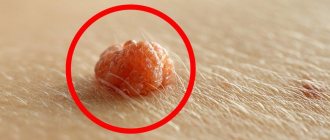
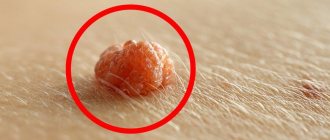
Papule
- a skin growth resembling a nodule that can occur in various parts of the body. Papules are growths of small size and round shape. They cause physical and mental discomfort in patients, since they are difficult to hide even under makeup.
The causes of the appearance of papules are hormonal disorders, especially those associated with age, dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, disruptions in metabolic processes under the influence of poor nutrition, excessive physical activity and stressful situations. Often the appearance of papules indicates the presence of infections in the body, allergic reactions, dermatitis and is regarded as one of the symptoms of an infectious disease.
How papules and pustules appear
The mechanism of pimple formation is very simple. Due to the increased secretion of sebum - sebum - the sebaceous gland duct is blocked. A sebaceous plug is formed, that is, a comedon; they can be open or closed. But if such a comedon is affected by the bacteria P. Acnes, then inflammation occurs; over time, the purulent contents break into the skin, spread, which leads to the formation of other papules, and with more severe inflammation, purulent pustules appear.
There are many reasons for such activity of the sebaceous glands, the most common being hormonal changes during puberty. Nutrition, stress, hygiene habits, and lifestyle also play a role.
Acne
Acne is a disease in which papules, pustules, and comedones appear on the face and body (several follicles are affected at once). The inflammation is widespread, often the pimples are painful to touch, and as soon as one goes away, others appear. If a person has only comedones - white and blackheads, then we are talking about a non-inflammatory type of acne. And if there are papules and pustules, cysts, this is an inflammatory type. Pustules on the face should not be pressed, this will only worsen the situation; the contents may not break out, but subcutaneously.
It is worth saying that papules and pustules can appear not only as part of acne, for example, papular dermatosis with sterile papules is sometimes found, that is, P. Acnes is not detected in them, but acne is still the most common cause. Papular rashes also occur with psoriasis.
Symptoms
Structurally, the nodules are bandless formations of various colors. They can be red, gray, brown. Some papules have a noticeable bubble on the surface; they are called serous. Red formations are usually inflammatory in nature.
The size of a single growth can vary: from the head of a pin to the size of a nail. Large papules are called plaques.
In addition to the external defect, papules can cause physical discomfort, causing itching, inflammation, burning sensation and irritation of the skin. When pressed, the formations turn pale.
The appearance of unpleasant growths on the skin always makes you want to get rid of them as quickly as possible. But not all patients seek help from a doctor, and many self-medicate. Such therapy not only does not eliminate the defect in appearance, but can serve as a favorable condition for the further spread of infection.
In addition, papules can be symptoms of serious diseases that require immediate treatment.
How to treat papules and pustules
Now that we have found out what papules and pustules are, the question arises whether they need to be treated. In this case, everything depends on their number and frequency of occurrence. If they are isolated and rarely appear on the face and body, for example, due to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, then there is no need to worry. You can simply choose suitable care cosmetics from a cosmetologist and cleanse your face efficiently. But if there are a lot of rashes, they can merge together and form spots; papules and pustules should be treated by a dermatologist.
Treatment of acne, papules and pustules is complex.
Lifestyle adjustments and adherence to doctor's recommendations are required. A non-hormonal ointment is used as a local remedy, which does not cause withdrawal effects in the future. Before treatment, the doctor will prescribe tests for hormones, the content of certain vitamins and a general blood test. This way you can choose an individual treatment plan. June 23, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Skin rash is the most common reason for visiting dermatologists. In this article we will consider in detail papular rashes, their characteristics and diseases accompanied by the morphological element of the skin - papule
Papula is a morphological element of skin rashes, which is a cavity-free formation, dense or soft on palpation, rising above the skin level. Nodules are the primary elements of the rash, appearing on unchanged skin, and in some cases can transform into vesicles, pustules, plaques and be combined with other changes in the skin.
Classification of papules
- by element size:
– miliary – have the shape of a cone. Small-sized miliary papules (1–2 mm in diameter, about the size of a millet grain);
– lenticular – have a flat, round shape. Their size is 5–10 mm, about the size of a lentil;
– nummular – large elements. They can reach the size of a coin, up to 2 cm. They arise as a result of the fusion of small papules or form independently. More than 20 mm – plaques.
- by placement depth:
– superficial – flat papules no more than 5 mm in size. They are pink or red in color. They arise due to disruption of the functionality of the upper layer of the epidermis. Do not cause pain; – deep – appear between the layers of skin of the epidermis and dermis. May have a reddish or bluish tint. When pressing on such a papule, an unpleasant, painful sensation is felt.
- according to the nature of the manifestation:
– inflammatory papules arise as a result of local vasodilation, immigration of immune system cells caused by the release of inflammatory inducers, for example, in psoriasis, syphilis. In this case, the papules usually have a pink or red color due to vasodilation. Papules have a uniform size in secondary syphilis, lichen planus, amyloidosis, and mucinosis. With psoriasis, on the contrary, they are always of different sizes;
– non-inflammatory papules occur due to excessive proliferation of epidermal or dermal cells. For example, flat warts. In this case, the papules are pale in color. In some cases, the rash regressions without a trace, but there is a possibility of transition to a secondary element of the skin - spots, erythema.
Molluscum contagiosum is characterized by the appearance of small formations similar to nodules.
Papular rash etiology and pathogenesis
Papular rash occurs as a result of certain diseases, being a sign of serious chronic dermatosis. It can be of bacterial, viral, parasitic or infectious etiology, as well as of an allergic nature (to certain irritants) and be a consequence of immunological reactions. In the case of allergic genesis, the provoking factor is contact with allergens, which can be various foods, medications, household chemicals, plant pollen, animal excretions and even ordinary house dust.
In case of liver disorders, papular rashes are accompanied by a yellow tint of the skin, vomiting, nausea, stool disturbances, a bitter taste in the mouth, sudden weight loss, changes in the color of the tongue, the appearance of small cracks on it, and an increase in temperature.
Papular rashes distributed throughout the body most often indicate an infectious pathology. Dermatological elements in the form of papules occur in diseases of a viral nature in children and adults: measles, rubella, enterovirus infection, chicken pox, molluscum contagiosum. Papules of infectious origin represent only one of the stages in the development of morphological types of diseases. Such a skin reaction can be caused by many different factors, but more often it is an independent disease. And it is usually accompanied by fever, chills, loss of appetite, indigestion, pain in the throat and abdomen, as well as headaches.
Chickenpox begins with rashes on the scalp, which cover the entire skin in a few hours, and looks like many small papules and blisters filled with liquid. Rubella appears as a mild rash on the face and neck area, after which it spreads throughout the body within a few hours. Such rashes look like round redness with a diameter of up to 10 mm. Measles, as a rule, begins catarrhally, the rash affects the skin only a few days after the onset of the disease and in the first hours - on the face, and then spreads to the skin of the arms and chest.
With molluscum contagiosum in children, small flesh-colored nodules with an umbilical depression in the center of the element are initially observed; they appear on the skin of the face, limbs or torso, and in adults, more often on the genitals, buttocks, lower abdomen, and thighs. When squeezed out, a curd-like mass emerges from the elements.
With molluscum contagiosum in children, small flesh-colored nodules with an umbilical depression in the center of the element are initially observed; they appear on the skin of the face, limbs or torso, and in adults, more often on the genitals, buttocks, lower abdomen, and thighs. When squeezed out, a curd-like mass emerges from the elements.
Urticaria and angioedema in children
Atopic dermatitis: causes, diagnosis, treatment
Allergic toxicoderma caused by the drug sulfadimezin:
erythema - papular rashes on the skin of the chest, abdomen and upper extremities.
A herpetic rash is characterized by the formation of small blisters and papules on the face, especially on the lips.
Scabies manifests itself in the form of vesicles or papules with noticeable scabies in the form of whitish lines, and is characterized by severe itching in the area of the rash, which intensifies at night. The favorite localization of the tick is the interdigital spaces, the anterior surface of the wrist joint, the extensor side of the forearms and elbows, the lateral parts of the body, the umbilical area, buttocks, thighs, and genitals.
Arthropod bites can also cause a papular rash. Papules are found in secondary and recurrent syphilis, psoriasis, lichen planus and its many varieties, lichenoid parapsoriasis, papular form of lichen rosea, amyloid lichen, limited neurodermatitis of the Vidal type, Fox-Fordyce disease, Devergie lichen planus pilaris, papular urticaria, etc. d.
Elements of papules characteristic of lichen planus - a chronic disease of toxic-allergic origin: flat pink-violet papules with a shiny flaky surface and polygonal outlines with a tendency to merge into plaques appear on the skin and mucous membranes, most often localized on the forearms and shins (flexor and extensor surfaces, respectively), thighs, inguinal and axillary areas. After the rash disappears, persistent pigmentation remains in its place. The most common subjective sensation is itching, sometimes very intense. Lichen linearis is a skin pathology of unknown etiology, with a papular rash in the form of narrow stripes on the limbs and torso, which correspond to the location of the nerve trunks.
Papules of secondary recurrent syphilis are most often expressed in lenticular rashes - round, hemispherical, densely elastic, copper-red in color, with a flaky surface. The syphilitic rash is bright, symmetrical and profuse. It is located on various parts of the body, but most often in the genital area, on the palms and soles, and face. When pressing on the center of the nodule, sharp pain occurs. There are several types of papular syphilides: coin-shaped, psoriasiform, seborrheic, condylomas lata.
Papular rash due to HIV infection.
The papular rash in HIV infection is small in size, hemispherical in shape, normal skin color, dense consistency without a tendency to merge and is localized on the head, neck, torso, and limbs in quantities from several units to several hundred.
Thus, the spectrum of probable pathology of papular rashes is very diverse. Papules (nodules) also appear with parasitic infestations (scabies, demodicosis), allergic reactions, dermatoses (lichen planus, psoriasis), autoimmune process (vasculitis, lupus erythematosus), venereal diseases (syphilis). And accordingly, each case of papules is considered individually with differential diagnosis and, depending on the provoking factor that caused the appearance of the rashes, as well as the location of their localization, an examination is prescribed.
The examination includes: general blood test; analysis for RW (Wassermann reaction); serological tests (RIF, ELISA, RPGA); microscopy of scrapings; allergy tests; histological examination (in difficult cases, a biopsy of the affected areas of the skin is performed with their further histological examination, since most types of dermatoses are quite difficult to diagnose and differentiate).
Based on the results of a comprehensive examination, a diagnosis is made and therapy is prescribed, aimed primarily at eliminating the cause of the rash and treating the underlying disease.
Sania Ospanova, dermatovenerologist, dermatocosmetologist, Ph.D. ,
Elena Lipatova, dermatovenereologist, dermatocosmetologist, RSE at the PCV “Kazakh Scientific Center of Dermatology and Infectious Diseases” of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Almaty