But sometimes such fun plays a cruel joke on little researchers. After all, there are many pathogens of infectious and fungal skin diseases in the environment. The baby’s immune system is not yet ready to cope with the abundance of infections. This is where a disease called microsporia, or ringworm, occurs.
It is important for parents to know what microsporia is and how to prevent it. After all, many unpleasant situations may not happen to the baby if mothers and fathers are vigilant and protect their child. You need to understand what the treatment of skin diseases is aimed at, when you can get by with traditional medicine, and when you need to sound the alarm and run to the doctor.
Microsporia or ringworm?
Ringworm is a highly contagious fungal infection of the skin, nails and hair. But it is not entirely correct to call ringworm microsporia, because there are several causative agents of ringworm. If the cause of lichen is caused by fungi of the genus Trichophyton, the disease is called trichophytosis. When infected with Microsporum fungi, microsporia appears.
Microsporia most often occurs in children, because the disease is very contagious, and it is transmitted from domestic animals and from sick people. Trichophytosis can only be contracted from a sick person.
Risk factor
A shingles quarantine in a children's institution is announced when one or two cases of the disease are observed. The highest incidence of fungus among children occurs in the warm season. As for lichen of viral origin, it, on the contrary, becomes more active in cold seasons.
The development of this pathology in children and adolescents is predisposed by a lack of vitamins, weakened immunity, excessive sweating, fatigue, the presence of ARVI, vegetative neuroses, allergic reactions, and minor damage to the skin.
Causative agent of microsporia
The culprits responsible for the appearance of fungal skin lesions in children include Microsporum fungi. Scientists have identified more than 12 species of fungi of this genus, the most common of which is Microsporum canis.
The fungus is highly resistant in the external environment and can infect others for several years. The pathogen is found in hair, animal fur, dust or skin flakes.
Once on the skin, the fungus penetrates and forms its own colonies in the hair follicles. This occurs both on the surface of the scalp and in the vellus hair follicles throughout the body. Rarely, microsporia appears on the palms, soles and nails, although there are no hair follicles there.
Children of preschool and school age are most susceptible to the disease. In adults, the disease is much less common, which is due to the properties of the immunity of adults.
Although microsporia is a highly contagious disease, not all children become infected with fungi. There are certain risk factors, the combination of which increases the possibility of infection several times.
Risk factors for developing fungal skin diseases are as follows.
- The disease is more common in children with chronic diseases and weakened immune systems.
- For the development of fungi, sufficient moisture is needed - warm and rainy weather. Therefore, an increase in the incidence of microsporia is observed in spring and summer – in May, June and in autumn – in September and October.
- Unfavorable sanitary and hygienic living conditions for children contribute to the spread of the pathogen.
- Increased sweating and moisture in the baby's skin are an excellent environment for fungus to multiply.
- Hormonal problems - hypothyroidism and diabetes.
Features of different types of disease
In childhood, lichen occurs more often than in adults. Experts associate this fact with the child’s lifestyle.
Children's pityriasis rosea almost always occurs after intestinal or respiratory infections, acute fever or vaccination. The exact cause of this type of disease is not known. However, scientists suggest that its causative agent is the seventh herpes virus. The infection can be transmitted not only by contact, but also by airborne droplets. Typically, pityriasis rosea occurs in children over 10 years of age. Although it can often be observed in adults under 35 years of age.
Depriving quarantine in kindergarten is a mandatory event. This is especially true for cases associated with the occurrence of a ringworm type of disease.
Ringworm has two types (trichophytosis and microsporia). People and animals with a fungal infection are at risk of contracting this disease. It is often transmitted through personal belongings and household items that contain spores.
Versicolor or pityriasis versicolor refers to mycoses caused by three types of yeast-like fungus. The latter can live quietly on the child’s skin and at the same time not cause absolutely any pathological changes. However, infectious diseases, seborrhea, hormonal disorders, hyperhidrosis, leukemia, rheumatism, hereditary predisposition or lymphogranulomatosis often become a kind of impetus for the fungal process.
It should be noted that lichen versicolor is not very contagious. Most often, this disease is observed in adolescents. The most common habitats of this type of fungus are areas with a large number of sweat glands.
The reasons for the development of lichen planus are not well understood. Therefore, experts adhere to several theories (hereditary origin, viral, neurogenic, immunoallergic, intoxication).
Children's shingles - what does it look like? How to treat this disease? In medical practice, this disease is called herpes zoster. Its causative agent is Varicella zoster, which is also the causative agent of chickenpox. As soon as a child has chickenpox, the virus “settles” in the nerve ganglia. In the presence of unfavorable factors (for example, with reduced immunity), it is activated.
As with herpes, shingles is accompanied by a small blistering rash that spreads over the child's body (on the back, stomach, sides). To treat such a disease, you should consult a pediatrician. Usually, when the herpes virus is activated, doctors recommend taking medications containing the active substance - acyclovir.
How does microsporia become infected?
Microsporia is a contagious disease that is most often spread by sick animals.
Both domestic and wild animals can suffer from fungal disease. Among domestic animals, cats, dogs, rabbits, and cattle are susceptible to microsporia, and among wild animals - foxes, arctic foxes, and monkeys.
Direct contact with an animal is not necessary to become infected with microsporia. It is enough for hair or scales from surrounding objects to come into contact with human skin, for example, when grooming or feeding a pet.
Children most often catch the disease through contact with infected cats and kittens, and less often through contact with dogs or through infected care items.
A person with microsporia who releases the pathogen into the environment also poses a danger. For children, the source of infection is often a sick child, for example, playing in a sandbox or visiting a children's group.
Infection is possible from sick family members, through contact with household items, or clothing contaminated with fungus. It is dangerous to use the same comb or wear a hat for a person with microsporia.
By following the rules of hygiene and thorough hand washing, the disease can be prevented. The contact of fungal spores on the surface of human skin does not indicate the inevitability of the disease, although the risk of infection remains high.
Recommendations for parents
All parents who have been in contact with a patient with lichen, or those who are just about to go out into the garden after a long illness, must be informed about the possibility of infection. Parents of contact children should take preventive measures:
- wash all the clothes the child was wearing at high temperatures;
- disinfect the apartment with antiseptics;
- go to an appointment with your local pediatrician, find out about further actions, ask to prescribe immunotherapy.
Those who have just suffered from an infectious disease are advised to refrain from visiting kindergarten until the situation stabilizes, because a child with weak immunity risks getting sicker than others. Usually, groups in kindergartens are not closed, and responsibility for the choice to drive or not to drive the child is placed on the parents. If you do not want your child to become infected, ask the doctor for a certificate until the epidemic ends. The doctor is obliged to issue such a document and has no right to refuse you.
Classification of microsporia in children
From the type of fungus
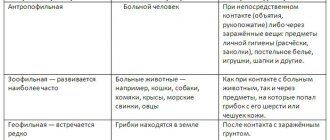
Depending on the type of Microsporum fungus, epidemiologists distinguish the following types of microsporia.
- Zoonotic microsporia. This type of microsporia is caused by fungi, the main host of which is animals. Infection occurs through contact with an animal or while caring for it.
- Anthroponotic microsporia. They become infected with anthroponotic microsproria from a sick person. This form is typical for children, children's groups, kindergartens, and schools. It is enough to touch things on which hair or scales containing fungal spores remain, and the disease develops.
- Geophilic microsporia. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Microsporum, which lives in the soil. A child can become infected by digging in soil contaminated with fungal spores.
From localization
Depending on the location and location of the affected area, the following types of disease are distinguished.
Microsporia of smooth skin
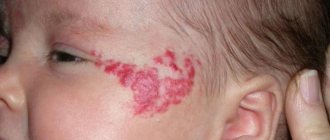
The first symptom of infection is the appearance of a small round or oval spot on the skin.
The affected area has clear boundaries and rises slightly above the rest of the skin surface. Doctors call this spot a lesion. Gradually, the area of the lesion increases, the spot becomes larger and denser to the touch. The outer edge of the lesion swells and transforms into a cushion, which consists of crusts and bubbles. In the center of the lesion, inflammation, on the contrary, decreases, the skin becomes pale pink in color and becomes covered with scales.
It happens that the fungus re-enters the ring and infects the skin again. Then a new round-shaped spot appears in the middle of the lesion, and then a ring. Repeated infections can be repeated, then the shape of the lesion resembles a target and consists of several rings, which is very characteristic of anthroponotic microsporia.
The lesions are located on the upper extremities, neck, face, at the site of pathogen penetration. The diameter of the spots varies from 5 mm to 3 cm, but sometimes the lesions reach 5 cm. Adjacent lesions can merge, forming extensive skin lesions.
This infection does not cause significant discomfort in the child and is often painless. There are even abortive forms, when the clinical manifestations of microsporia are not expressed, and the skin remains pale pink, the affected area does not have clear boundaries. Severe pain and itching indicate a serious inflammatory process in the affected area.
For children under 3 years of age, an erythematous-edematous form of the disease is characteristic. This form is characterized by the appearance of a red, swollen lesion with pronounced signs of inflammation. Peeling and the appearance of scales are not typical for microsporia in children; these manifestations are minimal.
Microsporia of the scalp
If fungi get on a child's hair, microsporia of this area develops. This localization is typical for children from 5 to 12 years old and rarely occurs in adults. This is explained by the peculiarity of the hair follicles of adults.
With the onset of puberty, hair follicles produce acid, which prevents the development of Microsporum fungi. Therefore, there are known cases of spontaneous cure of the disease in children who have reached puberty.
The disease microsporia is very rare in children with red hair, the reasons for this are not yet known.
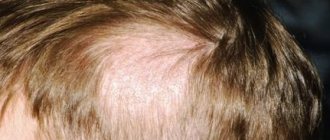
Damage to the scalp is manifested by the formation of lesions on the crown, crown and temples. On the head you can see round or oval spots with clear edges.
After fungal spores get on the skin of the scalp, a small flaky area forms at the site of the lesion. The hair in this place is surrounded by ring-shaped scales. After a week, it is easy to detect hair damage in this area. Hair loses color and elasticity, breaks easily, leaving only fragments about 5 cm long.
The affected area is an island, a group of hair fragments covered with a grayish coating. A large amount of the pathogen is found in plaque and scales located on the scalp.
The number of affected areas of the scalp usually does not exceed two. But between the lesions small secondary screenings appear, up to 2 cm in diameter.
Microsporia of nails
Involvement of areas devoid of hair follicles, nails, palms or soles is very rare. With nail microsporia, a gray spot forms on the baby’s nail, which grows and increases in size. Over time, the color of the spot changes to white, and the nail plate loses its properties and is destroyed.
From the depth of the lesion
Depending on the depth of skin damage, the following types of pathology are distinguished.
- superficial microsporia;
Damage to the skin in this form is superficial, mainly the upper layers are damaged. Microsporia manifests itself as peeling and redness of the skin. When the fungus spreads to the scalp, hair loss and breakage occurs. Superficial microsporia is most often found in children with anthroponotic infection.
- infiltrative-suppurative microsporia.
In severe suppurative form of microsporia, the inflammation process penetrates deep into the tissue. Focal fragments covered with pustules form on the skin. When pressure is applied to the affected areas, purulent exudate is released. The patient’s well-being due to the suppurative form is disturbed.
Diagnosis of microsporia in children
To make a correct diagnosis, a consultation with a dermatologist is necessary. The specialist examines the affected area of the skin and scalp. Then the doctor conducts a survey and establishes the possibility of contact of the child with a patient with microsporia or an infected animal.
The final diagnosis is established after additional research.
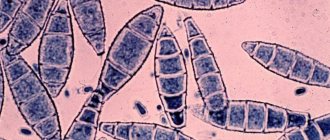
- Dermatoscopy and microscopy. To see the fungus under a microscope, scrapings from the affected skin or pieces of hair are taken. When examining skin flakes, threads of mycelium and fungal bodies are revealed. A large number of fungal spores are detected on damaged hair.
- Cultural research. Sowing scales or hair on a nutrient medium will help to more accurately diagnose, prescribe treatment and determine prevention. 2 - 3 days after sowing, colonies of fungi appear in the Petri dish. By the appearance of the colonies, you can determine the type of pathogen and select a treatment that will definitely affect this type of fungus.
- Luminescent study. Using a Wood's lamp, you can quickly determine the disease in a child. During fluorescent examination, the affected hair begins to glow green. A prerequisite for diagnosis is cleansing the lesions from ointments and crusts and conducting the study in a dark room.
Thus, only an experienced doctor can accurately determine the cause of the disease, correctly diagnose and prescribe effective treatment.
Ringworm: how many days of quarantine in kindergarten?
If such a disease is detected, quarantine in a kindergarten must be at least 45 days. At the same time, absolutely all children from the institution undergo a mandatory examination by a specialized dermatologist for the next 5 days. If the disease affects several children, the quarantine is extended, and the premises are thoroughly disinfected (carpets are cleaned, soft toys are thrown away).
A child’s sick leave is closed only when all external signs of the disease disappear. In this case, the study of lesions under a Wood's lamp plays a decisive role. This type of analysis is carried out three times. The cessation of lichen is spoken of if the results of all three studies are negative.
Treatment of microsporia in children. General principles
To quickly cure microsporia in a child, it is necessary to start therapy on time and choose the right antifungal treatment. Long-term ineffective treatment or smoothing out the symptoms of the disease with folk remedies leads to suppuration of the lesions and frequent relapses of the disease.
Only a dermatologist can determine how to properly treat microsporia in children.
Therapy for various forms of microsporia has its own characteristics, but the principles of treatment are similar.
- If the fungus has affected only the skin, and the vellus hair is untouched, then the use of local preparations will be sufficient.
- If the scalp is affected or symptoms of infection are visible on vellus hair, it is necessary to take antifungal drugs orally.
- Treatment with drugs against fungal infection continues at the same dose for a week after the symptoms of the disease disappear. This measure prevents the recurrence of the disease.
Complications
Ringworm does not pose any danger to the life of a child or adult. With adequate and timely therapy, the hair and skin are completely restored. However, there are situations in which complications of the disease arise if the wrong treatment regimen was prescribed or the doctor was consulted late. The consequences may appear in the following form:
- inflammation, suppuration of the skin (as in the photo);
- Bald spots appear on the head.
- Irreversible hair loss develops.
Treatment of smooth skin microsporia
Ointments, creams and solutions are widely used for local therapy. The most popular use of ointments containing antifungal drugs. For example, Clotrimazole, Itroconazole, Bifonazole. A widely used antifungal cream is Lamisil, which has a pronounced antifungal effect. It is recommended to treat the affected area 2 - 3 times a day.
If the doctor has detected a pronounced inflammatory process at the site of the lesion, then combined ointments are prescribed. In addition to the antifungal component, such ointments also contain hormonal agents that reduce swelling and inflammation, and reduce itching. In severe suppurative forms of the disease, ointments containing antibacterial drugs, for example, Triderm, are often used.
Treatment of microsporia of the scalp
Therapy for this form of the disease should begin when the first symptoms appear in order to prevent the formation of a cosmetic defect on the child’s head.
You should shave the hair from the affected area daily and treat the lesion with antifungal ointments or apply a Griseofulvin patch. Until the end of treatment, you need to wash your hair 1-2 times a week.
Complex treatment of the disease must necessarily include the use of antifungal drugs; Griseofulvin is most often prescribed. The general course of treatment lasts about 1.5 - 2 months.
The duration of treatment for microsporia, the dosage and frequency of taking drugs is determined by the doctor. Incorrect or prematurely completed treatment often leads to recurrence of the disease.
Folk remedies
In consultation with your doctor, home recipes may be used as additional therapy. Folk remedies can only help in the initial stages of pathology or be used for prevention. The following recipes can be used:
- squeeze the juice from the onions, moisten the napkins and apply to the affected areas every day;
- tincture of lilac flowers: add 2 tbsp to 100 ml of 70% alcohol. l. dried flowers, then strain and lubricate the inflamed areas;
- wash the affected areas with a decoction of celandine: 1 tbsp. l. dry herbs, take a glass of boiling water and hold on low heat for 10 minutes, then cool, strain.
Prevention of microsporia in children
- Maintain personal hygiene. The child must be taught to regularly wash his hands, use an individual towel, and a comb. Explain to your child that you should not exchange mittens or hats with other children.
- Preventing contact with infected animals. Warn your child that stray animals can carry the disease; do not allow children to play with them. Examine your pets carefully and treat them promptly.
- Medical examinations in preschool institutions. To prevent the disease in children, it is necessary to promptly identify and isolate patients with microsporia. A child with a fungal skin infection must be treated in a hospital, and his things must be disinfected.
- Quarantine measures. The kindergarten or school the child attends is subject to quarantine for 2 to 3 weeks.