From this article you will learn:
- Causes of foot hyperkeratosis
- Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet at home
- Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet in the podiatrist’s office
- Treatment of hyperkeratosis of the skin of the feet with medications
- Hardware treatment of foot hyperkeratosis
- Effective prevention of foot hyperkeratosis
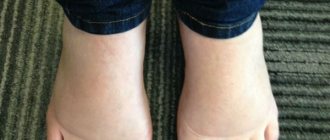
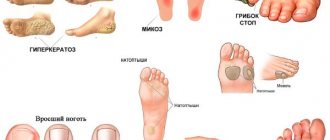
Hyperkeratosis of the feet is excessive keratinization and thickening of the epidermis in the sole area. As a result, the skin becomes rough and dry, calluses and even bleeding cracks may appear. That is why such a pathological process applies not only to cosmetic problems.
If you are also familiar with this condition of the dermis, which makes it difficult to wear light sandals and flip-flops in the summer heat, you may want to pay extra attention to your feet. The disease can be diagnosed by a podologist, dermatologist or orthopedist. But you will learn about methods of treatment and prevention of hyperkeratosis of the feet from our article.
What symptoms should you see a doctor urgently?
People often resort to self-diagnosis of diseases when identifying changes in the skin. The Internet is replete with articles detailing the symptoms and treatment of diseases. But there are many dangerous symptoms, if detected, you should immediately contact a specialist.
1. Rash
. The rash is a symptom of many diseases, both skin and related to other organs. Rashes can be a symptom of an allergic reaction, stress, gastrointestinal pathology, and even cancer. If the rash is brightly colored and does not go away for more than 48 hours, do not delay visiting a specialist.
2. Warts
. The appearance of warts on the skin is caused by various strains of the human papillomavirus. The virus is transmitted from person to person, so if you find papillomas or condylomas on any part of the body, you should make an appointment with a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist.
3. Peeling
. A seemingly harmless symptom can serve as a signal of a dangerous disease. If peeling skin is accompanied by prolonged itching, redness and severe dryness, it is better to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. If peeling has become the skin’s response to exposure to frost, sun or wind, then we recommend that you protect your skin more carefully and use special creams.
4. Change in skin color
. A change in skin color after tanning or peeling is quite understandable, but if you find suddenly appearing spots on your body or face, this is a reason to make an appointment with a doctor. Red spots can signal an acute allergic reaction or gastrointestinal diseases, yellowing of the skin is one of the symptoms of hepatitis B and C, dark spots can indicate necrotic processes.
Discoid dermatitis
Discoid dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of round or oval spots in symmetrical areas, often on the extensor surfaces, usually in adult patients. Exogenous causes must be excluded.
Dyshidrosis is a variant of eczema in which recurrent vesicles or bullae affect the palms, fingers, toes, or both. The disease is characterized by remissions and exacerbations, which are sometimes provoked by fever, emotional stress, and active fungal infection.
TOP 5 skin diseases
Skin diseases are quite common and can appear at any age. They cause physical discomfort to a person, force them to hide the affected areas under thick clothing or use cosmetics to hide imperfections.
Fortunately, modern dermatology successfully fights skin diseases. And here are the 5 most common of them.
1. Acne.
Acne, or acne, is an inflammatory skin disease that occurs as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands. More than 80% of the world's population is prone to acne, most of them are teenagers. The disease begins with the appearance of acne, blackheads and papules (inflammatory nodules). If you are the parent of a teenager with acne, bring him to see a doctor in order to treat the disease in time and prevent its complications, or come yourself if you suddenly encounter the disease as an adult.
2. Atopic dermatitis.
Another inflammatory skin disease is atopic dermatitis. The disease is especially common among children (10–15% in developed countries). The disease is accompanied by redness of the top layer of skin, dryness and severe itching. A complete cure of the patient is impossible, but to mitigate the course of the disease, moisturizing medicinal ointments and local immunomodulators are used. Ignoring the disease can lead to serious complications and the development of skin infections.
3. Psoriasis.
Another common disease (about 5% in developed countries) is psoriasis. This is a chronic inflammatory non-infectious disease, which is characterized by the appearance of bright pink or red plaques on different parts of the body and head. In addition, there is severe burning and itching, dry skin. If left untreated, the risk of stroke increases and internal organs such as the liver and kidneys are also affected.
4. Herpes simplex.
One of the most common viral skin diseases. Antibodies to this virus are found in 90% of people. The main symptom of herpes is blisters filled with liquid that appear in the mucous membranes, most often the lips or nose. Lack of treatment can provoke a decrease in immunity and, as a result, an increased risk of acquiring new diseases.
5. Viral warts.
A common viral skin disease caused by the papilloma virus entering human skin cells. The virus is often transmitted through everyday contact (shaking hands, using objects of the carrier) or sexually. Convex nodules called warts form at the site of virus penetration. The danger of the disease is that the virus has oncogenic strains that can lead to the development of cancer.
Fortunately, there are few such strains, but it is worth checking to eliminate risks. This is especially true for women, because HPV is the first and most important cause of cervical cancer.
Why is arthritis of the ankle and foot dangerous?
The disease is dangerous because it often goes unnoticed and leads to a complete loss of joint function, that is, the person becomes disabled. Acute purulent complications of ankle arthritis are also dangerous.
Arthritis of the foot and ankle begins gradually, unnoticeably
Stages
There are several stages of disease development. The inflammatory process develops gradually, turning into a degenerative-dystrophic one:
- Early – inflammation
. The synovial membrane swells, and inflammatory exudate appears in the joint cavity. Pain is moderate, swelling and redness are absent or only slightly expressed. - Explicit – inflammatory-proliferative process
. The synovial membrane increases in volume, erosions appear on the cartilage, and soft granulations of connective tissue grow in the articular cavity (the process of proliferation - growth). The inflammatory process intensifies. Externally, this is manifested by increased swelling, redness and pain. - Progressive - mild ankylosis
. The cartilage is destroyed, soft granulations turn into dense connective tissue that grows in the joint cavity. Bone growths appear. The joint gradually loses its mobility. Pain, swelling and redness continue to bother you constantly or during exacerbations. - Advanced - complete immobility (bone ankylosis).
There is no cartilage tissue, bone growths connect the articular surfaces of the ankle, which eliminates movement in the ankle and foot (ankylosis of the ankle). The pain is constant, arthritis of the foot develops with limitation of its function.
Possible complications
If ankle arthritis is left untreated or treated independently with home remedies, the following complications may develop:
- purulent processes - abscesses, phlegmon, sepsis;
- subluxations and dislocations of the ankle;
- development of foot arthritis;
- immobility of the ankle and inability to move without assistive devices.
How to treat skin diseases
Unfortunately, there is no one universal remedy for treating skin diseases. After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment that is appropriate in your case. It can be:
- Healing ointments and balms (healing, anti-inflammatory, hormonal, antibacterial)
- Oral medications (antibiotics, hormonal agents, immunomodulators)
- Physiotherapy (laser, magnetic therapy)
- Cosmetic procedures (cleansing, peeling, moisturizing masks)
- Cosmeceuticals (lotions, tonics, creams, masks)
Should you prescribe treatment yourself? Everyone decides for themselves. But we still want to warn you. Of course, if you have gone a little overboard with tanning or have several inflammations on your face due to the approaching critical days, then you can do without a doctor. But when it comes to serious diseases - psoriasis, allergies, dermatitis - self-medication can lead to worsening symptoms.
Contact specialists who will help you choose effective treatment. In the “Health” network of clinics, appointments are conducted by dermatologists and dermatovenerologists. They will conduct an examination, prescribe the necessary tests and help cope with the disease.
We are waiting for you at any of our branches!
Irritative dermatitis
In irritative dermatitis, the rash may be caused by physical or chemical irritation and damage to the skin, in which case it is not usually associated with an allergy. This type of damage can be caused by soap, detergents, food products, and building materials.
The necessary examination and adequate modern treatment for each form of dermatitis can be determined by highly qualified specialists of our center - the Three I Immunology Clinic - allergists and dermatologist. Come visit us at Novosibirsk, st. Galushchaka, 2, we will help solve your problems!
Approach to treating the disease at the Paramita clinic
Treatment of arthritis of the foot and ankle in our clinic is carried out after a preliminary examination using modern laboratory and instrumental techniques. After the diagnosis is established, an individually selected comprehensive treatment is prescribed, which includes:
- the latest Western methods of treating this pathology;
- Eastern techniques that restore balance in the functioning of all organs and systems of the body, which helps eliminate the pathological focus.
This approach allows you to quickly eliminate inflammation and pain, suppress the progression of the disease and restore limb function. At the Paramita clinic they will help you even with advanced disease!
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Types of arthrosis development
For treatment of arthrosis of the foot joints to be successful, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis. Each stage of disease development requires a different set of therapeutic measures. Doctors distinguish the following stages of pathology development:
- First. At this stage, noticeable fatigue of the lower extremities appears, as well as “pulling” pain after long walks or excessive physical exertion. At this stage, the patient may not even suspect that he is developing a disease, because he attributes the symptoms to banal fatigue. But if you do not visit a doctor, the disease will begin to gain momentum;
- Second. All the symptoms of the first stage begin to appear more actively. The pain becomes longer and more severe. Calluses may appear on the heels due to improper foot position, the knuckles become thicker;
- Third. The joints undergo serious changes, so the person begins to limp severely. Joint mobility decreases. X-rays show that the gaps between the joints are significantly reduced or disappear completely.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor must conduct an examination and diagnosis. It includes:
- taking an anamnesis, when the doctor asks the patient about all his complaints;
- X-rays and other examinations that will make it possible to accurately determine the condition of the joints, cartilage and bones, and also identify possible changes in their structure;
- examinations that will allow you to study the condition of muscle tissue;
- tests to find out about the state of the body and the nature of inflammation in it;
- measuring the size of the foot so that you can track the dynamics of treatment for arthrosis of the toe or any other joint.
Classification
Classification of panaritium is carried out according to the location and nature of tissue damage:
- cutaneous - mild form, an abscess in the thickness of the epidermis;
- periungual - an abscess near the nail fold;
- subungual - an abscess under the nail plate;
- subcutaneous - on the surface of the palm;
- bone – accompanied by bone rotting;
- articular – interphalangeal joints and metacarpophalangeal joints;
- osteoarticular – a progressive form of articular, affects the joint and bones of the phalanges;
- tendinous - the most dangerous, affects the tendons.
Other causes of pain
Plantar fasciitis (Morton's neuroma) occurs due to increased pressure on the nerve and is characterized by pain at the base of the toe.
Chronic injuries in this area may also be the cause.
Diabetes may cause numbness in the feet and toes.
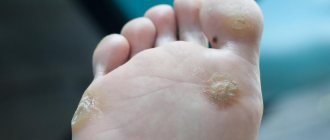
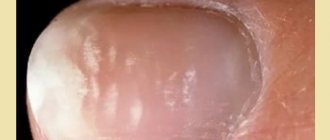
The growth of dead cells, the so-called hardenings, on the pads of the toes often have a root (nucleus), and especially often occur with large and prolonged pressure on the toes.
A nail that has grown into the skin is very unpleasant. To minimize discomfort, trim your nails carefully. Otherwise, severe pain or infection may develop.
Another cause of pain in the toes can be flat feet.
Patients are recommended the following types of treatment:
- Kinesiology and osteopathy
- Complexes of physical therapy (isometric kinesiotherapy)
- Massage
- Mud therapy
- Treatment with active oxygen
Diagnostics
Only after accurately determining the type and shape, the doctor decides how to cure panaritium. Therefore, it is important to get tested promptly. Diagnosis begins with the collection of complaints and symptoms of the pathology. The form of the disease is determined by palpating the location of the abscess with a button probe.
X-rays are performed to identify lesions of bones and joints. In this case, for the articular form of the disease, x-rays are taken on the same fingers of both hands (both healthy and affected).
At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) you can undergo any diagnostic test with high accuracy of results.
Basal cell skin cancer
Basalioma is the most common, but at the same time the safest type of skin cancer. Death from basal cell carcinoma is possible only in very advanced cases or with aggressive forms (basosquamous) tumor. The favorable course of basal cell carcinoma is due to the fact that it almost never metastasizes (only 0.5% of cases).
Symptoms and signs
Most often, basal cell carcinoma occurs on the skin of the nose, a little less often on the face and much less often on other parts of the body.
The peak incidence occurs over the age of 40 years. The youngest patient diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma by histology was 39 years old.
What basal cell skin cancer looks like depends on the form:
- Nodular form (synonymous with nodular). The tumor is presented in the form of a nodule. It can be distinguished from other skin formations by an increased number of vessels on the surface, a waxy sheen and small gray-blue inclusions. All these signs are visible in the photo.
Nodular form of basalioma
In addition, on the surface of nodular basalioma there may be another characteristic sign - ulceration.
Nodular basal cell carcinoma with ulceration
- The superficial form of basal cell carcinoma in most cases is presented as an area of redness on the skin. Elements of peeling and the waxy sheen already mentioned above are also possible.
Superficial form of basalioma
- Scleroderma-like form of basalioma is very rare and often presents difficulties in diagnosis. It is characterized by a lighter and harder seal compared to the surrounding skin.
Scleroderma-like form of basalioma
- The pigmented form of basal cell carcinoma makes up a very small part of the total number of these tumors. It is distinguished by a large amount of pigment. In this regard, basal cell carcinoma is often mistaken for melanoma when examined without a dermatoscope.
Pigmented form of basalioma
- The ulcerative form of basalioma can reach very large sizes and in advanced cases is practically untreatable.
Ulcerative form of basalioma
Photos in the initial stage
Unfortunately, basal cell skin cancer is extremely difficult to diagnose in the early stages, i.e. when it is minimal in size. Here are some photos:
Basalioma of the skin of the nose, nodular form, size 5 mm
Basalioma, nodular form, 3 mm in diameter
Nodular basalioma of the temporal region, diameter 2 mm
Diagnosing basal cell carcinoma in the early stages, when the tumor is small, can present significant difficulties. Only a combination of a comprehensive examination of the entire skin, a thorough determination of the history of the existence of the formation and dermatoscopy will help in establishing the diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma at an early stage.
Basaliomas with high and low risk of recurrence (NCCN, 2018)
Area H: Facial mask (including eyelids, eyebrows, skin around eyes, nose, lips [skin and red border of lips], chin, lower jaw, skin/grooves in front and behind the auricle, temples, ears), genitals, palms and feet .
Area M: cheeks, forehead, scalp, neck and legs
Region L: trunk and limbs (excluding shins, palms, feet, nails and ankles)
Notes
- Localization, regardless of size, may be a sign of high risk
- Histological forms of low risk: nodular (nodular), superficial, keratotic, piloid, with differentiation towards skin appendages, Pincus fibroepithelioma
- Area H means high risk regardless of size
- Morphea-like, basosquamous (metatypical), sclerosing, mixed infiltrative, micronodular in any part of the tumor
To assign a tumor the status of “high risk of recurrence”, only one of the factors from the right or left column is sufficient.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma
The main goal of treatment for basal cell carcinoma is complete removal of the tumor while maximally preserving the cosmetic properties and functions of those parts of the body where this tumor has developed.
As a rule, the best results are achieved by surgical methods. However, the desire to maintain functionality and cosmetic properties may lead to the choice of radiation therapy as the primary treatment modality.
Depending on the degree of risk of relapse (see above), the approach to treating basal cell carcinoma may vary.
In patients with superficial basal cell carcinoma and a low risk of recurrence, when surgery or radiation therapy is contraindicated or inappropriate, the following treatments may be used:
- 5-fluorouracil ointment;
- Imiquimod ointment (Aldara, Keravort);
- photodynamic therapy;
- cryodestruction.
Mohs micrographic surgery may be recommended for patients at high risk of recurrence.
Chemotherapy for basal cell carcinoma includes drugs that are inhibitors of the hedgehog signaling pathway – vismodegib (Erivedge) and sonidegib (Odomzo). These drugs can help in cases where surgical methods, like radiation therapy, are not applicable or contraindicated.
What you need to know about basal cell carcinoma?
- In the vast majority of cases, basal cell carcinoma does not pose a threat to life.
- If a histological examination of a distant formation results in basal cell carcinoma, there is nothing to worry about. It is important to make sure that the formation is completely - be sure to consult with an oncologist.
- If, after removal of a basal cell carcinoma, the histological examination contains the phrase “tumor cells in the resection margin” or something similar, further treatment in order to completely remove the tumor.
- strongly do not recommend removing basal cell carcinoma without histological examination, since even a very typical-looking formation may not be what it seems at first glance.
- Basalioma needs to be treated . Observation is a bad option for a diagnosis like this. Treatment of advanced forms (see photo of ulcerative form) is extremely difficult and expensive.
- If you have already had a basal cell carcinoma removed, you should regularly have your entire skin examined by an oncologist in order to possibly identify another such tumor.
- The likelihood of metastasis in the metatypical (basosquamous) histological type is higher than in other types.
Types of skin cancer
There are 3 types of common malignant skin tumors. They differ both in incidence (i.e., the chance of getting sick) and in the degree of danger to life - basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
Melanoma is one of the rare and dangerous skin tumors. It accounts for only 4% of the total number of malignant skin tumors, but is the cause of almost 80% of deaths in this localization. You can read more about melanoma here.
Sign up for the webinar “Carcinogens in cosmetics: truth, lies and... marketing”
Acute obstruction of the arteries of the extremities
The consequences of acute arterial obstruction are severe. According to domestic and foreign authors, the development of acute occlusion of the aorta and main arteries of the extremities leads to the death of 20-30% of patients, in 15-25% of cases treatment ends with amputation of the extremities. In some reports, the mortality rate reaches 41% and even 64.5%.
Despite the successful development of vascular surgery in recent decades, the sad statistics on acute arterial obstruction do not have a significant tendency to improve. The main causes of acute arterial obstruction are embolism 57% and acute thrombosis 43%. The incidence of acute arterial obstruction tends to increase
Acute arterial obstruction (AAO) is a collective concept that includes embolism, thrombosis and arterial spasm:
- Embolism is the separation of a blood clot from the site of its initial formation, its transfer through the vascular bed with the blood flow and subsequent blockage of the artery.
- Acute thrombosis is a sudden cessation of arterial blood flow caused by the development of a blood clot at the site of a vascular wall changed as a result of disease or injury.
- Spasm is a functional condition that develops in arteries of muscular and mixed type in response to external or internal provoking moments (direct or indirect injury, fractures, etc.).
The main treatment for the disease is emergency surgery.
Acute venous blockage
Blockage of the venous system is called thrombosis. A pathology such as thrombosis often leads to local disturbances in blood flow, and in advanced forms, to global systemic changes in blood circulation. The deep veins of the legs are at greatest risk - it is in them that blood clots most often form.
Thrombosis (thrombophlebitis) develops against the background of acute or chronic venous insufficiency.
Experts identify the following reasons for the development of this pathology:
- Long standing work.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Physical inactivity.
- Excess weight.
- Heavy physical activity, heavy lifting, long periods of standing or sitting.
The appearance of a pathology such as thrombosis is fraught not only with the possibility of trophic damage and blockage, but also with a risk to life - the occurrence of pulmonary embolism. This is due to the possibility of a detached blood clot penetrating into the lung through the bloodstream, which can cause instant death.
Flat feet
According to RNIMU (Russian National Research Medical Institute) named after. Pirogov, from 40 to 60% of the Russian population are susceptible to flat feet . Of these , there are 4 times more women than men .
According to medical statistics from ROSZDRAVA: - by the age of two, 24% of children show the first signs of flat feet, - by the age of four - in 32%, - by the age of six - in 40%, - by the age of twelve - 50% (every second teenager is diagnosed with flat feet ), - by the age of twenty - 60% .
Flat feet can be either congenital or acquired.
Congenital flatfoot in its “pure” form is rarely observed - in approximately 5% of cases . Acquired flatfoot is more common .
Of all cases of acquired flatfoot, transverse flatfoot is in first place in frequency ; it is diagnosed in approximately 65% of cases. In second place in the frequency of detection (about 33% of cases) is longitudinal flatfoot with concomitant flatness of the forefoot. Longitudinal flatfoot is usually combined with hallux valgus . The frequency of this pathology is about 11% of all foot diseases.