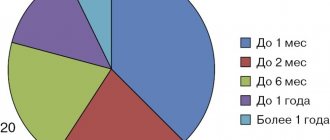
You are in the section: Home » Articles » DERMATOLOGY: inguinal athlete's foot (dermatomycosis)
Review
Athlete's foot (also known as tinea inguinalis, eczema fringe, ringworm, Tinea cruris, etc.) is a fungal infection of the trichophytosis class caused by Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton fungi that affects the skin of the groin area, including the genitals, inner thighs and buttocks.
Skin lesions manifest themselves in the form of an itchy red, often ring-shaped rash, predominantly located in the warmest and most humid areas of the human body that are constantly covered by clothing. Tinea groin is common in people who sweat a lot, such as athletes. It is also more common in overweight people.
This disease, as a rule, is not serious, although it causes a lot of inconvenience to its carriers. For cure, it is usually sufficient to maintain hygiene of the groin area and use local antifungal drugs.
Symptoms
Fringed eczema usually begins as a red patch of skin that spreads from a crescent-shaped crease in the groin to the upper thigh. The border of the rash may consist of a line of small blisters. The rash often itches or burns, and the skin may peel or become scaly. This, by the way, is where the names groin itching or lichen come from.
When to see a doctor
Call your doctor if you have a skin rash that does not go away on its own within two weeks, or if it appears again within a few weeks of finishing over-the-counter medications.
Causes
Athlete's foot is caused by fungi that can be spread from person to person through direct contact or by sharing contaminated towels or clothing. Tinea cruris in athletes is often caused by the same fungus that infects the feet and causes athlete's foot (Tinea pedis). Usually in these cases the infection is transferred from the foot to the groin folds through the hands or wet towels.
Risk factors
Microorganisms that cause itching in the groin prefer the moist environment of skin folds and hidden places of the human body. Those most at risk are:
- men;
- teenagers or young adults;
- lovers of wearing tight underwear;
- are overweight;
- sweating heavily;
- having a weakened immune system;
- susceptible to diabetes (excessive urination in diabetes insipidus).
Prevention
To reduce your risk of developing athlete's foot, simply follow these principles:
Maintain good body hygiene . It is important to keep the groin area clean and dry. Dry the genital area and inner thighs thoroughly after showering with a clean, ironed towel. To prevent diaper rash, use powder in the groin area.
Wear clean clothes . If you sweat a lot, change your underwear at least once a day or more often. Wash your workout clothes after each use.
Choose clothes that fit . Make sure clothes fit your body, especially underwear and sportswear. Avoid tight-fitting clothing, which can chafe and itch your skin. Try wearing boxer shorts instead of briefs and trunks.
Don't share personal items . Do not allow others to share your clothing, towels, or other personal items. And do not take these items from others yourself.
Treatment of athlete's foot . Control foot infections to prevent them from spreading higher into the groin area. If you frequently visit public places, such as gym showers, public saunas and steam baths, wearing sandals will help prevent athlete's foot infection.
Diagnostics
In most cases, diagnosing tinea groin is not difficult. To determine the disease, simply look at the rash. If the diagnosis is not clear, the doctor may take skin scrapings or samples from the affected area and examine them under a microscope. To rule out other pathologies, your doctor will likely send the sample to a laboratory for culture.
Treatment
For mild tinea groin, your doctor may suggest using an over-the-counter antifungal ointment, lotion, powder, or spray first. With these treatments, the rash may disappear fairly quickly, but you must continue to use the drug as directed for one to two weeks. If tinea pedis is also detected, it is necessary to treat both of these diseases simultaneously. An integrated approach will significantly reduce the risk of relapse.
For severe ringworm or a form of the disease that is resistant to over-the-counter medications, prescription creams or ointments or even antifungal tablets may be needed.
Treatment of severe inguinal athlete's foot, complicated by tinea pedis or other underlying disease, as well as the consequences of self-medication, can take a long time and require a certain amount of patience from the patient. However, it is not incurable and is quite successfully treated by experienced dermatologists at the Clinic of Dr. Filatov.
Causes
In most cases, athlete's foot is diagnosed in men. Cases among children and adolescents are extremely rare.
The causative agent of the disease (fungus) is transmitted through contact and household contact. You can become infected with athlete's foot, for example, in a bathhouse or after using someone else's personal hygiene products.
Factors that provoke the development of the disease include:
- high temperature and humidity of the environment;
- excess weight;
- skin microtraumas;
- increased sweating;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Causes of inguinal mycosis
The disease occurs due to a combination of several reasons: the action of a pathogenic or opportunistic pathogen, the characteristics of the body and unfavorable external conditions. Inguinal mycosis of the skin in 40% of cases is caused by Epidermophyton floccosum, in 25% by Trichophytom mentagrophytes var. interdigitale and in 20% - Trichophytom rubrum. In other patients, the disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida, mold microorganisms, or their combination with dermatomycetes.
- E. floccosum and T. rubrum often lead to the development of a chronic form of the disease, and T. Mentagrophytes causes an acute inflammatory process.
Damage to the inguinal folds is often combined with atopic dermatitis and mycosis of the feet.
Inguinal ringworm is easily transmitted from person to person by using the same towels. In addition, the fungus can be transferred independently from the area of the sole with mycosis of the foot.
Fungi thrive in warm, moist places. They secrete enzymes that destroy the surface layer of the skin. This allows them to gain a good foothold in the groin areas. There are conditions that increase the risk of contracting this mycosis:
- male gender;
- obesity;
- excessive sweating;
- immunodeficiency;
- dermatitis in the groin area;
- diabetes;
- use of tight underwear;
- frequent exposure to wet clothes or a bathing suit;
- living in a tropical climate.
Prevention
To avoid the possibility of inguinal athlete's foot, you need to follow the rules of personal hygiene, especially in saunas and swimming pools. Use a personal towel, washcloth, and underwear.
If a person has suffered this disease, his household items, linen and clothing must be thoroughly disinfected.
If symptoms of inguinal athlete's foot appear, SM-Clinic specialists recommend not delaying going to the doctor and not delaying treatment. You can make an appointment in St. Petersburg by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Symptoms
Rashes with inguinal mycosis are reddish spots with a brown tint, slightly raised above the skin. Their borders are well defined and have a round or oval shape. The surface of such spots peels off finely.
The lesions gradually enlarge and merge with each other, forming polycyclic forms with scalloped edges. The lesion extends beyond the border of the inguinal fold, spreading to the thighs, abdomen, buttocks, and in men - to the penis and scrotum.
Gradually, the central part of the spot becomes paler. The edge, on the contrary, takes on the shape of a cord, becomes swollen, red and rises above the skin. In the summer, as well as with strong friction or sweating, an exacerbation of inguinal mycosis occurs. It is manifested by the appearance of small blisters and crusts at the border of the lesion, accompanied by itching.
If you do not consult a dermatologist and self-medicate, the disease becomes erased over many years, with aggravation in the summer, bringing significant inconvenience to the patient. In this case, the cost of treatment will be significantly higher than timely started therapy.
Pimples in the groin and pubic area: what they look like and why they occur
Formations in the groin and pubic area are a nuisance that can affect both women and men of any age. Sometimes acne in the groin is caused by completely harmless and easily removable factors - insufficiently careful hygiene, incorrectly selected underwear or poor shaving technique.
However, there are also more serious reasons, signaling that something is wrong in the patient’s body. We will dwell on them in more detail.
Infectious and viral diseases as the cause of acne on the pubis and groin
This is the option that our clinic’s specialists suggest first. The most common diseases are:
- lice pubis: small purulent pimples appear at a certain stage of the disease;
- syphilis: this disease is characterized by the appearance of one or several pimples on the pubic part of men (often looks like an ulcer and is located on the genital organ itself). In women, in addition to the pubis, they are sometimes observed on the labia. This formation is called chancre. It has a smooth surface with shiny edges, does not cause pain, but is a colorful symptom of the development of a dangerous disease in the body;
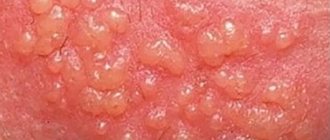
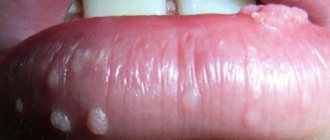
- genital herpes: one of the signs of the disease is small, blistering-like pimples on the pubic area in women and on the genitals and testicles in men;
- human papillomavirus: its filamentous variety almost always affects the pubis and in a non-inflamed state is a wart, but only until the patient, by directed or random actions, provokes its inflammation and suppuration;
- mycosis: a fungal disease, one of the external signs of which may be pimples like burn blisters between the legs, in the gluteal fold, on the genitals and in the lower abdomen;
- molluscum contagiosum: a pathogen transmitted sexually or through household contacts that provokes pubic acne in women and men with cheesy contents.
Other causes of acne in the inguinal-pubic area
In addition to specific diseases, acne in intimate places can break out for the same reasons as on any other parts of the body: due to endocrine disruption or disruption of internal organs, excess weight, improper diet, hypothermia, diabetes. In addition, acne in the groin in women can form during ovulation and PMS, during pregnancy, lactation and premenopause.
It is not worth determining the initial prerequisites on your own, and even more so trying to get rid of acne by squeezing, independently selecting medications and folk remedies - this is fraught with much more serious consequences than just education in a sensitive area. Therefore, anyone who has a similar problem is expected to see highly qualified specialists at our medical center.
Diagnosis of causes and treatment at the Private Practice clinic
The first step in treating acne, including in the inguinal-pubic area, is to establish the causes of its appearance. Based on this, further tactics of working with the patient are determined. Sometimes recommendations related to personal hygiene, caring for problem areas of the skin and following hair removal rules are sufficient.
In more complex cases, we prescribe a comprehensive examination, including examination of stool for intestinal microflora, blood tests for general indicators, biochemistry and hormones, ultrasound of the digestive organs and kidneys, scrapings, cultures and biopsy. If an infectious etiology is suspected, we refer the patient for STD testing. All laboratory and instrumental studies are performed in our clinic, which is equipped with a modern laboratory and equipment.
Based on the results of the research, our dermatovenerologists select effective complex therapy that is guaranteed to cure groin acne in men and women with a minimal risk of relapse.
Pimples on the pubic area should not be taken lightly, because they can serve as a symptom of dangerous sexually transmitted infections. In this case, the success of treatment largely depends on the stage of the disease. See your doctor on time and be healthy!
You can make an appointment at a convenient time. The doors of our clinic are open for you every day from 09:00 to 21:00.
You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling
+7+7 (495) 980-13-16
Diagnosis of pain in the leg closer to the groin
Joint pain cannot be ignored. Any unpleasant sensations indicate a violation of the functionality of the body and pathology of the internal organs. Contact KDS Clinic. Experienced specialists will provide assistance at any time. The patient is sent for tests and a comprehensive examination of the body. With such symptoms, the patient should undergo an X-ray of the joints and ultrasound diagnostics. General tests will show details of the body's internal indicators. To get a more accurate result, it is worth doing magnetic resonance imaging. The procedure is prohibited for pregnant women, women during the lactation period and children under sixteen years of age. Consult your doctor before undergoing the examination.
Make an appointment with a specialist by number. In some cases, the patient is left in the hospital to monitor improvements in indicators. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with prices for all services on the official website of the medical institution.
Pathogen and routes of infection
The causative agent of athlete's foot is the parasitic fungus Epidermophyton floccosum. In the acute phase, the disease is contagious and is transmitted in the following ways:
- autoinoculation - transfer of the fungus from the source of inflammation on the arms or legs;
- indirect route - infection through household items on which there are scales of the epidermis with a pathogenic fungus: clothing, towel, sheet, seat;
- direct – transmission from a carrier during sexual intercourse.
Risk factors contribute to the active development of epidermophytosis of the inguinal folds:
- high humidity and local hyperthermia - the peak incidence is observed in residents of tropical and subtropical climates in the summer;
- tight, dense clothing that does not allow air to pass through - synthetic materials with thick thread;
- increased sweating;
- obesity, diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states;
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasmosis;
- trichomoniasis.
In men, such damage to skin folds occurs 3 times more often than in women, according to incidence statistics in the United States.
Types of rashes in women
Skin rashes manifest themselves in different ways. There are such types of rashes that affect the skin in the intimate area:
- A pimple
is a small bump or nodule protruding above the general layer of skin. The formation is often filled with serous fluid; - An abscess
is a large pimple with a watery texture. The formation is filled with purulent fluid; - Erythema
- bright red spots with clear boundaries. They stand out strongly against the background of healthy skin; - A blister
is a formation filled with fluid. Occurs due to mechanical injuries, burns; - An ulcer
is a non-healing wound that most often forms on the mucous membranes; - Condyloma
is a small formation of the papillary type on a stalk. Localized on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. - A node
is a dense formation in the deep layers of the epidermis. It appears in the form of a tubercle that protrudes above healthy tissues; - Plaque
– multiple formations in the form of small spots. They rise above healthy skin.
A rash in the groin area in women can simultaneously manifest itself in several types of skin lesions. Each type of rash is a signal of developing pathology, poor hygiene, unsafe sex life or other intimate problems.
Who is at risk: causes of the disease
The optimal conditions for the development of fungal infections are heat and humidity. Male professions (driver, military man) oblige a person to wear warm, unventilated clothes for long hours, day after day creating an optimal habitat for the causative agent of the disease.
A weakened body, the presence of mycosis on other areas of the skin, contact with people who are carriers of mycoses, metabolic disorders are factors that increase the risk of epidermophytosis.
Knowing the causes of the disease, we can identify the main categories of men who are at risk:
- elderly people;
- patients with diabetes and (or) obesity (treated and advised by an endocrinologist);
- men with hyperhidrosis (this means profuse, uncontrollable sweating);
- people with immunodeficiency;
- drivers, military, police, rescuers, etc.
Diagnostics
The doctor evaluates the clinical picture and prescribes instrumental and laboratory tests:
- microscopic analysis of a preparation of scales;
- bacteriological culture;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- Wood's lamp examination.
During the differential diagnosis, the venereologist excludes pathologies such as erythrasma, neurodermatitis, herpes virus, allergic and seborrheic dermatitis, candidiasis.
The Center for Urology, Gynecology and Reproductology in Moscow carries out laboratory and differential diagnosis of inguinal epidermophytosis with further treatment.
Athlete's foot is a fungal disease of smooth skin that occurs as a result of infection with a pathogen such as Epidermophyton floccosum. As a result, characteristic rashes appear on the skin of the groin area (most often, sometimes the axillary areas and chest are also affected), represented by flaky spots of various sizes that tend to merge. With inguinal epidermophytosis without treatment, in addition to the protracted course of the disease, the development of secondary bacterial infection, fungal folliculitis due to the use of corticosteroids or the lichenoid form in people with a tendency to allergic reactions is possible.
Transmission of the disease occurs anthropophilically (from an infected person to a healthy person). Infection usually occurs through direct contact with a sick person or his household items. Most often, infection occurs in public baths, saunas, swimming pools or showers. This disease most often affects males. Predisposing factors for this disease include excessive sweating, obesity, damage to the skin, wearing tight synthetic underwear, diaper rash, hormonal disorders, somatic diseases (especially diabetes), decreased immunity, and poor personal hygiene. The disease is usually less acute than rubrophytia, has a tendency to seasonal exacerbations in the warm season, and frequent relapses if not treated correctly.
Symptoms of athlete's foot include the appearance of a characteristic rash in the groin folds, inner thighs, scrotum, and intergluteal region (occasionally in the armpits and chest). The rashes are initially represented by pink scaly spots up to 1 cm in diameter, which tend to merge and form larger ring-shaped elements of red color (less often yellowish or brown) with a lighter central zone. The lesions have clear scalloped outlines with an infiltrated ridge on which blisters and pustules may appear. Patients usually complain of moderate to severe itching and burning in the affected areas.
Diagnosis and treatment of inguinal fungus is carried out by a dermatovenerologist.
Differential diagnosis in typical cases should be carried out with candidiasis, erythrasma, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, rubrophytosis and other skin diseases.
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a clinical examination to identify characteristic rashes in the groin area (round pink spots with clear boundaries; foci of polycyclic shape with a pronounced continuous edematous peripheral ridge; blisters, micropustules, erosions, crusts, scales). If there is doubt about the diagnosis, special examination methods may be additionally prescribed that will allow the pathogen to be identified: using a Wood's lamp, differential diagnosis with erythrasma (bacterial skin lesions) is carried out, and with microscopic examination, by treating the resulting material with 20% potassium hydroxide, threads of the fungal mycelium can be identified . The etiology of the disease can be definitively established by performing a cultural study with isolation of the pathogen. Also, all patients undergo a general analysis of urine, blood, and a biochemical blood test (which is repeated during therapy with antifungal drugs).
Treatment includes prescribing a specific diet and medications. For inguinal athlete's foot, local use of antifungal drugs is indicated. When inguinal fungus is combined with damage to nails and hair or there is no effect from external therapy, the prescription of systemic (oral) antifungals is indicated. To relieve unpleasant subjective sensations, antihistamines can be prescribed. In case of secondary bacterial infection, and there is no effect from various treatment methods, hospitalization in a hospital is indicated. If there are concomitant diseases, consultation with related specialists may be indicated.
If a fungal disease occurs not for the first time, then in addition to full treatment, it is necessary to carry out prevention, which includes: maintaining personal hygiene both at home and when visiting public places, maintaining immunity, wearing comfortable underwear made of natural materials, combating excessive sweating, ensure that the skin of the groin and adjacent areas always remains dry.
Treatment options
Only based on the test results can it be stated that the inguinal fold is affected by epidermophytes. Treatment of inguinal athlete's foot in men consists of the following areas:
- etiotropic: fungicides, fungistatics to combat the cause of pathology;
- symptomatic: drugs to eliminate itching, discomfort, cosmetic defects;
- pathogenic: to eliminate risk factors.
The treatment regimen is prescribed only by a specialist. He will assess the presence of a secondary infection, the stage of the disease, and prevent its further spread.
Stages of development
Initially, the disease does not manifest clinical symptoms - the incubation period lasts up to 3 weeks. Then the first signs appear and rapidly develop - from a couple of weeks to several months.
Further scenario for the development of the disease:
- chronic form with frequent relapses is the most common option;
- asymptomatic carriage - determined only by laboratory diagnostics;
- Spontaneous healing is an extremely rare case.
If you do not contact a venereologist in time, athlete's foot will bother you for years, becoming especially severe in the summer.
Possible complications
If athlete's foot in the groin area is not treated, cosmetic defects and complications are possible. The first includes hardening of the affected area of skin, like a callus. Complications include the addition of a secondary infection, which, depending on the pathogenesis, can affect the penis and urethra.
Differential diagnosis and treatment of athlete's foot in adults is carried out by specialists from the Dr.AkNer clinic in Moscow. Get professional help to prevent complications from a fungal infection. Effective painless techniques, proven by 40 years of experience.
Urologist, andrologist Akopyan Nerses Grigorievich.
Back to list of articles
1.General information
Itching is an extremely unpleasant skin reaction; if it “itches”, it is impossible to concentrate on something else, it is impossible to be distracted, to hide, to work, to take a forced position, to wait, to sleep. Only with the utmost effort of will can you restrain the persistent movement of your fingers in the direction of the itchy area, and sometimes this fails, and then the “combed” area itches even more, and you have to again...
The problem is greatly aggravated if the skin itches - and itches unbearably - in a place that cannot be declassified under any circumstances in the presence of other people. For example, in the perineum. And all that remains is to feign deep attention to the words of the interlocutor, but in reality make imperceptible movements on the chair, or shift from foot to foot, or sneak a glance at the watch: this torture must someday end.
Itching in the perineum, in principle, cannot be “normal,” “common,” or unimportant. This is a desperate attempt by the body to attract attention to the problem. Whatever the reasons (and there is no such thing as causeless itching), they are always pathological and always require a response, and the most appropriate response in this case is to see a doctor.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Diagnosis of mycosis of inguinal folds
Most cases of inguinal mycosis can be recognized by examination by a dermatologist. Additional examination may include:
- scraping the skin from the affected area, treating it with potassium hydroxide and examining it under a microscope to identify fungal cells;
- placing a scraping sample on a nutrient medium so that fungal cells grow in large numbers, which will allow them to study their biochemical properties.
Sometimes inguinal mycosis is misdiagnosed. In this case, it occurs under the guise of other diseases, for example, eczema. Treatment of inguinal mycosis may not be effective enough. In this case, you may need to be examined by a dermatologist using a Wood's lamp or even a biopsy of the affected area.