- Pimple on the eyeball: causes
- 4 main causes of eye bumps:
- Diagnostics
- Signs and symptoms of acne inflammation on the eyeball
- SUN PROTECTION TIPS
- Treatment of acne on the eyeball
- Treatment of acne around the pupil
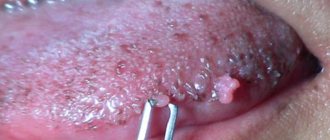
A pimple on the eyeball is usually caused by the growth of conjunctivitis, or the clear ocular membrane covering the white part of the eye. Depending on the color of the bump, its shape, and where it is located on the eye, there are a number of conditions that can cause bumps on the eyeball.
Pimple on the eyeball: causes
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun is the main cause of pimples on the eyeball, and frequent exposure to dust and wind also appear to be risk factors for their appearance. Dry eye disease can also be a contributing factor to the growth of eye inflammation.
Pimples on the eyeball and near the pupil are more common in middle-aged or older people who spend a lot of time in the sun. But they can also occur in young people and even children, especially those who are exposed to the sun frequently without sunglasses or a hat.
To reduce your risk of getting a pimple, it's important to wear sunglasses outdoors, even on cloudy days, because the sun's ultraviolet rays penetrate the cloud cover. For best protection, choose sunglasses with quality lenses that block more sunlight than regular glasses.
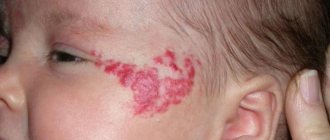
Causes of herpetic rashes
Natural tears protect the visual organ well from viruses if there are no violations. Immunoglobulins contained in tear fluid block the spread of infection.
Causes of herpetic rashes:
- weakened immunity due to a stressful situation, infectious pathologies, hypothermia;
- injuries to the visual organ;
- pregnancy;
- use of immunosuppressants.
Important! You can become infected with ophthalmoherpes through contact with a source of infection (mucous mucous membranes of intimate organs, oral cavity), through household items (towels, personal hygiene items).
Signs and symptoms of acne inflammation on the eyeball
For most people, eye inflammations such as conjunctivae or pingueculae do not cause many symptoms. These symptoms are usually associated with disruption of the tear film. Since pingueculae are increased inflammation on the eyeball, the natural tear film can be unevenly distributed on the surface of the eye around it, causing dryness. This can cause symptoms. dry eye such as burning sensation, itching, blurred vision and foreign body sensation.
Another symptom of pinguecula is the appearance of extra blood vessels in the conjunctiva covering the capillaries, causing red eyes.
In some cases, red pimples on the eyeball may become swollen and inflamed. This is called pingueculitis. Irritation and redness of the eyes from pingueculitis usually occurs due to overexposure to sunlight, wind, dust, or extremely dry conditions.
Eye diseases in humans: list, symptoms
The reason for this is many factors. For example, the rapid development of computer technology and the deterioration of the environmental situation every year. Next, we will consider the most common diseases, and also highlight their characteristic symptoms.
Pathology of the optic nerve
Glaucoma
- a chronic disease. Due to increased pressure inside the eyes, optic nerve dysfunction occurs. As a result, vision decreases, which may disappear in the future. The disease progresses very quickly, so the patient risks completely losing his vision if he delays going to the doctor. Signs: impaired lateral vision, black spots, “hazy” images, inability to distinguish objects in the dark, colored rings appear in bright light.
Ischemic optic neuropathy
– circulatory disorders in the intraocular or intraorbital region. Symptoms: decreased visual acuity, appearance of “blind” spots in some areas. Reducing viewing angle.
Ischemic neuropathy
Neuritis
- infection. An inflammatory process in the optic nerve is characteristic. Signs: loss of sensitivity in the area around the eye, pain, weakening of the muscles associated with the optic nerve.
Nerve atrophy
– a disease characterized by dysfunction of arousal conduction. Color perception and viewing angle are impaired. Vision decreases and a person can become completely blind.
Nerve atrophy
Pathology of the eye orbit, eyelids, lacrimal canals
Blepharitis
- inflammation that occurs along the edges of the eyelids. Symptoms: swelling of the tissue, accompanied by burning and redness. The patient feels as if a speck has gotten into his or her eye. There is itching and characteristic discharge. Bright light is difficult to perceive, tearing, pain. Dry eyes and peeling of the eyelid margins may occur. After sleep, purulent scabs form on the eyelashes.
Blepharitis
Cryptophthalmos
- a common disease in which the edges of the eyelids fuse together. This causes the palpebral fissure to narrow or even disappear.
Lagophthalmos
– a pathology characterized by a violation of the closure of the upper and lower eyelids. As a result, some areas remain open all the time, including during bedtime.
Turn of the century
– the place where eyelashes grow is turned towards the eye socket. This creates severe discomfort due to rubbing and irritation of the eyeball. Small ulcers may form on the cornea.
Turn of the century
Coloboma of the century
- disturbance in the structure of the eyelids. Usually occurs along with other morphological defects. For example, cleft palate or cleft lip.
Swelling of the eyelid
– localized accumulation of excess fluid in the tissues around the eyelid. Symptoms: local redness of the skin, discomfort. Eye pain worsens when touched.
Swelling of the eyelid
Blepharospasm
- looks like a convulsive contraction of the facial muscles, as if the person is quickly squinting his eyes. Not controlled by the will of the patient.
Ptosis
– drooping of the upper eyelid. Pathology is classified into several subtypes. In some cases, the eyelid droops so much that it completely covers the eyeball.
Ptosis
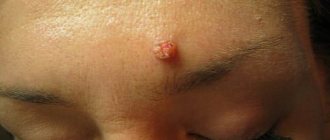
Barley
– an infectious disease of an inflammatory nature that occurs with pus discharge. Signs: swelling of the edges of the eyelids, redness and peeling. Pressing is accompanied by severe pain. Discomfort (feeling of a foreign object in the eye) and lacrimation are common. The acute form is characterized by signs of intoxication - loss of strength, fever, headache.
Barley
Trichiasis
– improper eyelash growth. The danger is that pathogens can easily enter the eyes. This provokes inflammation, conjunctivitis and other problems.
Dacryocystitis
– an infection of the tear duct that causes inflammation. There are several types of pathology: acute, chronic, acquired, congenital. Symptoms: painful sensations, the lacrimal sac is red and swollen, suppuration of the canals and constant tearing.
Dacryocystitis
Pathology of the tear-producing system
Dacryodenitis
- damage to the lacrimal glands. It occurs due to chronic pathologies, or due to infection entering the body. If there is a disruption in the functioning of the circulatory system, the disease can take a chronic form. Symptoms: the upper eyelid becomes red and swollen. In some cases, the apple of the eye protrudes. If dacryodenitis is not treated, the inflammation spreads, ulcers form, a high temperature rises, and general malaise appears.
Dacryoadenitis
Lacrimal gland cancer
– develops as a result of abnormal activity of gland cells. Tumors can be either benign or malignant. The second group includes, for example, sarcoma. Signs: pain in the eyes and head. Associated with an increase in formation that puts pressure on the nervous tissue. In some cases, the pressure is so strong that it causes delocalization of the eyeball, making it difficult for them to move. Additional symptoms include swelling and loss of vision.
Pathology of the connective membrane of the eye
Xerophthalmia
– an eye disease during which tears are produced less than normal. There are several reasons for this: chronic inflammatory processes, various injuries, tumors, long-term use of medications. Elderly people are at risk.
Conjunctivitis
- inflammation that occurs in the conjunctival mucosa. It can be allergic, infectious and fungal. All of these varieties are contagious. Infection occurs both through physical contact and through everyday objects.
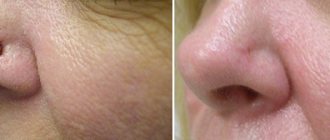
Tumors of the conjunctiva
– appearing in the coal on the inner side of the mucosa (pterygium) and forming in the area of the connection with the cornea (pinguecula).
Lens pathology
Cataract
– gradual clouding of the eye lens. The disease develops very quickly. It can affect one eye or both. In this case, either the entire lens or one part is damaged. The main category of patients is elderly people. It is this disease that can reduce vision in a very short time, even to the point of blindness. In young people, cataracts are possible due to injuries or somatic diseases. Symptoms: rapid loss of vision (this forces you to change lenses very often), inability to distinguish objects in the dark (“night blindness”), impaired color perception, eyes get tired quickly, and in rare cases, double vision.
Cataract
Lens abnormalities
– cataracts, bifaf, spherophakia, lens luxation, coloboma developing from birth.
Retinal pathology
Retinitis (retinal pigmentary dystrophy)
– a disease manifested by the occurrence of inflammation in various parts of the retina. The causes include injury to the organs of vision and prolonged exposure to sunlight. Symptoms: the normal field of vision narrows, visibility decreases, the image doubles, insufficient visibility at dusk, characteristic colored spots appear before the eyes.
Retinal detachment
– a pathology in which destruction of the retina is observed. Its inner layers begin to peel away from nearby epithelial tissues and blood vessels. In most cases it is treated surgically. Lack of treatment results in vision loss. Signs: “fog” before the eyes, distortion of the geometric shape of objects, sometimes flashes of light and bright sparks flash through.
Retinal detachment
Retinal angiopathy
– destruction of the structure of the choroid in the eyes. This disease is caused by physical trauma, high intraocular pressure, disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, diseases of the circulatory system (arterial hypertension), poisoning, and pathological defects in the morphology of blood vessels. Symptoms: noticeable decline in vision, blurred vision, foreign flickers, image distortion. In the most severe cases, vision loss occurs.
Retinal dystrophy
– an extremely dangerous disease that can have a wide variety of causes. The tissue of the retina of the eye dies or decreases. This can happen if qualified assistance from specialists is not provided in a timely manner.
Corneal pathology
Keratitis
– an inflammatory process that affects the cornea of the eye. As a result, clouding of the cornea and the occurrence of infiltrates. The cause may be an infection: viral, bacterial. Injuries can also trigger the development of the disease. Symptoms: lacrimation, redness of the mucous membrane of the eye, atypical sensitivity to bright light, the cornea loses its normal properties - shine, smoothness. If treatment is neglected, the infection spreads to other areas of the visual system.
Keratitis
Belmo
– formation of scar tissue on the cornea of the eye, its persistent clouding. The cause is prolonged inflammatory processes in the body or injury.
Belmo
Corneal astigmatism (keratoconus)
– degeneration of the cornea, which occurs due to increased pressure inside the eye. This leads to a change in the shape of the cornea of the eye. Symptoms: light fringe around the light bulbs, immediate decrease in vision in one of the eyes, myopia.
Keratoconus
Change in eye refraction
Myopia (myopia)
– a refractive error in the eye, in which a person has difficulty seeing distant objects. In case of myopia, the image is fixed in front of the retina. Signs: poor discrimination of distant objects, discomfort, rapid eye fatigue, pressing pain in the temples or forehead.
Myopia
Farsightedness (hypermetropia)
– a refractive error in which the image is read behind the retina, is the opposite of myopia. In this case, the patient has difficulty seeing both near and distant objects. Symptoms: very often there is blurriness before the eyes, sometimes the patient exhibits strabismus.
Farsightedness
Astigmatism
– the disease is characterized by the inability to focus light rays on the retina. Usually appears in people with physiological disorders of the visual organs: cornea, lens. Symptoms: blurred and unclear image, a person gets tired quickly, often complains of a headache; in order to see something, one has to strain the eye muscles.
Astigmatism
Other eye diseases
Nystagmus
– uncontrollable oscillatory movements of the eyeballs.
Lazy eye syndrome or amblyopia
– a pathology in which the eye, due to damage to its muscles, stops working and making movements.
Anisocoria
– difference in pupil size. Basically, it appears with all kinds of eye injuries. Involves acute sensitivity to light and decreased vision. Sometimes this pathology indicates a disruption in the functioning of one of the parts of the brain - the cerebellum.
Anisocoria
Episcleritis
- inflammation that forms in the episcleral tissue. First, redness appears near the cornea, then this area swells. Signs: feeling of discomfort, eyes hurt from bright light. There are discharges from the connective membrane. In most cases, episcleritis goes away on its own.
Episcleritis
Aniridia
– complete absence of the iris of the eye.
Aniridia
Polycoria
– an eye defect when a person has several pupils.
Polycoria
Ophthalmoplegia
– a disease when the nerves of the eye that are responsible for its movement cease to function correctly. This causes paralysis and the inability to rotate the eyeballs. Symptoms: eyes are turned to the nose, do not change this position.
Exophthalmos
– pathological exit of the eyeball beyond the orbit of the eye, occurs due to swelling of its tissue. In addition to the main symptoms, redness of the eyelids and pain when touching the inflamed area are noted.
Diplopia
– a disorder of the visual system, consisting of constant double vision of visible objects.
Treatment of acne on the eyeball
Treatment for pimples on the eyeball depends entirely on the cause of the bump. If it is a common cause such as pinguecula, treatment usually involves the use of lubricating eye drops and the use of sunglasses to protect them from UV rays even on cloudy days.
If your eye is inflamed or swollen, your eye doctor may prescribe special steroid eye drops to reduce swelling. They may also recommend that you purchase special scleral contact lenses for dry eyes or photochromic glasses lenses so that they darken automatically, turning them into sunglasses. when you go outside.
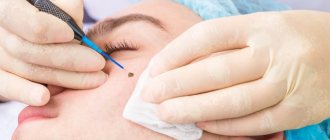
Surgical removal of a pimple on the eyeball is also a solution, depending on the cause of its formation. In the case of conjunctival tumors, surgery and chemotherapy may be required. In other cases, such as with limbal dermoids, doctors may try to avoid surgery unless it is absolutely necessary .
Treatment methods
Experts advise not to remove bumps on the eye if they do not interfere , do not affect the quality of vision and do not grow.
It is worth noting! Patients themselves tend to adhere to this advice, but many remove these formations solely for aesthetic reasons.
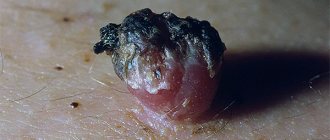
The most rational way to get rid of a tubercle on the eye is to remove it surgically . This can be done in different ways:
- Diathermacoagulation. The cone is exposed to high temperatures, causing its tissues to disintegrate.
- Cryodestruction. The bulge is treated with liquid nitrogen, frozen to a temperature of -60 degrees. As a result, its tissues are destroyed and subsequently excreted with tear fluid.
- Laser coagulation . The lump is treated with a medical laser, which burns it out.
- Radiation therapy. The tissues of the tubercle are exposed to irradiation. This type of removal is used only in the presence of malignant tumors.
All these methods are suitable for removing benign bumps.
Keep in mind! The specialist chooses a specific method based on the examination results and the size and characteristics of the lump.
It is not necessary to remove hemangiomas surgically.
If the formation is small and has appeared recently,
medication methods may also be effective.
Although in general, according to statistics, such treatment helps in only two percent of cases.
can be used :
Clinical course
Typically, ophthalmoherpes is the result of the awakening of the virus, and not of primary infection. In this case, eye damage can be expressed to varying degrees.
Ophthalmologists distinguish several clinical forms of the disease:
- Damage to the anterior part of the eye (conjunctivitis, keratitis, recurrent corneal erosion, blepharoconjunctivitis, episcleritis);
- Damage to the posterior part of the eyeball (uveitis, perivasculitis, central serous retinopathy, acute retinal necrosis syndrome, anterior ischemic retinopathy, neonatal retinochorioretinitis).
How to quickly cure stye
If barley appears on the eye, how to treat it depends on the stage of development of the infection. If you take action at the initial stage, there is a chance that the inflammation will not spread and the swelling will go away in 1-2 days. For this:
- Treat the problem area with an antiseptic. Suitable medical alcohol, which is diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio, a solution of brilliant green or iodine, and calendula tincture.
- Perform dry heating. To do this, heat sea salt or any cereal in a frying pan. You can take a hard-boiled egg. The selected heat source is wrapped in a clean cloth and applied to the inflamed area until the compress has cooled.
If inflammation does develop, it is better to consult a doctor, since treatment of barley with medication is necessary. Purulent masses must come out of the affected area. If this does not happen naturally, the abscess cannot be squeezed out, so as not to infect the blood and other organs. In such cases, the ophthalmologist makes a puncture under sterile conditions. It leaves no scar.
To destroy bacteria, drops from barley in adults are used - Tobrex, Albucid, Levomycetin, Vigamox, Gentamicin. They are instilled 3–5 times a day. It is important not to let the bottle touch your eye.
Quick treatment of stye at home is ensured by combining drops with antibacterial ointments. The latter are placed at night, as they can temporarily reduce vision. But when purchasing them at the pharmacy, be sure to specify that you need the drugs specifically for the eyes. Many of these medications are also produced for the skin; the content of active substances in them is higher, which can harm the visual system. These include Tetracycline, Syntomycin, Hydrocortisone, Erythromycin, Maxitrol.
How long barley goes away depends on the type of pathology. The internal one takes longer to treat than the external one - complete recovery requires from 1 month.
Why is herpes infection dangerous?
If the rashes are located on the surface, then complex therapy makes it possible to prevent the development of secondary pathologies. When inflammation affects the deep layers, negative consequences are possible:
- clouding of the cornea;
- blurred vision;
- hemorrhages;
- gradual death of tissues, their detachment;
- glaucoma, cataract;
- loss of vision.
Important! The development of dangerous pathologies is not observed from primary herpes under the eye, but in the absence of adequate treatment, the virus will gradually penetrate into the deeper layers of the organ, which will lead to serious consequences.
Causes of stye on the eye
Staphylococci, which prefer to settle on human skin and hair, do not manifest themselves in any way with strong immunity. Their intensive reproduction is triggered by a decrease in the protective properties of the body, its hypothermia, severe illnesses and hypovitaminosis, and the consequences of helminthic infestation. Penetrating into the structure of the hair follicle, streptococci cause inflammation and suppuration as a reaction to a pathogenic microorganism. This is the main cause of stye on the eye in patients of all ages. With an unbalanced diet, increased physical activity or stressful situations, the disease can occur in the form of several or multiple suppurations on the eyelids or mucous membranes. Also among the factors contributing to the appearance of stye on the eye is the habit of touching the eyelids with dirty hands, a large amount of dust indoors or outdoors.
The risk group for the likelihood of the appearance of barley includes:
- patients with reduced immunity;
- persons with diseases of the endocrine system;
- patients with gastrointestinal pathologies;
- persons whose professional activities involve working outdoors or in premises with difficult climatic or unsanitary conditions;
- patients who have suffered inflammatory diseases of the eyes and eyelids, as well as those who have not completed the prescribed course of treatment.
Types and stages of development of hordeolum
Depending on the location of the lesion, it can be of the following types:
- External stye
. More common according to statistics. The infectious-inflammatory process is localized at the edge of the eyelid, since the infection settles in the sebaceous gland of Zeiss or in the ciliary bulb. - Internal stye on the eye
. It has another name - meibomite. It is caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the passage of the meibomian glands located on the back side of the eyelid margin.
By type they distinguish:
- Hot barley
. It is characterized by the classic development of the disease; infection is localized in the ciliary pocket - the bulb or Zeiss gland. With therapy it goes away in about a week. - Cold stye (chalazion, meibomian cyst)
. The inflammatory process affects the meibomian glands. It develops very slowly. Recovery takes 1–2 months. If there is a very large stye, surgical removal is possible.
Inflammation goes through the following stages:
- Formation of a purulent core
. A small reddish swelling causes discomfort when moving the eyelids. - Formation of an abscess
. The patient’s condition at this stage can only be alleviated by medications. - Breakthrough of pus.
It does not indicate recovery, but the patient feels much better. During this period, you need to keep your eyes clean and use prescribed medications and ointments.
Prevention
UV rays will cause much less harm if a person protects his vision with glasses and a wide-brimmed hat.
To avoid the appearance of acne in the visual area, you must adhere to the following recommendations from doctors:
- UV eye protection. When exposed to the sun for long periods of time, wear sunglasses and wide hats.
- Correct selection of optical means. If the lenses cause irritation to the mucous membrane of the eye, then you should switch to other models or use glasses.
- Visit to an ophthalmologist. In order to diagnose and stop the process of degeneration in the cornea in time, you need to undergo regular examinations.
- Vitamin complex. The diet should contain a sufficient amount of vitamins.
Complications of ophthalmoherpes
If treatment for herpetic eye lesions is started in time, the effectiveness of therapy is usually high, since the infection is located on the surface of the cornea. If the deep structures of the eye undergo changes, then clouding of the cornea and vitreous substance occurs, which leads to a decrease in visual acuity. Sometimes even corneal blindness occurs.
If the infection is chronic, symptoms of cataracts and glaucoma may appear. With necrotic changes in the retina, hemorrhages and detachment (complete or partial) occur.
Treatment of a pimple on the white of the eye
Medications
In case of severe irritation and acute inflammation, ophthalmologists do not recommend using contact lenses, as they further damage the cornea.
The patient can use Lacrisifi if the popped formations are transparent.
If a transparent pimple appears in the eye, doctors advise additionally moisturizing the mucous membrane of the eye. You can use drops “Bestoxol”, “Lakrisifi”, “Artificial tear” or “Taufon”. An additional advantage of the drugs is the mitigation of irritation, as well as the prevention of further thinning of the cornea. In case of severe inflammation and swelling of the tissues of the eyelids, the ophthalmologist prescribes drugs that destroy pathogenic microorganisms - Tobradex, Vitabact, Ciproled, Diclofenac or Uniflox.
Folk recipes
It is impossible to destroy a benign neoplasm using alternative medicine, however, to strengthen the cornea, it is recommended to use the following methods:
- Healing beetroot. The vegetable should be grated and consumed on an empty stomach every morning. The leaves of the root vegetable can be soaked and used in the form of compresses to relieve irritation and fatigue of the visual organs.
- Blueberry compresses. Squeeze the juice out of the berries and strain. A piece of gauze folded 3-4 times is soaked in liquid and applied to the affected areas.
- Berries with sugar. For breakfast you need to eat 100-150 g of fresh or dried blueberries, which have been softened in water.
- Herbal lotions. To stop inflammation and also moisturize the eyes, you should brew decoctions of calendula, chamomile or lemon balm. Cotton pads are moistened in the cooled liquid and placed on the eyes.