An incomprehensible spot appeared on the skin.
Then one more thing.
Soon, a whole demonstration of unknown neoplasms is built on the face, hands or other areas.
These are usually flat warts.
Such formations are small, smooth growths with a diameter of up to three millimeters. They are almost invisible and rarely hurt.
Doctors call them juvenile warts because the growths primarily affect children and adolescents.
There are always a lot of growths. Typically, from 20 to 200 formations appear, which are grouped in one area. A single wart is almost no different from the skin. A large group of neoplasms stand out much more and often become a cosmetic problem.
Why do they grow?
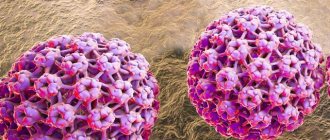
Due to the human papillomavirus or HPV. Scientists have identified over 100 types of the disease, and flat warts are caused by types 3, 18, 28 and 49. These types of the virus are benign, unlike other types that increase the risk of developing cancer of the uterus and genital organs.
The likelihood of growths increases:
- Direct contact with wart carriers
- Scratches and other damage
- Touching a contaminated object
- Poor hygiene
- Weakened immunity due to illness or treatment
In most cases, a colony of warts surrounds scratches and wounds. Often the virus enters the body through damage, so that neoplasms grow in the neighborhood.
Non-genital types of HPV affect up to 10% of the world's population. Most of them are teenagers 12-16 years old. It’s not for nothing that these growths are called juvenile warts, because children are more likely to become infected and spread the human papillomavirus.
Their tumors grow on different parts of the body.
Reducing the risk of spread
Since the site of infection is most often public places with high humidity, you must be careful when visiting them. You should never touch the toilet rim with your skin when visiting a public toilet. Swimming masks must be used in the pool to prevent the virus from entering the body through the mucous membrane of the eyes. You should never wear someone else’s shoes, and you should also give even your close friends your towel, toothbrush, comb and other personal items.
It is important to carefully monitor the state of your immunity, avoid stress and eat properly so that the body has the strength to resist infection by both this virus and other diseases.
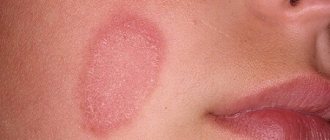
Types of flat warts
All juvenile warts are almost the same. They are flesh-colored or brown in color and are only slightly raised above the skin. Therefore, they are difficult to detect.
Based on location, growths are divided into:
- Flat plantar warts
- Flat warts on the face
- Flat warts on the body
The greatest problems are caused by neoplasms on the face. Yes, flesh-colored growths, even in large quantities, are almost invisible, but with a different color they stand out on the skin. Mostly, patients want to remove warts on the face.
The formations on the legs and arms are not so obvious. At the same time, growths on your hands increase the risk of infection to people you come into contact with.
Should they be removed?
Hard to tell. These warts are completely safe and never turn into malignant tumors. Yes, they are contagious. But there is no threat to health or life.
Is it painful to remove warts?
Removing warts using cryodestruction is painful.
Painful sensations are observed both during the period of removal and after it, when an inflammatory reaction is formed.
If electrocoagulation or laser is used, there is no pain.
Because anesthesia is used.
When a wart is located on the scalp, topical anesthesia is usually used.
A cream containing prilocaine and lidocaine is applied to the skin.
After a few minutes, skin sensitivity disappears.
The doctor can remove the wart, and the patient does not feel anything during the procedure.
After its completion, when the anesthesia wears off, there is no pain either.
Why do flat warts appear?
We have already talked about this. Such neoplasms arise due to the human papillomavirus.
HPV enters the body. Mostly through scratches or cuts, but maybe through undamaged skin. The virus affects skin cells and they mutate - they grow larger than usual and form warts.
HPV is not only transmitted from person to person. It also spreads within the same body. For example, a teenager touches and scratches growths on his face, and then touches his neck with his fingers. Now a source of infection may arise there too.
Or another example: flat warts appeared on the fingers. The man wiped his hands with a towel, and after a short time he also wiped his face - this is how the virus spread from his fingers to his cheeks or forehead.
Remember the reason for the appearance of flat warts. This will help you effectively treat tumors and prevent their return.
Removal methods
Previously, only folk remedies were used to treat papillomas. But modern medicine offers new methods for removing warts that can get rid of tumors in one day and without side effects.
Treatment methods for viral warts
Vulgar papillomas bother people most often. To treat them, you can use home and folk remedies. The following methods are popular:
- Spot cauterization of growths using iodine or vinegar.
- Removal with celandine or tea tree oil.
- Tying propolis, aloe and other medicinal plants to problem areas.
These methods can be used to treat children and adults, but only if you need to get rid of recurrent papillomas. And if they arise for the first time, then consultation with a doctor is mandatory.
What to do if they grow
Since papillomas are a viral disease, an increase in the effect of infection on the body may periodically be observed. If the growths increase in size and number, you should consult a doctor. After removing tumors from the body, the doctor will prescribe therapy with interferon drugs and other medications that weaken the effect of HPV and improve the functioning of the immune system.
Can they disappear on their own?
Papillomas are formations consisting of skin cells modified by a virus. And if in one person they may disappear on their own after a few days or weeks, then in the situation with other people, medication or even radical treatment may be required.
When should you see a doctor for flat warts?
In any case, we recommend making an appointment with a dermatologist. Yes, it is easy to diagnose growths. Flat warts have characteristic features and you can easily determine the type of tumor. However, there are also difficult cases.
Sometimes the growths don't look like typical flat warts. In such situations, you cannot do without the help of a doctor, because a dermatologist has a much better understanding of neoplasms. He can also perform a dermatoscopy. This is the name of the study of formation using a special apparatus - a dermatoscope.
So, the doctor helps with the diagnosis.
What about treating warts?
It is not necessary - in most patients the formations disappear on their own. Yes, not right away. Scientists conducted a study on this topic and found out the approximate lifespan of flat tumors. Up to 23% of warts disappear within two months. Up to 73% in two years. That is, in a couple of years, most of the formations will disappear.
When should flat warts be removed?
Treatment will be required if the growths:
- Bleeding
- Grow
- Change color
These are alarming signs in which it is best to go for an examination with a dermatologist. The doctor will determine the degree of danger of the formations. Sometimes they need to be removed. Usually no.
So operations are often performed at the request of patients, and not due to medical necessity.
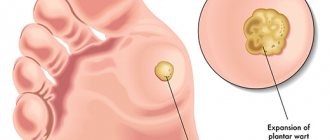
Plantar (spike) warts
Plantar warts are a type of vulgar wart. The manifestation of the disease is most often observed in children and at the age of 20-30 years. Of all skin warts, plantar warts occur in 30%.
Warts on the soles appear as hard, round lumps with papillae in the middle. Inside the wart, characteristic black dots are visible - many small thrombosed capillaries. Along the edges there is a small roll of keratinized skin. The visible part, rising above the surface of the skin by only 1-2 mm, can reach 2 cm in diameter and is only a quarter of the total size of the plantar wart, which mainly forms in the deep layers of the epithelium (skin).
Externally, the spine resembles a callus. A plantar wart can be differentiated (distinguished) from a callus by the visible interruption of the skin pattern in accordance with the wart.
This type of neoplasm usually affects the feet (sole, sides and toes), and less commonly the palms. They appear on the skin as small whitish, pinpoint skin lesions, sometimes itchy. Over time, their surface becomes rougher and changes color - from yellow to dark brown.
Plantar warts themselves do not pose a threat to health, but when walking they cause a person significant discomfort, cause pain, which often intensifies, and can even bleed. This is due to the location of the tumor and the specifics of its growth. Since the spine grows inward, the weight of the body when walking compresses the pain receptors.
The incubation period of the disease ranges from several days to several years. The infection enters the body and goes into waiting mode for a favorable environment to activate. Plantar warts regress without treatment in 50% of cases. But this process lasts from 8 months to one and a half years.
Without treatment, plantar warts will enlarge and multiply, even to the point of producing large clusters of tumors. This can even lead to temporary loss of a person's ability to work due to unbearable pain that prevents walking.
Based on the characteristics of the lesion and its location, plantar warts are divided into 3 types:
- simple;
- periungual;
- mosaic.
Treatment of flat warts
Although these tumors disappear sooner or later, not all people are ready to wait for months for a joyful moment. They want to speed up this process.
For example, with the help of improvised means, salicylic acid is very popular, which gradually destroys the tissue of warts.
Unfortunately, this method has not been properly studied at this time. No studies have been conducted.
Doctors do not recommend using salicylic acid, as it can leave scars and burns on the skin. To treat flat warts, it is better to use proven methods. One option is for dermatologists to prescribe special creams that irritate the upper layer of growths. After treatment, the tumor is simply torn off.
Creams are not always effective. Sometimes get rid of flat warts only by surgical methods.
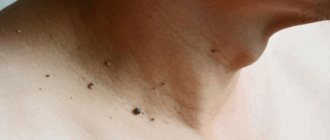
Common (simple, vulgar) warts
Common warts are dense, dry growths characterized by an uneven and rough surface to the touch, variable size and rounded shape. They look like a hard, keratinized bubble up to 1 cm in diameter, significantly rising above the surface of the skin.
The surface of common warts is often covered with grooves and projections, which is why the new growth vaguely resembles a cauliflower or raspberry with black dots inside.
This is the most common type of wart, accounting for up to 70% of all such skin neoplasms. Simple warts can appear on the skin at any age, but most often they affect children and young people. This is due to the fact that they have weaker immunity than adults.
Common warts usually appear on the hands (fingers and backs of the hands), knees and elbows, sometimes on the face or feet, and extremely rarely on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
A scattering of small growths may form next to the large “parent” wart. Young neoplasms usually remain flesh-colored; over time, they acquire a dirty gray or grayish-brown tint, less often yellow or pinkish. This is due to their uneven porous surface, which accumulates dirt.
Vulgar warts usually do not cause concern: they do not cause unpleasant symptoms, do not hurt or itch. However, they may cause pain if they are in areas subject to impacts or in contact with clothing. The growths may heal on their own over time, especially if they occur in childhood.
How to remove flat warts
Now doctors remove tumors using different methods.
It is important to note that in rare cases, new growths appear after surgery. Therefore, be sure to consult a dermatologist about treatment and its possible consequences.
Procedures for removing flat warts:
- Surgical excision
Previously, this method was widespread, but now patients often choose more technological methods. The doctor cuts out the wart with a scalpel. It also removes the thin layer of skin around the tumor, which prevents the tumor from returning. A wound remains at the site of the wart. As it heals, a scar appears.
- Cryotherapy
The dermatologist freezes the growth with liquid nitrogen. The wart gradually dies and falls off - a wound forms in its place, which heals in a few weeks.
- Laser therapy
The doctor burns out the tumor. The tissues of the formation are completely destroyed, and the adjacent vessels are baked. The wound is covered with a protective crust and heals in three weeks.
The choice of appropriate therapy depends on the location of the flat warts, as there is a risk of scarring. The size of the formation and the health of the patient affect the rate of healing.
Do not schedule surgery without consulting a dermatologist. He will tell you how to remove flat warts and how to maintain healthy skin, without scars and scars.
Laser therapy is very popular. Many people prefer to eliminate tumors using this method.
Why?
Laser surgery is simply superior to other procedures in some respects.
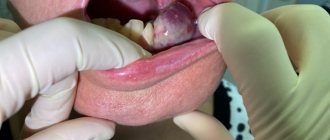
Anogenital warts (condylomas)
Among sexually transmitted diseases, anogenital warts are especially common. They are flat and elongated neoplasms or elastic elastic growths in the form of cauliflower or cockscomb. Such warts reach 1-1.5 cm and are gray, pink or flesh-colored.
Typically, this type of neoplasm is transmitted sexually: during vaginal/anal sex or even simply through contact with intimate areas without penetration. After oral sex, warts can appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, vocal cords or trachea. Such growths are called oral, or acute, condylomas. In rare cases, infection occurs through household contact or from mother to newborn.
Based on their appearance and structure, there are several types of genital warts:
- Pointed - loose polyps of pink, flesh-colored or red color, on a stalk or a wide base, reminiscent of cauliflower. They can occur either individually or in the form of multiple clusters. Genital warts are prone to rapid reproduction;
- Papillary - round, smooth growths without a stalk, rising above the surface of the skin by several millimeters;
- Keratotic - very dense, thickened formations that protrude significantly above the skin. Typically affects the female labia majora;
- Giant (Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas) are a rare type of wart. They are prone to rapid growth, accompanied by destruction of surrounding tissues. In extremely rare cases, giant condyloma degenerates into a malignant form;
- Flat - formed both singly and in the form of multiple clusters. There are practically no symptoms, sometimes itching and discharge may occur. The affected area of flat growths is the vaginal mucosa and cervix in women.
The appearance of anogenital warts and the deterioration of their condition are often accompanied by other sexually transmitted diseases (ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc.). It is impossible to protect yourself or your partner from infection using a condom, since in this case it is ineffective. It is necessary to completely abandon intimate relationships until complete recovery.
Anogenital warts occur equally often in people of both sexes who are sexually active (usually from 20 to 25 years). The incubation period for this disease varies from three weeks to nine months, with an average of about three months.
In men, condylomas are most often found on the foreskin, scrotum, inside the urethra and on the penis. They can be localized around the anus and rectum, especially in homosexual men. In women, warts appear mainly at the level of the vulva, vaginal wall, cervix and perineum; The urethra and anal area may also be affected.
Genital warts are more common in immunocompromised patients. The rate of growth varies, but pregnancy, immunosuppression (suppression of the immune system), discharge from the urethra, vagina or rectum, accumulation of smegma, or skin maceration (the natural process of swelling of the epidermis (layer of skin) with prolonged contact with liquid) can accelerate the growth and spread of warts.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- severe itching at the location of the growth;
- painful and uncomfortable sensations;
- burning;
- pain during and after sexual intercourse;
- foreign body sensation;
- problems with defecation when the wart is located in the anus;
- bleeding when condyloma is damaged.
In most cases, anogenital warts are benign, but they can degenerate into carcinoma. For this reason, in order to prevent cancer, condylomas, regardless of their position, shape and size, are always removed.
Anogenital warts are usually diagnosed clinically. Their morphology distinguishes them from typical lateral condylomas of secondary syphilis, but in any case, serological tests for syphilis are necessary in the initial phase and after 3 months. A biopsy is required to rule out carcinoma and is mandatory in cases of bleeding, ulceration or persistent warts.
Endocervical and anal warts can only be visualized by colposcopy and anoscopy. Application of a solution of 3-5% acetic acid for a few minutes before colposcopic examination causes the growth to change color to white, improving visualization and detection of small warts.
Recurrence of anogenital warts is promoted by:
- promiscuity;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- installation of an intrauterine device, termination of pregnancy using surgical traumatic methods or other medical procedures.
This type of wart is dangerous due to a number of complications:
- Lack of careful intimate hygiene or irritation of growths due to constant friction against underwear leads to ulceration of growths by secretion of purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- In the absence of timely treatment, genital warts are prone to suppuration;
- Lack of therapy leads to the formation of a large number of warts. In particularly advanced cases, not even a small area of healthy skin remains;
- In the presence of anogenital warts, a strong decrease in immunity is observed, which is associated with a person’s susceptibility to any infectious disease. If the patient already has a chronic inflammatory disease (in particular, of the pelvic organs), it will necessarily get worse;
- Threat of degeneration into a malignant form.
Causes of warts.
The cause of warts is HPV, which almost every person is infected with. The main reason for the appearance of warts is considered to be a weakened human immune system.
Rice. 3. Warts on the sole of the foot are called plantar warts.
Warts are transmitted:
- In personal contact with the patient.
- When using only things and untreated manicure tools.
- When walking barefoot in a public bath or swimming pool.
- Genital warts may appear during sexual contact.
- When wearing tight shoes.
Rice. 4. Plantar warts can merge into one.
A favorable environment for the appearance of warts is considered to be a weakened immune system, stress, lack of sleep and poor diet.
What is the best way to treat?
Warts can be removed in almost any way. The surgical method, electrocoagulation, laser and cryodestruction, as well as radio wave surgery are used.
Radio wave surgery
, in my opinion, is a more effective method that allows you to remove wart tissue under visual control. When using this method, the tissue is not burned, but is excised along with a small piece of healthy skin. Thus, the likelihood of warts reappearing becomes minimal.
See all photos before and after removal
Histological examination during removal is mandatory if there is the slightest doubt.
Laser wart removal
Today, laser surgery is one of the best ways to get rid of warts. This is a painless and safe procedure that can be used in areas of maximum sensitivity. Laser removal of tumors is very effective: the likelihood of relapse is minimal. This is significantly influenced by the severity of the disease.
Warts are removed by layer-by-layer cauterization of the affected area, thanks to which the doctor controls the depth of the effect. At the same time, the laser beam cauterizes the blood vessels, thereby preventing bleeding at the site of exposure.
Three methods of laser coagulation are common:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Procedures using this laser are more painful. Although the CO2 laser seals the blood vessels, it also kills the wart tissue. In this process, there is a possibility of damage to healthy tissue. Wound healing usually takes longer, and scar formation is possible. The efficiency is about 70%.
- Erbium laser. It is characterized by a shorter wavelength. The likelihood of scar formation after healing is significantly reduced.
- Pulsed dye laser. This laser more effectively seals the blood vessels that feed the wart. It does not damage much of the healthy tissue like a CO2 laser does. It is also the only type of laser approved for use on children. The effectiveness of this treatment method is about 95%.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Minimum likelihood of scar formation (depending on the degree of neglect of the pathology) | High price |
| Fast tissue healing | |
| High efficiency of the method | |
| Minimal damage to healthy tissue | |
| Speed of the procedure |
Wart removal is performed under local anesthesia. A crust remains at the cauterization site, which disappears within 14 days. After the procedure, the patient quickly returns to his normal lifestyle, provided that all doctor’s recommendations are followed.