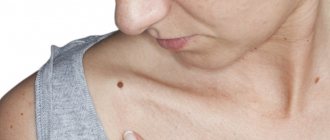
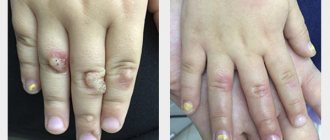
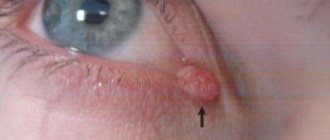
A mole or nevus is a pigmented formation on the skin. It contains melanin and melanocyte cells. Moles appear on the body as a person grows older and depend on solar activity. Nevi can develop on any part of the body, become more voluminous or increase in size, causing some aesthetic inconvenience. In addition to their external beauty, nevi can degenerate into malignant melanoma through the process of metastasis. Can this be avoided? Yes, it is enough to remove the mole surgically in a trusted clinic. How exactly does the removal take place, what are the risks/consequences, and how often should I visit a dermatologist?
General characteristics of formations
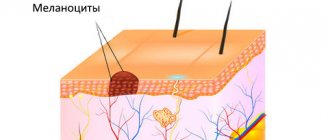
A mole is a pigment formation of one of the shades of the brown palette. The base contains melanin and the melanocyte cells that produce it. Melanins are high molecular weight pigments. They are characterized by a heterogeneous structure and complex chemical composition. Pigments are found not only in moles, but also in all skin, hair, iris, inner ear and even some parts of the brain.
Content:
- General characteristics of formations
- Indications/contraindications for the procedure
- What you need to know about melanoma?
- How to properly prepare for mole removal
- Technique of the operation
- Possible complications and side effects
- Features of rehabilitation
It is important not to confuse nevi and birthmarks. Moles do not form in the prenatal period, but as a person grows older and are closely related to his lifestyle. The cause of the formation of pigment spots can be a hereditary factor, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, or hormonal changes.
Each mole is a separate formation with a unique life cycle. At first it is a flat spot, which can increase and rise slightly above the skin as it grows and develops. The size and location of the formation depends on the level of melanocytes. If they are in the epidermis (top layer of skin), the mole will be flat. The deeper the melanocyte is immersed in the dermis, the higher the formation is located on the surface of the human body.
Convex nevi, which rise slightly above the skin, should not frighten their owners. This condition has no negative consequences and is considered a variant of the norm. The main thing is that the mole is miniature, round and uniform (in terms of color and structure) throughout its life cycle.
Can a mole disappear on its own and how safe is it? Yes, the formation can disappear without the influence of mechanical factors. This happens gradually and can alert a person. First, a white outline is formed around the formation, which resembles an orbit. This contour begins to increase and gradually covers the surface of the entire formation. The nevus disappears, and a small white spot remains in its place. Most often this occurs after severe sunburn. The disappearance of moles can also be a harbinger of the rare disease vitiligo.
If you notice changes in a mole (increase/decrease, uneven edges, change in shade or structure), be sure to consult a specialist.
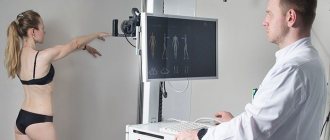
Necessary examinations before removal
The condition of nevi is assessed in 2 stages:
- examination with a magnifying glass and palpation;
- dermatoscopy (conventional or computer).
Sometimes an ultrasound is also required.
Hardware examinations are not traumatic and safe, but they make it possible to examine the mole in detail.
During the examination, under no circumstances should you damage the mole, and under no circumstances should you take a piece of it for histological examination (biopsy).
If you are offered such a study, refuse it - it can be dangerous.
Indications/contraindications for the procedure
The surgical method is most often used when malignant degeneration of a nevus is suspected. Doctors recommend removing formations that are constantly in contact with clothing or located on the scalp, which increases the risk of damage. Moles in the groin, neck, chin, back or in the folds of the skin are most often damaged - consult a dermatologist to decide whether to remove them. Large formations on “legs” also pose a colossal danger. They can come off or become twisted, which can cause pain and infection.
Excision covers not only the affected area, but also healthy tissue, which prevents recurrence of skin growths. The main advantage over more modern laser removal or cryodestruction is the obtaining of material for histological examination. The excised tissue is sent for diagnostics in order to better understand the causes of the disease, understand the possible risks and create a preventive course for the patient.
Surgical procedures can only be performed in specialized medical institutions. Beauty salons or home procedures are not suitable for this and can cause irreversible consequences for the body.
| Indications | Relative contraindications |
| Increasing the size of education | Infectious diseases regardless of stage |
| Deep penetration of the mole under the skin | Acute inflammatory processes |
| Bleeding, change in color or texture | Chronic pathologies in the acute stage |
| Frequent injury to the mole, the formation causes pain or inconvenience | Pregnancy and breastfeeding period |
| Aesthetic discomfort |
There are no direct contraindications to surgical removal of nevi. In case of relative contraindications, the patient must undergo additional tests and consult a specialist.
The doctor will determine the advisability of removal, indicate possible complications and features of rehabilitation. In some cases, surgery will have to be postponed until the patient fully recovers.
Melanoma, nevi, lentigo, birthmarks, basal cell carcinoma, skin and epithelial tissue tumors
A newly born child is examined; there are many birthmarks and moles on his skin; they say about such a baby that these are signs that the child will be lucky and happy.
This is not true; few people know that birthmarks and moles sometimes pose a threat not only to health, but also to life. Previously, superstitious people said that they were the devil's marks. Specialists who diagnose skin tumors are called oncodermatologists. So they state: age spots and moles are areas potentially dangerous for the development of skin cancer, a terrible disease - malanoma. Birthmarks, melanocytic or nevoid neoplasms, nevi are limited pigmented spots or elevations of the skin, consisting of accumulations of melanin-containing cells - melanocytes (there are also many of them in Negroids) or nevus cells. Each of us has a certain number of moles or birthmarks. They all look different and can be of different sizes and colors, can be flat or raised, smooth, hairy or warty; flattened or located on a long base, like on a stalk.
There are two periods in a person’s life when skin growths require special control: pregnancy and adolescence, when hormonal levels undergo serious changes; during these periods, skin growths can undergo changes. 40-50% of skin cancer (melanomas) originate from melanocytes of birthmarks (the rest - from melanocytes of normal skin), which are divided into Lentigo - a pigment spot (macula) that does not rise above normal skin in brown tones (beige, brown, black).
Skin nevi are usually flattened, sometimes rising above the main level of the skin. They are also painted in beige, brown or almost black colors, sizes - from 1 to 10 mm in diameter. Complex nevi are often raised and dark brown or black in color. Sutton's moles or Sutton's nevi are special; they contain both pigmented areas and areas of whitish skin without pigment. These moles may disappear on their own; malignant tumors appear from them very rarely.
Dysplastic nevi: this group of nevi is under special attention of oncologists - these are often inherited large, up to 5-12 mm in diameter, raised pigmented spots with unclear boundaries of beige, light brown, dark brown, even black on a bright pink background.
An average person has on average a dozen ordinary moles on their skin, while dysplastic nevi can number more than a hundred. Why does melanoma appear? As a rule, this requires an irritant, such as insolation - excessive exposure to the sun. Trauma, or constant injury to a mole, is an equally important risk factor for its degeneration. Skin neoplasms that are located in places where they are constantly injured by clothing - a chain on the neck, a washcloth, a bra in women - are a risk factor. Tanning: ultraviolet radiation in intense doses causes irreversible changes in skin cells, greatly increasing the risk of their degeneration. The country that faces the most intense problem with the problem of a deadly tumor, melanoma, is Australia. There is very intense insolation here, and just like here in Russia, there are a large number of people with fair skin and light-colored corneas, often freckled people, red-haired people, but it is they who most often develop melanoma.
And special attention to people with a large number of moles!!
With prolonged insolation, the skin must be protected from ultraviolet irradiation, which leads to melanocytic reactions. Intense tanning is always invisible burns; they reduce local immunity. In response, the skin does not forgive excessive sunstroke and responds with the malignancy of moles and age spots, and the emergence of all kinds of neoplasms.
How to protect yourself from melanoma?
- Regularly show your skin to an oncodermatologist once a year. To identify melanoma-dangerous diseases and skin tumors that may be dangerous, the oncodermatologist will perform a dermatoscopy - examination using a special oncological device for examining the skin. After consultation with you, the doctor will carefully and painlessly remove dangerous tumors.
- After swimming in the sea or river, you need to rinse in the shower and dry off, because... The water droplets act as powerful lenses for the skin.
- Insolation during the daytime is very dangerous!! From 11 a.m. to 3 p.m., it is better to use shade. Remember about your legs when you wear shorts or short skirts - in men, melanoma affects the thigh in 4.9% of cases, the lower leg in 6.7%; in women, thigh – in 6.7%, lower leg – in 26.3% of cases
- Particular attention for pregnant women and children - their skin is most exposed to the danger of radiation
- Use sunscreen, don’t go to the beach without it, so as not to expose yourself to not just danger, but mortal danger, such as melanoma!
What you need to know about melanoma?
Every mole on the human body can degenerate into a malignant melanoma. What it is? Melanoma is one of the types of malignant tumors. It also contains melanocyte cells (producing melanin), but in melanoma the cells are more aggressive.
They constantly divide, displace healthy cells, enter the vascular bed and spread throughout the body. As soon as the first aggressive cell approaches the brain or, for example, the lungs, it settles inside the organ and begins to rapidly divide. This process is called metastasis.
Melanomas are extremely dangerous because they quickly metastasize and divide at an incredible rate. The main thing is to detect the pathology in time. Surgical removal of melanoma will prevent the process from spreading throughout the body and guarantee a complete cure. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner or complete refusal of treatment can result in death.
How can moles be dangerous?
Basically harmless nevi can, under certain circumstances, degenerate into malignant neoplasms. In this way, one of the most aggressive forms of cancer tumors, melanoma, often appears. Particularly dangerous in this regard are moles of the dysplastic type, which are externally and internally not similar to typical nevi.
Mandatory removal of moles is recommended:
- unevenly colored or beginning to change color;
- rapidly increasing in size and changing shape;
- with cracks and redness of the surrounding skin;
- bleeding, causing pain or discomfort.
It is also necessary to remove nevus on the head, neck, lower back and other traumatic places where moles are exposed to physical impact. Their frequent damage by a comb, cutting and shaving tools, friction or squeezing by clothing, or pinching by fasteners can contribute to their degeneration into malignant neoplasms. The more nevi a person has, the higher the risk. If your skin is “strewn” with moles, you should refrain from frequent visits to the solarium, and take sunbathing only with the use of protective equipment that prevents burns. Nevi that cause even the slightest concern should be removed.
How to properly prepare for mole removal
No specific preparation is provided before removal. The patient just needs to come to the medical center and follow the necessary instructions from the specialist. Before the operation, a painkiller must be administered to make the procedure as comfortable as possible. In most cases, drugs with lidocaine are used. If there is an increased risk of bleeding, the doctor selects a medication and administers it intravenously after pain relief.
Immediately before the procedure, the doctor conducts a short consultation. He explains the essence of the method, possible complications and skin care rules.
As soon as the nuances are agreed upon, the doctor begins work. The patient is placed on a couch and the skin is treated with a special solution. It disinfects the area so that pathogenic bacteria do not enter the open wound. At this stage, the preparation ends, and the specialist proceeds directly to the surgical intervention.
Injection of an anesthetic drug under the skin
Any local anesthetic drug causes an unpleasant tingling or burning sensation when it enters the skin through the needle. This is due to the fact that the drug pushes the tissues apart and has an irritating effect on them. In this case, a characteristic “button” forms on the skin.
In order to smooth out this moment, we use the most modern drugs for local anesthesia. They provide excellent pain relief using a minimal amount of substance. The smaller volume pushes the tissues apart less, the injection time is shorter, and the pain is less.
Technique of the operation
The removal technique depends on the location and size of the formation. The mole must be excised within healthy tissue. The area of excision is determined by the doctor, warning the patient about it. For example, if the nevus is located on the face, the specialist must remove a minimum amount of epidermis. On other parts of the body, the result of the intervention will be less noticeable, so the doctor can capture more healthy tissue.
There are two main methods of surgical removal. One of them is cutting off the mole without suturing. The doctor uses a scalpel to cut off the growth slightly below the skin level. If bleeding occurs during the procedure, the wound is cauterized and a local antibiotic is applied. A bandage is applied to the affected area and skin care rules are explained. Most often, the surgical area is prohibited from getting wet or subjected to mechanical or ultraviolet influence. Based on the individual characteristics of the patient, the doctor draws up a list of necessary medications, care products and sets a date for the next visit to assess the body’s reaction.
The second method is removal with sutures. Most often, the method is used in the treatment of dark or flat moles. The doctor cleanses the skin, injects an anesthetic, and excises the formation and its surrounding surface.
During the operation, the deep layers of the skin are affected, so suturing is a mandatory procedure.
The healing rate of the area is 7-14 days and depends on the individual characteristics of the patient. The operated area should be cleaned periodically, protected from damage, and ointments or oral medications should be regularly applied.
The main thing is not to self-medicate, but strictly follow the doctor’s instructions. After some time, you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist again. He will evaluate the condition of your skin, possible side effects/complications, and your overall body response to surgery.
The results of using techniques that reduce pain.
After implementing the pain management principles described above in our clinic, I conducted an internal study. 131 people took part in the survey. After the mole was removed, everyone was asked the same question: “How painful was the painkiller injection for you?” There were 3 possible answers:
- It hurts (only 8% of respondents chose this option)
- Sensitive (57% answered)
- Doesn't hurt (35%)
The same results in chart form:
Thus, we can quite reasonably say that the removal of moles, as well as warts and papillomas in our clinic is carried out almost painlessly.
Sign up for deletion
Possible complications and side effects
The main disadvantage of surgical removal is the postoperative scar. It will be noticeable even with a cosmetic stitch, despite the fact that over time the skin will lighten and restore its structure. The surgeon’s task is to make the scar as invisible as possible, so choose a medical institution and doctor responsibly.
There is a risk of developing a keloid scar. This is a tumor-like growth of rough fibrous connective tissue. It is formed in people with a corresponding predisposition. Most often occurs when suturing large wounds.
Another risk is relapse. A repeat process is possible provided that the doctor has partially removed the mole, which is a gross violation of the surgical technique.
Immediately after excision, redness of the skin, itching, and a feeling of discomfort are possible. All these symptoms go away on their own after a few days. If something worries you, be sure to tell your doctor about it.