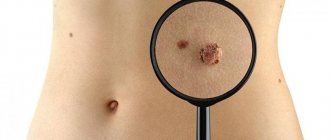
Melanoma is a malignant disease that affects the pigment cells of the skin - melanocytes. Studies have shown that the incidence of skin cancer has been steadily increasing in recent years. Among many types of skin cancer, melanoma causes changes in pigment cells. Although the disease is mainly observed on the skin, the painful process can also affect the mucous membranes, or, for example, the eyeball.
Cause of melanoma
The content of the article
The causes of melanoma can be different. Scientists include genetic and environmental factors among them. It is estimated that up to 10% of cases of the disease are associated with genetic complications. It is therefore recommended that the next of kin (for first degree relatives) of the patient undergo dermatological consultation and monitoring.
Environmental factors are also of great importance, among which sunbathing and associated skin burns stand out first.
Skin burn from sunbathing
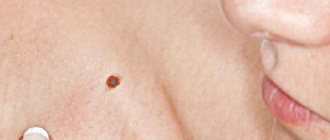
Melanocytic changes can also cause melanoma. They usually appear on the skin as small nevi. They can be congenital or acquired. However, assessing the change, whether it is just a harmless mole or cancer, is based on additional diagnostic tests.
Almost everyone is at risk of developing this disease because we are exposed to sunlight every day, which is a very important factor in the development of melanoma. Therefore, it is very important to regularly examine moles yourself and have an annual examination with a dermatologist. A timely removed mole will save you from painful procedures and difficult operations.
Melanoma symptoms
Symptoms of melanoma include new-onset skin lesions or those that arise from a pre-existing pigmented nevus (mole):
- It is often observed that in the immediate vicinity of these lesions thickenings form, changes in the existing surface, color and changes at the edges of the mole.
- You should also be concerned about sudden itching or the appearance of bleeding or bloody discharge.
- An inflammatory reaction associated with a mole is also a warning sign of melanoma.
- One symptom to look out for is blue and black moles. The occurrence of this type of pigmentation should be resolved as soon as possible by consulting a doctor.
For early diagnosis of melanoma, monitoring changes in moles, carried out by the patient individually, is of great importance.
If there have always been pigment changes on the skin, the following should alert you:
- sudden itching;
- bleeding;
- increase in lesion;
- changes in the structure of the mole.
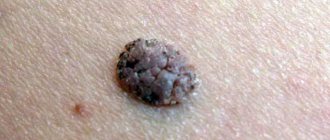
Particularly noteworthy is the fact of uneven pigmentation, which contains various shades of brown and pink. It is also worth paying attention to the new changes.
How to recognize melanoma?
To diagnose melanoma, it is necessary to carry out very extensive diagnostics. Of course, the basis is the medical interview conducted during the first visit. The information obtained from the patient concerns mainly information about the condition of the skin, with particular emphasis on changes in moles on the skin or the appearance of new ones.
Information regarding factors that have been identified as increasing the risk of melanoma is also very important to the dermatologist. This group usually includes sunburn or the use of tanning beds. It is also very important for the doctor whether there have been cases of skin melanoma in the patient’s family.
An in-depth interview is the basis for further action. The most important element of diagnosis is the skin examination, which the dermatologist performs during the visit.
Bad Signs
Rapid growth of a mole
What does "fast" mean? Which one is slow then? Without answers to these questions, almost any mole on the body can be safely classified as melanoma, because almost every one of them increases by a couple of millimeters over the course of a lifetime.
By fast, I mean an increase in the size of a mole faster than 1-2 mm per year. This is a very conditional border, because There are melanomas that grow more slowly, however, in my opinion, most of these tumors will show a growth rate that exceeds this value.
Color change
The production of pigment by the cells of a benign mole can normally lead to its darkening. On the other hand, proliferation of melanoma cells can also occur. How to distinguish one from the other? In my opinion, there are 2 ways.
The first is the speed at which the color change occurs. A benign mole has the right to darken a little over the course of several years.
The second is melanoma, unlike the latter, it will most likely have more than 2 colors, for example, light brown, black, red, white.
3.Change shape
There are a huge number of irregularly shaped moles, but only a very small proportion of them will turn out to be melanoma. Irregular shape usually means asymmetry along 2 axes in combination with an edge in the form of a “coastline on a map.”
I would not like to dwell in more detail on the bad signs. Everyone who could has already written about them. Today we will dwell in more detail on what types of
Dermatoscopy
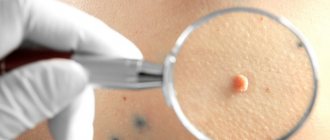
Dermatoscopy is an examination in which a dermatologist uses a dermatoscope. This is an instrument that combines a magnifying glass 10 or 20 times, magnifying the fragment under study, equipped with a standardized light source. In such conditions, the doctor may initially assess skin changes.
Dermatoscopy
Videodermatoscopy is a study that, in addition to the techniques used in dermatoscopy, uses visualization on a computer monitor. This allows the clinician to store the displayed image in the device's memory, which can be useful for comparative purposes at a later stage in treatment. In practice, several dermoscopic methods are used to diagnose melanoma.
The doctor, based on the appearance of the lesion, will evaluate whether there is a reason to remove it along with a margin of healthy skin, and send the material after the procedure for histopathological examination.
The specialist studies the characteristic features of the mole, in particular:
- Color—uneven color, darker and lighter areas, or pink and red areas are abnormal;
- Ragged edges - moles with smooth edges are less dangerous to health;
- Asymmetrical shape;
- Size greater than 5 mm - smaller lesions are usually not a cause for concern, but if they are growing dynamically or show other abnormalities, they need to be removed;
- Bleeding, ulceration, presence of discharge.
Diagnosis that confirms or excludes a skin neoplasm, which is melanoma, is possible on the basis of a histopathological examination, which is carried out after removal of the entire lesion.
Types of melanoma
Skin lesions diagnosed as melanoma do not always look the same. Thus, there are several types of melanomas, which define different clinical subtypes of the disease.
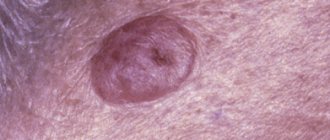
- Superficial melanoma
. It is indicated that the most common type of melanoma, which accounts for up to 60-70% of all cases of the disease, is superficial melanoma. This group of melanomas is most often based on pigmented lesions of a dysplastic nature. - Nodular melanoma
. Indicated as the most severe form of the disease, affecting 10-30% of patients. This group, in turn, includes two clinical subtypes. The first is lentiginous melanoma, which is a malignant form. Occurs in 5-15% of cases. It most often affects older people, especially in the neck or face. Lentiginous melanoma is caused by prolonged and prolonged exposure of the skin to sunlight. The second subtype is acral melanoma, which is observed on the inner surface of the skin of the arms and legs. - Colorless melanoma
. The disease also includes pigmented melanoma. Only 2% of patients suffer from it. This is a characteristic type of skin lesion in which pigment is absent. In this case, the symptoms are also quite specific, and the not very characteristic but enlarging pink-red papule should be of concern.
Superficial melanoma
Nodular melanoma
You should also pay attention to the so-called Spitz moles, which are a juvenile form of melanoma. Most often, scientists indicate that this is an active nevus, usually single, and occurs in young people.
The surface of a Spitz mole is very well demarcated from the surrounding area and has a smooth, red or bluish color. Most often it occurs on the face. When observing the lesion, there is no inflammatory reaction. Spitz nevi rarely become cancerous, although it is recommended to remove them before puberty.
Why does a mole hurt?
There are several main reasons why a mole hurts.
Most often, pain occurs as a result of injury.
This is also accompanied by minor bleeding, swelling and hyperemia of the surrounding soft tissue.
If the mole hurts and itches, and new nevi appear, hormonal changes are suspected.
This occurs more often in women during pregnancy.
Painful moles are caused by the following reasons:
- Injuries - a hanging mole in particular often hurts, which can easily be touched by clothing, a washcloth or jewelry, depending on its location. But other types of moles can also be injured, sometimes this happens in beauty salons when performing intense massage, using anti-cellulite cups, or performing depilation. More often, nevi located in the armpits, pubis, collar area, and on the folds of the lower and upper extremities are injured. Often the cause of pain is an injury to a mole while using a razor. Any damage to a benign formation should not be ignored, since even minor scratching can provoke malignancy, which poses a direct threat to human life.
- Increase in size - the cause of such changes is often hormonal changes, but sometimes the mole grows and hurts when the process becomes malignant.
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or staying in a solarium leads to burns. In this case, the mole hurts and may itch, but after 3-5 days the discomfort goes away on its own. If after being under the hot sun the pain does not disappear for 7 or more days, you should see a doctor and undergo an examination, the process of malignancy (malignancy) may have begun.
- Inflammatory processes - most often occur when a mole is damaged and infection enters, which causes hyperemia, pain and even swelling.
- Thermal burn of the skin - exposure to hot steam or liquid, fire, high temperatures causes burns of varying degrees of severity, the most sensitive areas are moles and age spots, where increased pain is felt.
- Hypothermia or overheating of the body - with any deviations in body temperature from the norm increases the sensitivity of the skin. Not only existing nevi can hurt, but also the site of a mole removed in the recent past.
Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor
Melanoma is one of the types of malignant skin tumors. The test that confirms or excludes the diagnosis is a biopsy, which confirms the diagnosis based on microscopic examination. The results of the performed biopsy provide information about factors that have a significant impact on the prognosis of the patient's treatment. This information allows you to determine the further course of the treatment process.
Melanoma biopsy
Examination of removed tumors for malignancy is carried out on the basis of macro- and microscopic examination. Among the factors that play a significant role in assessing the patient's health prognosis, primary outbreaks are of great importance. If there are no metastases in the progression of the disease, the change in thickness (Breslow scale) and the presence of ulcers observed in the primary lesion are assessed.
Due to the fact that melanoma is classified as a malignant neoplasm, some patients experience metastases to other organs. Therefore, during diagnosis and treatment, the surrounding lymph nodes are also checked.
Briefly about the main thing:
You should not try to make a diagnosis yourself; this should still be done by an oncologist. On the other hand, it’s also not worth making a mountain out of nothing out of the blue.
If your mole does not have a single “bad” sign, but has several good ones, you should still see an oncologist. Calmly, without haste and fuss, as time permits.
The main point of this article is not for you to be able to understand for yourself whether a mole is malignant or not. My goal is to help you not go crazy because of the horror stories you have previously read on the Internet.
If doubts still overcome you, you can ask me any question in the format of an online consultation.
When is melanoma dangerous?
Metastasis always occurs when the cancer process is far advanced and cancer cells damage subsequent internal organs of a person. First, stage III is indicated when regional lymph node metastases are diagnosed. To treat melanoma, it is important how many lymph nodes are affected by cancer cells.
It is indicated that a much more serious disease is the occurrence of macrometastases, that is, changes that indicate tumor foci in a significantly enlarged, clinically palpable lymph node. Particular danger and difficulties in treatment are indicated for those patients who are diagnosed with infiltrates outside the lymph node capsule.
Melanoma, as a malignant tumor, can also metastasize to distant organs. Then the progress of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment depend on the organs in which the metastases are located and the general condition of the patient.
Treatment of melanoma: what will happen with delayed examination and treatment?
When analyzing methods of treating melanoma, it is indicated that surgical treatment is the basis. However, you should know that only rapid diagnosis and radical action, that is, removal of the entire lesion, can determine the effectiveness of treatment. The basis for the treatment method is an excisional biopsy, which determines the malignancy of the tumor. The lesion is excised along with the edge of healthy tissue.
In special cases, re-treatment is carried out, during which the original lesion site is cut off. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is also performed to assess the severity of the disease. The selection of the sentinel node is made taking into account the location of the original lesion.
Excision of the lesion and histopathological result allow the selection of appropriate treatment. As a rule, if the lesion has been removed and the correct margin has been preserved, and lymphadenectomy has been performed, that is, removal of the lymph nodes, then there is usually no indication for further treatment, but it is necessary to be under constant medical supervision.
Metastases associated with melanoma can appear even several years after surgery to remove the primary lesion. The risk of metastases, as well as the time at which they may appear, depend on several factors, the most important of which is the thickness of the primary lesion.
Melanoma metastasis
What complications may arise after mole removal?
If the scar hurts after removing a mole, a relapse is possible.
This happens in cases where, during surgery, not all melanocytes were eliminated; new birthmarks begin to form from the smallest particles remaining.
If moles grow again, they may need to be removed again.
If the wound becomes infected during the postoperative period, the following symptoms may occur:
- increased feeling of itching, weeping
- bleeding
- purulent contents are released from the wound
- the place of the mole is swollen and hurts
- swelling of surrounding tissues (lasts more than three days)
- increase in body temperature (over 38 degrees)