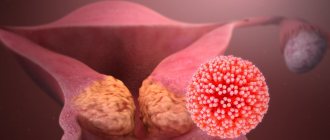
Among all papillomaviruses (and there are more than 100 types of them), human papillomavirus type 16 – HPV 16 – is considered one of the most dangerous.
This pathogen has been proven to have a very high oncogenicity.
That is, the ability to provoke malignant processes in men and women.
A huge problem is the lack of specific symptoms that make it possible to identify HPV 16 infection at an early stage, before cancer forms.
Therefore, the main focus must be on preventing infection.
If papillomas have already appeared, a detailed examination and development of individual tactics for treating the tumor are necessary.
HPV: general characteristics of the pathogen
Among more than 100 types of HPV, the genitals affect about 40.
They differ from each other only in the characteristics of the genetic material, and at the first stages they “work” the same:
- integrate their genome into the nucleus of epithelial cells
- as a result, they begin uncontrolled reproduction
- On the affected areas of the skin and mucous membranes of the genitourinary system, benign (initially) neoplasms appear - papillomas, condylomas
- synthesis of new copies of viruses and their release into the intercellular space is not observed
But then, several years after the first manifestations of HPV, some benign formations transform into malignant processes.
Thanks to the development of molecular techniques, doctors began to detect HPV type 16 DNA in many tumors of the male genitourinary system.
In this regard, the pathogen was classified as a papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk.
It is believed that papillomavirus 16 is responsible for the development of such diseases in men:
- 38% of all penile cancer cases
- 80% of all anal cancer cases
- up to 40% of scrotal cancer cases
The situation is aggravated by the fact that no one knows the exact prevalence of HPV type 16 among the stronger sex.
Prevalence
- 1Hapillomavirus infection is the most common sexually transmitted infection.
- 2Among the sexually active population, more than 50% are infected.
- 3The likelihood of infection with the human papillomavirus increases with the number of sexual partners.
- 4Non-genital skin warts are most common among adolescents, as well as adults working with meat products (incidence rate - 10%).
- 5 Papillomavirus most often affects women: the virus is detected in 22-35% of women and 2-35% of men. The incidence ratio among women and men is 1.4:1.
- 6Oncogenic strains cause about 5% of all cancers in the world.
Routes of infection with HPV 16
It can be argued that the largest number of infected people are in the age group of 17-38 years.
This is due to the characteristics of infection transmission.
Like any other papillomaviruses, HPV 16 is transmitted through direct bodily contact.
For a man, such situations are most typical at the age of puberty:
- Unprotected sex, when the papillomavirus infection is localized in the partner on the vaginal mucosa or on the cervix.
- Bodily caresses – petting, naked.
- Less relevant routes of infection are the use of hygiene items - washcloth, towel.
Adding to pessimism is the fact that epithelial cells of the human body have poor resistance to HPV infection.
Thus, the probability of becoming infected at the first contact is conventionally considered equal to 80%.
So for many men, even one-time sex with an infected partner (or partner) can lead to unpleasant consequences.
Especially if there was damage and microtrauma to the epithelium of the genital organs during contact.
Prevention of infection
- 1Indiscriminateness in sexual behavior (with an increase in the number of sexual partners, and during unprotected sex, the likelihood of infection with the human papillomavirus increases).
- 2 Refusal to have sex during treatment for papillomas/condylomas.
- 3Use of condoms. This contraceptive option does not lead to guaranteed protection, but significantly reduces the likelihood of infection (by 30-60%). A new condom should be used each time; the condom is put on before sex and removed only after it is finished.
- 4Vaccination (Gardasil, Cervarix vaccines) is used in men and women. Currently, vaccines have been developed that prevent infection with certain strains of HPV (all vaccines protect against types 16 and 18, some vaccines immunize the patient against other types of HPV). The vaccine can only be used for prevention and is not used to treat infection. Vaccination is most effective before the onset of sexual activity, the optimal time is 10-12 years.
Video Photo Tables
Clinical manifestations and symptoms
The first signs of HPV type 16 infection in men are nothing special.
The incubation period ranges from 30 days to 2 years, although periodically there are references to 10 years.
Such long periods are most likely associated with the latent course of the infection.
When only 10 years from the moment of infection a man notices that something is wrong with the skin of his genitals or in the groin.
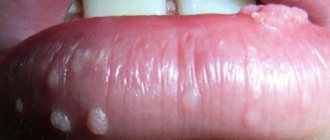
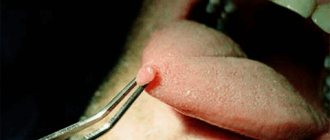
The first visible symptoms, the so-called visual form of HPV infection:
- a small formation appears on the skin of the foreskin, coronary sulcus or on the head - papilloma
- lesions are often single, size – from 1 mm in diameter
- formations are painless
- raised above the surface of surrounding tissues
- color – flesh-colored or reddish
- smooth surface
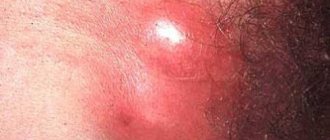
HPV lesions on the scrotum look somewhat different.
There they look more like a typical wart with a hard surface.
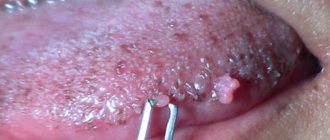
Localization on the mucous membranes leads to the formation of genital warts with their characteristic feature - the appearance of “cauliflower” or “cockscomb”.
Papillomas and condylomas grow slowly, causing virtually no discomfort.
The process can be localized in the meatus or in the scaphoid fossa (the final part of the urethra).
Then urination and ejaculation disorders appear quite early - the papilloma simply blocks the outflow path of urine and sperm.
Over time, the formations grow, their size and number increase.
Given the localization, secondary flora can attach to them, forming a typical inflammation.
The moment when benign symptoms disappear and the tumor becomes malignant is very difficult to notice.
You should pay attention to the following signs:
- the beginning of rapid growth, when the diameter of the lesion increases noticeably within a few weeks
- the appearance of scales and peeling on the initially smooth surface of the papilloma
- formation of ulcers along the diameter of the primary lesion
- bleeding
For HPV type 16, this picture always indicates degeneration into cancer, most often squamous cell with or without keratinization.
If a man ignores the early signs, then after a few months or even weeks the symptoms of a progressive tumor will appear.
The inguinal lymph nodes enlarge, the tissue at the site of the tumor is destroyed, and infection occurs.
Let us repeat: in the early stages, when the formation is benign, not a single visual sign can say that its cause was infection with HPV type 16.
The man needs help before something terrible happens.
So what to do if any tumors appear on the penis - the head, shaft or foreskin, on the scrotum, in the anus or just on the skin of the groin?
You need to contact an experienced and qualified dermatologist or venereologist for further examination.
Where to go for diagnosis and treatment of HPV
The doctor’s specialization depends on the location of warts, papillomas and other formations:
- It is necessary to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist during pregnancy to diagnose dysplastic and underlying diseases of the genital organs.
- If genital warts occur inside the urethra, you need to make an appointment with a urologist, if in the anus - with a coloproctologist.
- You should contact an oncologist and surgeon if you have Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma.
- If the patient has an immunodeficiency or the disease is recurrent, a consultation with an allergist-immunologist is necessary.
Diagnostic measures
Early detection of HPV type 16 infection is only possible using molecular diagnostics.
It allows you to establish unique DNA sequences that are unique to the desired papillomaviruses.
For this, three types of techniques are used:
- non-amplification
- amplification (PCR)
- signal amplification (hybrid trap system - Digene Hybrid Capture System II)
Tests of the first type are not used in practical medicine due to the high cost and complexity of their implementation.
Amplification methods, among which PCR is the most studied, are used quite widely and are well studied.
Allows you to establish the fact of infection with HPV 16.
They detect viruses of other types (it is quite possible to become infected with several representatives of papillomaviruses at the same time).
The real-time PCR technique also determines the DNA concentration of oncogenic viruses.
This indicator has important prognostic value in dynamics.
Initially large numbers at the start of treatment should gradually fall under the influence of special therapy.
And completely disappear after any destructive treatment or surgery.
If the concentration of viral DNA in the diagnostic material is initially low, the doctor may recommend a wait-and-see approach.
Sometimes there is a 20% chance that HPV type 16 with a low DNA concentration will spontaneously clear from the lesion.
Digene (or Daijin test) differs from PCR in its unprecedented accuracy and high speed of testing (within one day).
Daijin also allows you to perform a quantitative analysis (calculate the concentration) of viral DNA.
The only thing holding us back from introducing this technique into widespread clinical practice is the significant cost of research.
To conduct such rather complex and high-tech tests, a man should contact doctors with access to modern laboratory centers.
The use of oncocytology, the most well-known method for diagnosing tumor processes, is justified only for developing treatment tactics for a man.
The method allows you to determine whether the tumor cells have degenerated into a malignant process or whether the papilloma still remains benign.
This information, provided by oncocytological examination of a tissue sample from a suspicious lesion, is decisive for the development of treatment tactics.
An immunogram in its classical concept is of little value for diagnosing HPV type 16 infection in men.
With its help, you can only establish the approximate duration of infection - based on the types of immunoglobulins identified.
IgA and IgM are detected with recent infection, and IgG - when infection is several months old.
Therapeutic measures
Considering the high risk of developing a malignant tumor at the site of HPV 16 infection, all men with a confirmed diagnosis need to be treated.
Regardless of the concentration of pathogens.
Especially if the formation is large enough and/or located in the urethra, it interferes with urination.
The exception is when small concentrations of viral DNA are detected with small papillomas.
This gives a certain chance for independent recovery.
Moreover, it is necessary to ensure regular monitoring of the condition of papilloma.
But even here, according to individual indications, the doctor may still recommend treatment.
There are three general approaches:
- removal of external manifestations of infection - viruses are also removed along with the affected cells
- conservative treatment - the use of various types of drugs and preparations, both local and systemic
- combined approach – a balanced combination of surgical and conservative components
As a rule, the best effect is achieved using the third approach.
Therefore, it is better for a man to immediately assume that he will have to be treated in at least two institutions.
Surgical profile for the stage of papilloma removal and therapeutic profile - to consolidate the achieved results.
It will also be necessary to undergo periodic examinations to ensure the effectiveness of treatment or to detect early signs of relapse.
Everything is done on an outpatient basis, without wasting time and money.
Surgery
Until recently, it was believed that only removal of the affected lesion could guarantee complete elimination of type 16 virus DNA from a man’s body.
In this regard, many different methods have been developed to remove external manifestations of infection - papillomas:
- cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen
- burning with high frequency current
- laser vaporization
- simple excision with a scalpel
Each of these methods has its pros and cons.
But with regard to the treatment of HPV 16, the scalpel remains the most effective.
In addition, if the results of the examination confirm this type of virus, then after removal of the papilloma it is necessary to do an oncocytological study of the excised tissue.
Only traditional surgery can provide such diagnostic material.
Of course, the sooner you seek help, the less removal will be required.
How to get rid of HPV
So far, scientists have not been able to develop HPV treatment that would be aimed specifically at eliminating the papillomavirus infection. Official medical guidelines point to destructive methods of destroying external manifestations of the virus - cryodestruction, radiodestruction, electrocoagulation, laser destruction. If the disease is cyclical, it is necessary to repeat the destruction of genital warts, while simultaneously taking nonspecific antiviral drugs.
Chemical destructive methods involve the use of a 1.5% solution of zinc chloropropionate, a combination of several acids and a copper nitrate trihydrate solution, which is applied to the affected area.
In order to strengthen mucosal immunity, the patient takes immunomodulatory drugs.
Conservative treatment
No medicine can “get” HPV of any type, including 16, inside epithelial cells.
The only thing you can count on is to stop reproducing and infecting new cells.
And already formed foci will allow you to remove any option with destruction or removal of external manifestations of HPV.
The range of available drugs is now quite wide.
According to their mechanism of action, they are divided into several categories:
- Cytotoxic drugs. They are used topically; the main mechanism of action is disruption of cell division, primarily of infected cells, thereby stopping the progression of the infection. Efficiency ranges from 55% to 80%. It is better not to use it for the treatment of HPV on mucous membranes (urethra).
- Chemical destructive techniques. Also means of local action, allowing you to destroy tissues affected by HPV. Destruction of the lesion is achieved in 70-88% of cases. You need to be careful with the mucous membranes, as scars may form.
- Antiviral drugs. They disrupt the synthesis of viral DNA and simultaneously stimulate tissue immunity. They are used both topically in the form of a cream and by injection - into the lesion or area near it. They should be used only as part of a complex regimen, since monotherapy with them is not effective enough.
- Antiviral drugs with systemic immunomodulatory effects. Like the representatives of the previous group, they have a good effect only as part of the regimen and reduce the duration of treatment.
- Antiseptics. Naturally, when applied locally, they destroy the accompanying flora and have a very weak effect on HPV 16 itself.
- Vaccination. Increases the tension of both levels of immunity in relation to HPV, helps to “clean up” the viruses remaining in the skin.
You can achieve maximum effect if you combine these medications and use them in one balanced regimen.
Such prescriptions are usually made by an infectious disease specialist or a qualified dermatologist.
The same doctor determines the duration of treatment, when and what medications to add, and when to stop.
Thus, at the slightest suspicion of the development of a malignant process, immunological drugs must be abandoned until the details of the case are clarified.
The experience of a physician is very important.
Since most medications have a number of side effects.
The most common allergy is to a drug component or one of the excipients.
Particular attention is required for patients with concomitant HIV infection.
Serious immune disorders do not allow relying on an immunogram as a method of assessing the effectiveness of treatment.
Also, absolutely all of these men need antiretroviral therapy.
Otherwise, the progression of HPV 16 will be very difficult to stop.
A well-chosen and balanced treatment regimen allows more than 80% of men to achieve recovery.
If they sought help at a benign stage.
Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment
After removing the lesion from the skin of the penis or scrotum and consolidating the results using a conservative method, the man needs to be observed for some more time by the attending physician.
Repeated tests are carried out over several months to monitor the effectiveness of treatment:
- immunogram, in which the concentrations of specific immunoglobulins should gradually decrease
- PCR or Daijin with calculation of HPV DNA concentration from treated areas of the body
Such control studies, by analogy with gynecological smears, are necessary.
Their task is to confirm complete recovery and eliminate the risk of developing cancer caused by HPV type 16.
Relapse should be expected if high titers of antibodies to the virus remain in the man’s blood.
Even if tests from the skin and mucous membranes turn out to be negative.
The main reason for relapses is the ability of HPV to “retreat” to the cells of the basal layer of the epithelium and epidermis.
If the immune system does not eliminate them there, then after a few months or even years, the papilloma will begin to grow again.
Or an oncological process will develop.
To prevent failures, you need to be very responsible about doctors’ prescriptions during the first course.
And if control tests do not guarantee a complete recovery, then it is better to undergo re-treatment.
Until the moment when the tumor forms and becomes visually diagnosable.
This will serve as an ideal prevention of cancer complications caused by HPV type 16 in men.
Possible complications
The most dangerous complication is the occurrence of cancer.
If measures are not taken to treat cyclic respiratory papillomatosis, a person risks facing serious consequences due to obstruction of the respiratory tract.
Treatment is complicated by the fact that this infection is common in all countries, and its consequences can be serious. Diagnosis and treatment of associated diseases and complications require large financial costs - in terms of “expensiveness”, HPV ranks second after HIV infection.
causes of cervical cancer
If you ignore HPV 16 in men: complications
If a man ignores the initially benign process caused by HPV 16, then very serious consequences are expected.
Oncology – it’s better not to joke with it.
The surface of the papilloma begins to peel off (on the skin) or transforms into an ulcer (on the skin and mucous membranes).
The process begins to actively increase in size.
It spreads to adjacent areas of the penis and scrotum, grows deeper into the organs, and begins to bleed.
Already at this stage, erection, ejaculation, and therefore conception and pregnancy become painful or impossible.
During the first 3-6 months, in 50% of men, regional lymph nodes are affected by metastases.
After 10-12 months, there is an almost 100% guarantee that metastasis will occur in other pelvic organs.
If you respond in time, the initial stages of squamous cell carcinoma can be eliminated with high efficiency.
Only the volume of surgical intervention will be required much more extensive than when removing a benign papilloma.
These are removal of the penis, castration, pelvic lymphadenectomy and others.
Chemotherapy will also be different; you will have to use drugs with very pronounced side reactions.
Naturally, this will require treatment from an oncologist in a surgical hospital.