Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
HPV, also known as human papillomavirus, is not a single virus, but a whole group of them. They are transmitted from person to person (usually sexually) and become the cause of papillomas - benign formations. Some of these viruses are oncogenic, that is, they increase the risk of developing malignant tumors, for example, cervical cancer. But HPV is dangerous not only for women, but also for men, as well as for children.
Development and localization
To begin with, it is important to note that there are more than 600 strains of this virus. That is, there is not one diagnosis, one version of the consequences and one version of the manifestations. There are many different situations involving infection.
If the immune system is strong, it can easily cope with the virus on its own and within a few years “displace” it from the body. But at the same time, re-infection or illness with a different strain is also possible.
Papillomas and other symptoms of HPV in the form of formations that develop as a result of infection can appear in different places:
- on the skin anywhere;
- in the anogenital area;
- in the oral cavity, bronchi and upper respiratory tract;
- in the rectum, etc.
Formations can grow and form entire groups, or they can gradually dry out and disappear - it all depends on the specific situation.
Risk factors
These are conditions that increase the likelihood of contracting human papillomavirus. The following risk factors can be identified:
- 1Early onset of sexual activity, a large number of partners and their frequent change.
- 2 Neglect of barrier contraception (condoms).
- 3 Associated sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes, syphilis, trichomoniasis).
Vitamin deficiencies, other somatic diseases and factors leading to immunodeficiency increase the likelihood of clinical manifestations.
HPV strains
There are strains of the virus that have a high oncogenic potential. They are designated by numbers 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 68, 73 and 82. There are also options with medium (26, 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 53, 58 and 66) and low (6.11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81) oncogenicity. Cervical cancer is most often associated with infection with strains 16 and 18, therefore, when such a virus is detected, maximum monitoring of the patient’s condition is required.
Important clarification! Highly oncogenic viruses detected in the body do not mean that a person will necessarily have cancer. This increases the risk of developing cancer, but is not a 100% determining cause. Moreover, oncology is usually preceded by so-called precancerous conditions. With regular monitoring, doctors have a very high chance of “catching” the disease at an early stage and preventing it from developing into cancer. And cancer itself at the first stage is treated quite successfully. If you have been diagnosed with a virus, do not panic - with proper control, this is not a death sentence for your health and life.
Varieties
Doctors have developed several classifications of the virus that help navigate all its diversity.
To date, more than 100 strains are known, differing from each other in oncogenicity and a number of other indicators.
HPV classification makes the doctor's work easier.
First of all, viruses are divided into groups:
- low risk, provoking pathological tissue degeneration in exceptional cases
- medium risk, which can, under certain circumstances, lead to the development of oncological processes
- high risk, differing ability to cause cancer in a significant number of cases
HPV 18 in men, along with strain 18, poses the greatest oncological danger, causing tumors in 85% of cases.
In addition to the risk of oncogenicity, it is customary to classify the disease based on the severity of symptoms.
There are:
- latent form, characterized by the presence of the virus in the body, but the absence of symptoms of its manifestation
- subclinical form, characterized by vague symptoms
- clinical form with typical symptoms, characterized by the ability to greatly reduce the patient’s quality of life
Most often in medical practice, the latent form of the disease occurs.
Vivid clinical symptoms are in most cases a consequence of an exacerbation of the disease, provoked by external factors.
How the virus is transmitted
To properly prevent human papillomavirus, you need to know the routes of infection. There are several transfer methods:
- sexual. Infection is also possible when using a condom - for example, during unprotected oral sex or during kissing;
- from mother to child;
- in domestic conditions, for example, if a person uses an infected person’s towel, razor or toothbrush;
- in public places such as a swimming pool, gym, bathhouse;
- autoinfection. This means that a person can “spread” the virus to other parts of the body himself.
The first route is most common, because the virus does not survive very well in the external environment.
It is also important to understand that the cause of human papillomavirus is weakened immunity - it is under this condition that infection is most likely. The situation is aggravated if the patient already has an STD, has bad habits, and is constantly under stress. Immunodeficiencies and various injuries to the skin and mucous membranes also contribute to the acquisition of the virus.
Women are most often infected. And strains with a high risk of cancer become more dangerous for them.
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Table of contents
- How is the virus transmitted and how does it manifest?
- Why is HPV infection dangerous?
- Symptoms of HPV in women
- Treatment of different types of HPV in women
- Is it possible to prevent infection?
- Advantages of contacting MEDSI
Human papillomavirus (HPV) today is the most common infection
that affects residents of numerous countries.
The disease affects the mucous membranes and skin. Moreover, the virus can exist in human blood for a long time without detecting itself. Symptoms of HPV in women (as well as in men) appear when immunity decreases.
How is the virus transmitted and how does it manifest?
The disease is transmitted in the following ways:
- Sexual. Genital, oral-genital and anal
- Contact-domestic (by touching, using certain objects, etc.)
- During childbirth (child from mother)
A person infected with the virus suffers primarily from aesthetic problems. Unsightly growths form on his skin and can grow. Moreover, after removal the risk of relapse is very high.
Why is HPV infection dangerous?
Today, cervical cancer (CC) still ranks second in the world among female cancer pathologies, with more than 270 thousand women dying from this serious disease every year.
However, the disease can be prevented. It has been convincingly proven that one of the conditions for the development of cervical cancer is the presence of the human papilloma virus. Today, about 150 types of this virus are known and about 34 of them are associated with lesions of the anogenital area. Types 16, 18, 31, 33 and 39 are highly oncogenic. They can trigger the development of cancer of the cervix, vagina, penis and anus.
Symptoms of HPV in women
The disease in women usually manifests itself by the appearance of the following neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes:
External signs of pathology are often absent for a long time, so the patient does not suspect that she is at risk
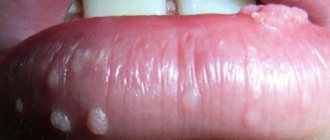
- Genital warts.
Such formations are among the most dangerous and appear mainly in the genital area. Condylomas are characterized by a flesh-colored or pale pink color and the shape of the papilla. Over time, such formations can degenerate into malignant tumors. - Flat warts.
Such neoplasms are benign and relatively safe. They do not cause cancer, but are contagious and are transmitted from person to person even by simple contact. Typically, flat warts grow on the face, legs and hands, are round in shape and small in size (up to 5 mm) - Bowenoid papulosis.
These formations appear on the genitals and in the perineal area, are quite dense, have a yellow or pink tint and the shape of plaques that rise slightly above the skin and mucous membranes
Also, human papillomavirus in women can manifest itself in the form of dysplasia. The epithelial cells of the cervix are affected by pathology. When HPV is present, they begin to change rapidly, causing a precancerous condition. With early diagnosis, the patient can be cured! In advanced cases, cancer occurs.
Important! External signs of pathology are often absent for a long time, so the patient does not even suspect that she is at risk!
Treatment of different types of HPV in women
Important! Widely advertised immunostimulants are ineffective in treating the virus. They have not passed the necessary tests and are not included in the protocols.
There are currently no effective treatments for the virus. You can only eliminate those pathological conditions that are provoked by HPV: remove papillomas and other formations on the skin and mucous membranes, treat dysplasia and cancer.
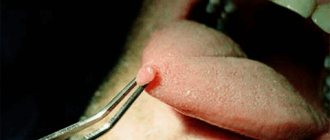
Today, neoplasms are successfully removed using radioknife, laser, cryocoagulation, etc. The procedure is carried out quite quickly and does not cause significant discomfort to the patient. After removal there are no large scars left. Surgical excision may also be performed.
The method of removing formations is selected individually. In this case, the doctor focuses on the patient’s characteristics, the size and location of the papilloma or other growth, as well as concomitant pathologies and existing indications and contraindications.
In MEDSI clinics, tumor removal is carried out using techniques such as:
- Electrocoagulation.
The formation is destroyed due to the effect of high-frequency current on it. A small wound usually heals quickly without leaving a scar. - Laser exposure.
This procedure allows you to quickly “burn out” the formation without leaving any traces. The intervention takes a couple of minutes and is suitable for removing warts and papillomas on open areas of the body (including the face) - Cryodestruction.
This technique involves exposing the formation to cooled nitrogen. Warts and papillomas are destroyed by very low temperatures and are independently rejected by the body - Radiosurgery.
To carry out the procedure, a modern instrument is used - a radio knife. It is capable of heating tissue in a non-contact mode and ensuring the evaporation of pathological cells. Radiosurgery, like laser surgery, is used to remove growths on open areas of the body - Chemical destruction.
During such interventions, acids and other drugs are used. They locally affect formations, violating their integrity - Surgical excision.
This technique is relevant for large or deeply sprouted formations. Due to the fact that the surgeon works manually, he can quickly remove the formation and send pieces of tissue for examination (to determine whether they are benign or malignant)
Important! If a woman has no complaints and no papillomas or dangerous changes are detected as a result of exposure to the papilloma virus on the body, treatment is not carried out! In this case, the patient should undergo regular examinations (PAP test and colposcopy).
Is it possible to prevent infection?
Yes! The high incidence rate has provoked the interest of scientists in the development of not only therapeutic, but also preventive measures. A real breakthrough was the creation and introduction of vaccines into world practice.
HPV vaccination in women and men: what is it and what vaccines are there?
Vaccination is a preventive measure! It protects against infection and helps prevent the risks of health and life-threatening consequences of the virus.
Today, 2 drugs are registered in Russia - Gardasil and Cervarix! Both vaccines are effective and safe. They have undergone extensive clinical trials and have proven almost 100% effective in preventing diseases associated with HPV (including cervical cancer pathologies).
A real breakthrough was the creation and introduction of vaccines into world practice.
However, it is better to use Gardasil. This is due to the fact that such a vaccine acts against 4 types of virus. It protects against cervical cancer, vulvar, vaginal, anal cancer, anogenital condylomas, cervical, anal, vulvar and vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ.
"Gardasil" can be used:
- Girls and women from 9 to 45 years old
- Boys and men from 9 to 26 years old
Vaccination involves the administration of 3 doses of the drug and is carried out according to the schedule: 0‑2‑6 months.
It can be prescribed even to previously unvaccinated people who have been diagnosed with the virus. This is due to the fact that the patient may not be infected with all types of HPV!
Important! Vaccination does not replace the need for screening tests and regular examinations by a gynecologist.
Today, Gardasil is included in the compulsory vaccination schedule in many European countries and the USA. Some countries have already proven effective reductions in morbidity rates.
Important data on reducing the incidence of cervical cancer among those vaccinated were obtained in Australia, where, from 2007 to 2016, 78% of 15-year-old girls and 72% of boys of the same age were vaccinated in this way. As a result, the prevalence of HPV among women 18–24 years of age decreased from 22.7% to 1.1% from 2005 to 2015, and the incidence of precancerous cervical lesions in the population of girls under 18 years of age decreased by 38%.
Advantages of contacting MEDSI
- Experienced specialists.
Our doctors are always ready to provide comprehensive medical support to all categories of patients. They will not only advise you, but will also carry out diagnosis, treatment (including the consequences of HPV in women) and prevention of various pathologies, if necessary. - Opportunities for effective diagnosis of HPV.
In our laboratory, you can take tests to detect the presence of oncogenic HPV serotypes (categories) in the body. This examination is especially relevant when immunizing patients over 25 years of age. - Possibilities for removing tumors.
We use classic and modern technologies. This allows you to choose the appropriate option for each patient. - Timely vaccination.
The drug for vaccination is always available. By contacting us, you will not be forced to delay vaccination. It is possible on the day of application - Using a modern, highly effective drug.
The safety and effectiveness of Gardasil have been confirmed by international clinical trials, which were conducted with the participation of a large number of study subjects.
Our doctors are always ready to provide comprehensive medical support to all categories of patients.
If you are planning to visit our clinic for the purpose of vaccination against HPV, examination for this virus, or treatment of precancerous conditions and cancer, call (495) 7-800-500. Our specialist will answer all questions and make an appointment for you at a convenient time.
Signs
If HPV does not manifest itself in formations (warts, papillomas and condylomas), then without special tests the patient usually does not know that he is infected. In this case, the symptoms of the human papillomavirus are precisely the neoplasms - they can be accompanied by itching and discomfort.
If formations appear in the genital area, they can also manifest as painful and unpleasant sensations during or after sexual intercourse.
Are you experiencing symptoms of human papillomavirus?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
How does HPV infection occur?
Papillomaviruses can only be transmitted from person to person.
Since some types can persist for a certain time in exfoliating skin cells, they may pose a risk of household contact infection.
This option is typical for the non-oncogenic group; for example, infection with the formation of plantar warts is likely in the presence of microdamages to the skin of the feet.
Low- and high-oncogenic viruses are transmitted sexually, including various types of sexual contact.
Infection of newborn children by sick mothers occurs occasionally.
Interestingly, women with diabetes, when their glucose levels are well controlled, do not have an increased risk of HPV infection.
The incubation period is quite long and can vary from three months to several years.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus includes a doctor’s examination, enzyme-linked immunosorbent test, PCR diagnostics, as well as special tests to determine the oncogenicity of the strain. Women undergo a Pap test, that is, a cytological examination, for which a smear is taken from the vagina. A colposcopy is required - a thorough examination of the cervix using a special device.
Why is papillomavirus dangerous?
The potential threat in viruses of this type is primarily the risk of growth of tumors of the urinary tract and genitals.
Slightly less commonly, viruses are responsible for tumor growth in the oropharynx area.
The long-term existence of the virus in epithelial cells sooner or later changes their structure and ability to divide uncontrolledly.
Any episode of infection should be diagnosed, monitored and, if possible, treated.
Errors in immune defense can occur at any stage of life.
In addition to external provoking factors, they can be caused by natural hormonal fluctuations.
Therefore, today there is an urgent question about creating artificial protection against papillomaviruses by vaccinating high-risk groups or children.
Treatment
Treatment of HPV does not imply the presence of any specific program that would completely destroy the pathogen. But patients are prescribed therapy that helps strengthen the immune system and self-heal. The assignments come down to several points:
- taking special medications. These are vitamins, antiviral medications and immunomodulators;
- removal of tumors. For this purpose, cryodestruction, laser, and electrocoagulation are used. Removal is possible using the classical surgical method;
- all kinds of strengthening of the immune system. A healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, giving up promiscuity - all this helps maintain immunity.
There are now vaccines for some types of HPV that are optimally used at 11-12 years of age (but can be used up to 26 years of age). Patients over 12 years of age are prescribed the vaccine if the doctor sees indications for this. The vaccine is not able to destroy the virus, but it can protect against other dangerous strains.
What are the consequences of HPV during pregnancy?
To date, there is no reliable evidence of a pronounced negative impact of infection on the course of pregnancy.
Pregnancy pathologies such as miscarriage, premature birth, etc., which are characteristic of other sexually transmitted infections, have not found unconditional confirmation of the connection with HPV.
However, if a woman’s primary infection occurs during pregnancy, there is a risk of developing various complications.
Anogenital warts in the mother caused by HPV types 6 and 11, localized in the area of the labia minora and the vestibule of the vagina, have some consequences for the fetus during pregnancy.
Such genital warts carry a small risk of infection of the fetus during childbirth, leading to the development of respiratory papillomatosis in the latter.
Respiratory, or otherwise laryngeal, papillomatosis (also called laryngeal papillomatosis) most often develops in children 2 to 3 years old.
As a result of infection from a sick mother during the latter’s pregnancy or immediately at birth.
The route of transmission during pregnancy through the placenta, during childbirth or immediately after it is not yet entirely clear.
The main symptoms of the disease are hoarseness, up to the complete disappearance of the voice, and difficulty swallowing.
As the disease progresses, shortness of breath and cough appear.
In severe situations, blockage of the upper respiratory tract and asphyxia are possible, especially in the case of formations with a long thin stalk.
During examination using a laryngoscope (sometimes a bronchoscope is also used), typical growths - condylomas - are found on the laryngeal mucosa.
This pathology has a rather aggressive course: after removal of the formations, relapses often occur, requiring repeated surgical interventions.
If pregnancy occurs due to infection with highly oncogenic papillomaviruses (especially HPV 16, 18), the woman must inform her obstetrician-gynecologist about the presence of infection.
The fact is that changes in a pregnant woman’s body can provoke more intense cell transformation.
Actually, such viruses do not affect the course of pregnancy itself or the child, but they pose a certain threat to the woman’s health.
In a situation where no infection was detected in the past, a cytological Papanicolaou smear (Pap test) is taken, among others, when registering.
If the analysis shows abnormalities, the doctor prescribes additional tests (for example, colposcopy).
Also, situations when pregnancy occurs in women with erosion require special attention.
PCR diagnostics are required to exclude infection with high-oncogenic risk HPV.
As a rule, in the routine practice of an obstetrician-gynecologist, such a combination as HPV and pregnancy is not specifically examined.
Tests for the virus are recommended only if pathological abnormalities are detected.
At the same time, there are research studies demonstrating the effect of the virus on pregnancy.
Thus, it has been shown that infection of women with HPV slightly reduces the likelihood of embryo implantation, and in men it reduces sperm motility.
And since in a married couple, as a rule, both partners are infected, the onset of pregnancy is associated with some difficulties.
As a result, when planning a pregnancy against the background of an infection caused by HPV, planning an IVF procedure, this factor should also be taken into account.
Questions and answers
How to get rid of the human papillomavirus forever?
It is impossible to get rid of it 100% using certain medical programs. But the virus can disappear from the body on its own, which does not eliminate the risk of re-infection.
How dangerous is the human papillomavirus?
The human papillomavirus is dangerous because some of its strains contribute to the development of cancer - in particular, cervical cancer.
If a virus is detected, will there definitely be cancer?
No, there is no absolute dependence in this case. We are talking about increasing risks, but this does not mean that cancer will definitely develop - people who have been diagnosed with the virus need to undergo regular examinations with doctors, and then the probable disease
Can an HPV infection be cured?
There are currently no treatments that specifically target HPV. Papillomas and condylomas, as well as precancerous changes caused by HPV, can be removed surgically, using a laser, or cryosurgery. When the cervix is affected, loop electrosurgical excision (removal of a pathological formation using a wire loop heated by an electric current) and conization (removal of a cone-shaped section of cervical tissue) are used. However, it is important to understand that surgery cannot remove the virus from the body.
How is HPV infection treated during pregnancy?
When infected with HPV, pregnancy and childbirth have some specifics.
Thus, in some women with HPV infection, during pregnancy, the manifestations of the disease may increase, such as changes in cervical cells and genital warts.
However, doctors are usually in no hurry to prescribe treatment.
Since the latter can provoke premature birth, in addition, after childbirth, the manifestations of infection may noticeably decrease on their own.
Therefore, it is recommended, if possible, to adhere to expectant management and dynamic monitoring of the pregnant woman.
However, there are situations when genital warts grow noticeably and their number increases.
They merge into giant formations.
Women may experience pain when walking, difficulty defecating and urinating.
During childbirth - traumatization of formations, bleeding, problems with the passage of the fetus through the birth canal, ruptures of the vaginal walls.
In such cases, it is necessary to remove condylomas before delivery.
If the removal of the formations could not be carried out on time, the doctor may decide to deliver the patient by cesarean section.
In routine practice, this measure is not used to prevent fetal infection.
Since there is no reliable data confirming that cesarean section prevents the development of respiratory papillomatosis in children of sick mothers.
If abnormal cell changes were detected during pregnancy, a Pap smear test should be repeated a few weeks after birth.
Often, after childbirth, both genital warts and cellular changes disappear on their own.
Accordingly, treatment of such conditions is not required.
In other situations, certain therapeutic procedures are carried out.
In pregnant women, removal of condylomas can be carried out through cryotherapy, using a carbon dioxide laser, electrocoagulation, or surgitron.
For large, easily traumatic formations, it is recommended to remove them surgically after the first trimester until the 36th week of pregnancy.
The use of drugs such as podophyllin, 5-fluorouracil, as well as the use of intralesional interferon is not allowed during pregnancy.