the area of tissue that needs to be examined. The corresponding laser radiation excites the fluorophore and the resulting fluorescence allows a contrast image to be obtained, which helps to display the histological structure due to the distribution of the dye.
With the VivaScope 1500 Multilaser it is possible to image various functional aspects of tissue changes in vivo. Living tissue can be visually examined sequentially using all available laser wavelengths.
Dermatoscope HEINE DELTA 20 T
Designed for dermoscopic examination for early diagnosis of malignant melanomas, for the study of non-melanocytic formations, basal cell carcinoma and dermatofibroma.
Dermatoscopy is a non-invasive method of visual diagnosis of the skin, which, thanks to the use of high technology, allows us to move from a subjective assessment of the condition of the skin to an objective one and document skin changes.
The essence of the method is that with the help of a special device - a dermatoscope, the surface layers of the skin are examined at 10x magnification. This allows a more thorough study of the symmetry of the neoplasm, its boundaries, and structure.
The main thing is to understand that there are ordinary moles, which, after testing according to the “ABCD” rule, may turn out to be alarming for all the symptoms - points, as well as skin melanoma, which does not fit any of the proposed criteria from this rule. Thus, all symptoms must be taken into account together. The final diagnosis of melanoma can only be established after a histological examination performed after total removal of the nevus (tumor). IF YOU DETECT SIGNS OF THE DISEASE, WE RECOMMEND YOU TO CONTACT OUR CLINIC. OUR SPECIALISTS WILL HELP YOU!
SKIN TUMORS OF MELANOCYTIC GENESIS
Intradermal pigmented nevus
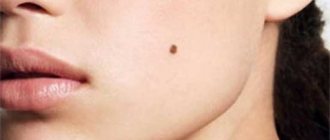
Intradermal pigmented nevus, or an ordinary birthmark, occurs in almost all people (from a few to several dozen). Characteristics: persistent hyperpigmentation, clear boundaries, soft consistency, absence of inflammatory phenomena.
Fibroepithelial nevus
It can exist from birth or appear at different periods of life. It is most often localized on the face or torso. These nevi can be single or multiple. It has the shape of a hemisphere, a wide base, rises above the level of the skin, and is occasionally located on a stalk. The consistency is soft, the sizes range from several. millimeters up to 1 cm. Color - from the tone of the surrounding skin to dark brown. Hair growth is preserved or even strengthened. May become inflamed due to injury.
Papillomatous and verrucous nevi
Clinically identical nevi exist from birth or early childhood and usually grow slowly. Papillomatous nevi are most often localized on the scalp, verrucous (warty) - on the skin of the trunk and limbs. They have a bumpy surface and protrude significantly above the surface of the skin. As a rule, there is hair on their surface; cracks are sometimes visible on verrucous nevi. Coloring ranges from normal skin color to black. Various sizes, up to 6-7 cm.
"Mongolian" spot
It is almost always located in the lumbosacral region. As a rule, it is a congenital formation, gradually decreases in size, changes color and in most cases disappears in childhood.
Halo nevus (Setton's nevus)
From the Greek word “halos” - ring, circle. A formation that slightly rises above the level of the skin, elastic consistency, reddish-brown color, 2-5 mm in diameter, with a characteristic feature - the presence of a depigmented rim in the circumference. This corolla is larger than the pigmented formation located in the center.
Juvenile melanoma
Occurs mainly in children. At first it grows quickly, and then remains stationary for years. Usually an asymptomatic tumor-like (bulging) formation of a flat or hemispherical shape, small in size (about 1 cm), with clear boundaries, dense consistency, color from light red to dark brown. The surface is smooth and hairless. Histologically, it is an epithelioid and/or spindle cell nevus. Malignant degeneration is rare.
Nevus SPILUS (Shpilus-nevus, spotted)
It is a pigmented spot (like “café au lait”, “scattered” nevus) of light brown color with small dark inclusions. Most often it is congenital or forms in childhood.
Becker's nevus (pigmented pilaris epidermal nevus)
It usually appears in adolescence as a single brown spot (usually on the shoulder), gradually enlarges and subsequently becomes overgrown with hair. Men are affected 5 times more often.
A single plaque with an uneven, slightly warty surface. The edges are jagged, the color ranges from yellow-brown to brown, the color is uneven, reaches a size of 20 cm. Covered with thick, dark hair, the boundaries of pigmentation and hypertrichosis do not coincide.
Borderline pigmented nevus (junctional nevus, intraepidermal nevus)
It develops at the border of the epidermis and dermis and is characterized by increased activity of pigment cells (melanocytes). A flat dark brown or black knot up to 1 cm in diameter with a smooth, dry surface. Most often congenital, but can appear in the first years of life. There is no favorite localization; it can be located on the skin of the face, neck, or torso. Pigmented nevi on the skin of the palms, soles, and genitals are almost always borderline. An important diagnostic sign is the complete absence of hair on it. The nevus grows slowly according to body weight. During puberty, patients may experience increased growth. If the diameter of the nevus exceeds 1 cm, it is a dysplastic nevus. Mechanical trauma is the predominant factor accompanying the malignancy of previously “quiet” nevi.
Blue (blue) nevus
It is a nodule sharply demarcated from the surrounding skin, dark blue or bluish in color (an optical effect arising from the deep location of melanin in the dermis), rounded in outline, and densely elastic consistency. The surface is smooth, without hair, and has the appearance of tightly stretched skin. The size, as a rule, does not exceed 1 cm. It is most often found on the face, limbs, and buttocks. Possible localization in the oral cavity. Usually the formation is single, but cases of numerous blue nevi have been described. Appears mainly after puberty.
Nevus Ota
Some authors call it dark blue orbital-maxillary nevus. The typical localization of this formation is the face (the area of innervation of the I and II branches of the trigeminal nerve). It consists of one large or many spots of grayish-bluish color merging with each other, located in the area of the cheek, upper jaw, and zygomatic arch. In this case, pigmentation is required in various parts of the eye: conjunctiva, sclera, iris. Sometimes the process involves the red border of the lips and the mucous membranes of the nose, soft palate, pharynx, and larynx. Nevus of Ota is congenital, but not inherited; most often occurs in early childhood or during puberty, unlike the Mongolian spot it persists until the end of life.
Congenital giant nevus
A giant pigmented nevus is always congenital, increases in size as the child grows, reaching a large size (from the palm of the hand or more) and sometimes occupies a large part of the torso, neck and other areas. Its surface is uneven, warty, with cracks. Hypertrichosis is often observed. The color varies from grayish to black and is often heterogeneous in different areas. Malignancy of a giant pigmented nevus occurs in 2-13% of patients, and according to some data - in 40%.
Dubreuil's limited precancerous melanosis
Some researchers classify Dubreuil's melanosis as pigmented nevi, while others argue that it is not a nevus or nevoid formation, but belongs to dermatoses. One way or another, Dubreuil's melanosis is a melanoma-dangerous formation. Mostly elderly people are affected. It usually begins with a small pigment spot. Further, the lesion, developing, acquires blurred boundaries and an uneven surface. In a developed state, it measures from 2 to 6 cm in diameter. The color is uneven - brown, gray, bluish. Frequent localization is open areas of the skin, especially the face (cheeks, nasolabial folds, nose, forehead). According to various authors, malignancy occurs in 30-75% of cases. Dubrey's melanosis transformed into melanoma is defined by domestic authors as “lentigomelanoma.”
Dysplastic nevus
It is considered a precursor to superficial spreading melanoma and is considered a risk factor for melanoma. Acquired pigment formation, histologically represented by a disorderly proliferation of polymorphic atypical pigment cells (melanocytes). Occurs on clean skin or as a component of a complex nevus. These are pigmented spots of irregular shape and with unclear boundaries, slightly raised above the skin level, their color varies from reddish-brown to dark brown. As a rule, larger than ordinary birthmarks, although they can appear anywhere, they are more often found in areas usually covered by clothing (on the buttocks, chest), or on the scalp. Usually multiple. Ordinary nevi usually appear during puberty, while dysplastic nevi continue to appear even after 35 years.
Cost of treatment
| Initial-repeated consultation with a dermatovenerologist | 2500 |
| Primary consultation with a dermatovenerologist - repeated after 20.00. | 3500 |
| Consultation with a dermatovenerologist, doctor of medical sciences/professor | 6000 |
| Primary consultation | 6000 |
| Repeated consultation | 3000 |
| Comprehensive 3D skin diagnostics | 5000 |
| 3D skin scanning | 3500 |
See the full price list
* The cost is indicated in the comprehensive procedure
*** The final cost of the procedure will be determined only after consultation with the specialists of our clinic.
"PresidentMed" guarantees its patients the best price-quality ratio!
Doctors Clinics
Nezgovorova Oksana Ivanovna
Doctor - cosmetologist, doctor - dermatovenerologist. Experience in the field of medical cosmetology and dermatology since 2006.
Skorodumova Olga Evgenievna
Doctor - cosmetologist, doctor - dermatovenerologist. Experience in the field of medical cosmetology and dermatology since 2000.
Kirilyuk Tatyana Igorevna
Graduated from the Medical Academy named after S.I. Georgievsky Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education “KFU named after. IN AND. Vernadsky" (Medicine). Red diploma.
Grishanova Natalia Alexandrovna
Doctor - cosmetologist, doctor - dermatovenerologist. Experience in the field of medical cosmetology and dermatology since 2003.
Oleynikova (Alekseeva) Svetlana Mikhailovna
Doctor - cosmetologist, doctor - dermatovenerologist. Experience in the field of medical cosmetology and dermatology since 2004.
Patient reviews
Natalya Ivanova, 04/28/17 The clinic has modern equipment and medications. I am very pleased with the work of the doctors. Thank you! Best regards, Natalia
Characteristic manifestations of verrucous nevus
The neoplasms rise above the skin by 2 cm, but sometimes they can be higher.
Moles look like a cluster of a large number of papilloma-like growths, which are located very close to each other and can merge into a single whole.
The surface of the new growths is slightly rough and quite dense.
The color of verrucous nevus varies from flesh-colored to dark brown.
Growths can appear on any part of the skin surface.
Both single neoplasms and large numbers can be observed, including they can be fused and have an individual shape, size and color.
Verrucous nevus is characterized by the presence of elements on one side of the body (right or left).
When located on the extremities, the localization of neoplasms is noted in the area of large vessels and nerve bundles.
Keratotic nevus grows very slowly, possibly the growth of new elements.
An increase in the size of moles is more often observed in the longitudinal direction than in the transverse direction.
The presence of moles does not cause discomfort, they do not cause pain or itching, and do not interfere with any movements.
Their presence on the body has a pronounced cosmetic disadvantage, especially if they are located on open areas of the body or on the face.
Navigation:
- When does a nevus need to be removed?
- Methods for removing nevi
Nevi can be located at the same level with the surface of the skin or rise above it. Sometimes dark moles and birthmarks are formed due to certain disorders during intrauterine development, that is, they are congenital. In others, they are formed during life under the influence of various factors and are called acquired.
These factors include:
- heredity, when nevi appear in large numbers and in certain places (for example, the father and child in the same place have neoplasms of the same shape, color and type);
- strong exposure to sunlight, which provokes the production of melanin;
- changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy, menopause or related to the functioning of certain organs;
- dermatitis, skin infections;
- strains of human papillomaviruses (cause the appearance of papillomas).
Nevi are divided into melanoma-mono-dangerous and melanoma-dangerous. The first, that is, with a low risk of degeneration into oncology, include Setton's nevus (halo-nevus), fibroepithelial nevus, "Mongolian spot", papillomomatous epidermal nevus, etc. The category of nevi prone to degeneration into skin cancer includes the following nevi: giant pigmented, blue, pigment borderline, dysplastic, Dubreuil melanosis.
Nevi are also divided by size (small, medium, large, giant) and by place of formation (intradermal, epidermal and border).
Diagnosis of keratotic nevus
Only a specialist can identify the presence of a warty nevus.
Based on external data and a conversation with the patient, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis.
For a more accurate diagnosis, laboratory tests will be required.
When examining a nevus, the doctor pays attention to the presence of the following features:
- coloring of moles
- size of tumors
- Locations of birthmarks
- shape of moles
- absence or presence of hair on the surface of the neoplasm
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests are performed:
- oncocytology. A scraping is taken from the surface of the nevus. The disadvantage of the technique may be a traumatic factor, which can provoke the development of complications such as infection or degeneration into melanoma. Therefore, this study is prescribed for those patients whose moles have been traumatized;
- Lumenescence microscopy technique. Its essence is to apply a special composition to the neoplasm, after which the birthmark is examined under a microscope. This research method is considered to be the safest, since the nevus is not injured during the procedure;
- conducting a computed tomogram , which allows you to examine the internal structure of moles using x-rays;
- blood tests . The blood is examined for tumor markers - specific proteins that are produced when the body is prone to cancer;
- histology . A piece of tissue is taken for examination. The resulting biomaterial is subjected to histological examination for malignancy of the nevus. This technique is informative enough to confirm the development of a malignant process.
Treatment of warty nevus
The basis of treatment for keratotic nevus is its removal using one of the most suitable methods.
The choice of method depends on the location of the warty nevus, its shape, and size.
The specialist decides which destruction method will be most effective.
To get rid of the manifestations of skin defects, the following techniques can be used:
- use of liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy)
- application of electric current (electrocoagulation)
- removal by radio waves (radiotherapy)
- destruction with a laser beam (laser therapy)
How to remove a warty nevus
Removal of a verrucous nevus is carried out using one of the following methods.
Surgical excision of moles is a classic method of ridding a patient of skin tumors.
After anesthesia and antiseptic treatment of the skin and surface of the nevus, it is cut out with a scalpel.
Then the wound is treated with a disinfectant and a sterile gauze bandage is applied.
This technique has negative aspects: infection of the wound surface and the formation of a postoperative scar are possible.
Removal of a nevus using radio wave radiation - this technique has many advantages:
- the ability to control the depth of exposure to radio waves, which avoids damage to healthy tissue around the tumor
- absence of bleeding due to their coagulation
- the procedure is painless
- the procedure is carried out very quickly
- radio waves can be used on any area of the skin
- There are no negative consequences after surgery
Laser therapy is one of the most common.
The laser beam can be used for keratotic moles on the scalp, as well as in the facial area.
Benefits of using laser:
- it is impossible for infection to penetrate at the site of exposure
- Coagulation of the wound eliminates the development of bleeding
- after removing the growth, a crust remains
- the risk of scarring is minimal
Removing nevus with liquid nitrogen: the use of low temperatures allows you to remove small tumors.
The procedure is painless.
Pain appears some time after exposure to nitrogen.
A disadvantage of the technique is also the need for repeated sessions, since the technique does not allow accurately calculating the time of exposure of the pathological tissue to nitrogen.
Electrocoagulation method - high frequency currents are used for treatment.
Before removal, the doctor administers local anesthesia.
As a result of exposure to electric current, a crust forms at the site of removal, which protects the wound from infection.
Treatment of epidermal moles
Epidermal moles persist throughout life, do not tend to disappear spontaneously and are primarily a cosmetic problem, especially on the skin of the face and neck. These are benign formations, although there are risks of developing cancer. A case of squamous cell carcinoma inside a nevus has been described in the literature. Treatment of epidermal moles is necessary for cosmetic reasons.
Treatment uses many different methods, varying in effectiveness and availability. When treating epidermal nevi, the following is used:
- surgical removal of the lesion;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryotherapy;
- dermabrasion;
- CO 2 laser;
- dye laser;
- tretinoin;
- 5-fluorouracil;
- acitretin;
- calcipotriol;
- dithranol;
- podophyllin;
- keratolytic drugs.
Conservative methods fail to achieve complete recovery, and scars remain after surgical removal of the lesion. The mechanism of action of individual methods is not always fully understood. For example, calcipotriol can affect the production and function of cytokines and normalize the differentiation of epidermal cells, 5-fluorouracil has an antiproliferative effect.
Some of the treatments that were used in the past are now only of historical significance.
According to many scientists, the most effective method of treating linear lesions in a small area is to remove the nevus by surgical excision; however, when completely removing large lesions, it is necessary to cover the defect with a free skin graft, which is often associated with the formation of an unaesthetic scar.
The effect of laser on moles
Features of care for verrucous nevus
If elements of a wart nevus are found on a patient’s body, doctors suggest removing it to remove the cosmetic defect.
If the patient for some reason does not want or cannot do this, then he must follow a number of rules that will help avoid the development of complications.
The basic rules are as follows:
- Eliminate factors that may cause overheating of moles. Prohibited: visiting saunas, baths, spa treatments.
- In the warm season, avoid being under the rays of the sun during the hours of its greatest activity: after 10 a.m. and before 4 p.m. Avoid visiting the solarium. It has been proven that protective agents cannot prevent the development of melanoma;
- Before taking hormonal medications, you should first consult with a specialist.
- Monitor the condition of the nevus elements and consult a doctor at the first symptoms of malignancy of moles.
You should pay attention to the following changes:
- accelerated nevus growth
- the appearance of unpleasant sensations that were not there before: pain, itching, burning, etc.
- change in the color of the neoplasm, it may become multi-colored
- appearance of peeling
- formation of cracks on the nevus
- hair loss
- asymmetrical growth, torn edges
- acquisition of granularity by a mole
- formation of outgrowths
- the appearance of discharge of various types
If at least one of the above symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If treatment turns out to be timely, then birthmarks will not pose a danger to a person in terms of malignancy.
And modern treatment methods will eliminate the presence of discomfort, both physical and cosmetic.
It is important to understand that self-medication can cause irreparable harm to health.
Removal of tumors should only take place in a medical facility and be carried out by a specialist.
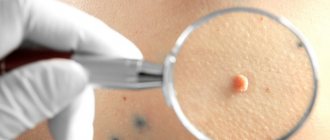
Papilloma
Papilloma is a formation of connective tissue covered with stratified epithelium. There are different types - warts, senile papillomas, cutaneous horn, condylomas, etc.
Most often, papillomas are located on the skin, but can also occur on mucous membranes (for example, the oral cavity, larynx). Papillomas should be distinguished from skin cancer.
Papilloma on the skin is usually a small (2 to 15 mm in diameter) formation that rises above the surface of the skin in the form of a papilla; it can be flat or pedunculated. The epithelium covering the papilloma may have the form of papillae, sometimes the papillomas are covered with horny masses (keratopapilloma). If injured, they can bleed, and if they are large, they can ulcerate (photo below).
Why is a warty nevus dangerous?
This type of mole among other nevi is the safest.
A certain group of factors can contribute to its degeneration.
The possibility of infection due to injury to a mole can provoke the development of an inflammatory process.
If a keratotic nevus is localized on the head or in another area of increased risk of injury, they should be removed as quickly as possible after their formation.
In some cases, manifestations of a systemic warty neoplasm can serve as a sign of hydrocephalus and other lesions of the nervous system, as well as melanoma.
In this case, therapy should be carried out simultaneously by several specialists: oncologist, neurologist and dermatologist.
Preventive measures for warty nevus
Verrucous nevus can provoke the development of oncological pathology.
But with proper prevention it is possible to avoid complications.
Prevention of complications is as follows:
- eliminating the possibility of injury to neoplasms
- Seeing a doctor for excision of growths
- you need to forget forever about saunas and solariums. Even the use of sunscreen cosmetics cannot protect against the development of melanoma
- in hot weather, avoid going outside to prevent overheating of tumors
- stay indoors after 10 a.m. and before 4 p.m.
- If at least one of the signs of malignancy appears, immediately go to the doctor
- Regular visits to a specialist to monitor moles